IB DP Biology- C1.2 Cell respiration- IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
▶️ Answer/Explanation
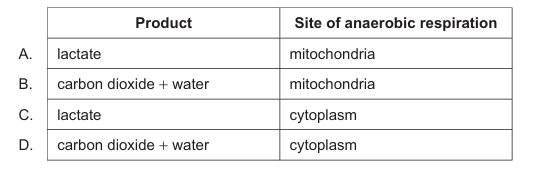
In human cells, anaerobic respiration (glycolysis followed by lactate fermentation) occurs in the cytoplasm and produces lactate as the end product. Carbon dioxide and water are products of aerobic respiration in mitochondria.
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
A respirometer is used to measure the oxygen consumption of germinating seeds. The distance that the oil drop moves is measured at 15-minute intervals.

What is the function of chemical X?
A. Absorbs carbon dioxide so the oxygen released by the seeds can be measured
B. Absorbs carbon dioxide so the oxygen absorbed by the seeds can be measured
C. Absorbs oxygen so the carbon dioxide released by the seeds can be measured
D. Absorbs oxygen so the carbon dioxide absorbed by the seeds can be measured
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: B. Absorbs carbon dioxide so the oxygen absorbed by the seeds can be measured
Explanation:
This setup is a respirometer, used to measure respiration—specifically oxygen consumption—in germinating seeds.
- During respiration, the seeds absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
- If CO₂ remains in the chamber, it would counteract the volume decrease caused by O₂ absorption, making the oil-drop movement inaccurate.
- Chemical X (commonly sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide) is used to absorb the carbon dioxide.
- This ensures that the only gas change is the loss of oxygen, allowing accurate measurement of oxygen uptake (shown by movement of the oil drop toward the seeds).
Options Evaluation:
A. Incorrect – Seeds do not release oxygen; they absorb it during respiration.
B. Correct – Removing CO₂ ensures that the oxygen absorbed by seeds is measured properly.
C. Incorrect – Chemical X absorbs CO₂, not oxygen.
D. Incorrect – Seeds release CO₂; they do not absorb it.
Question
Which compound is a waste product of anaerobic respiration in humans?
A. Carbon dioxide
B. Ethanol
C. Lactate
D. Pyruvate
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: C. Lactate
Explanation: 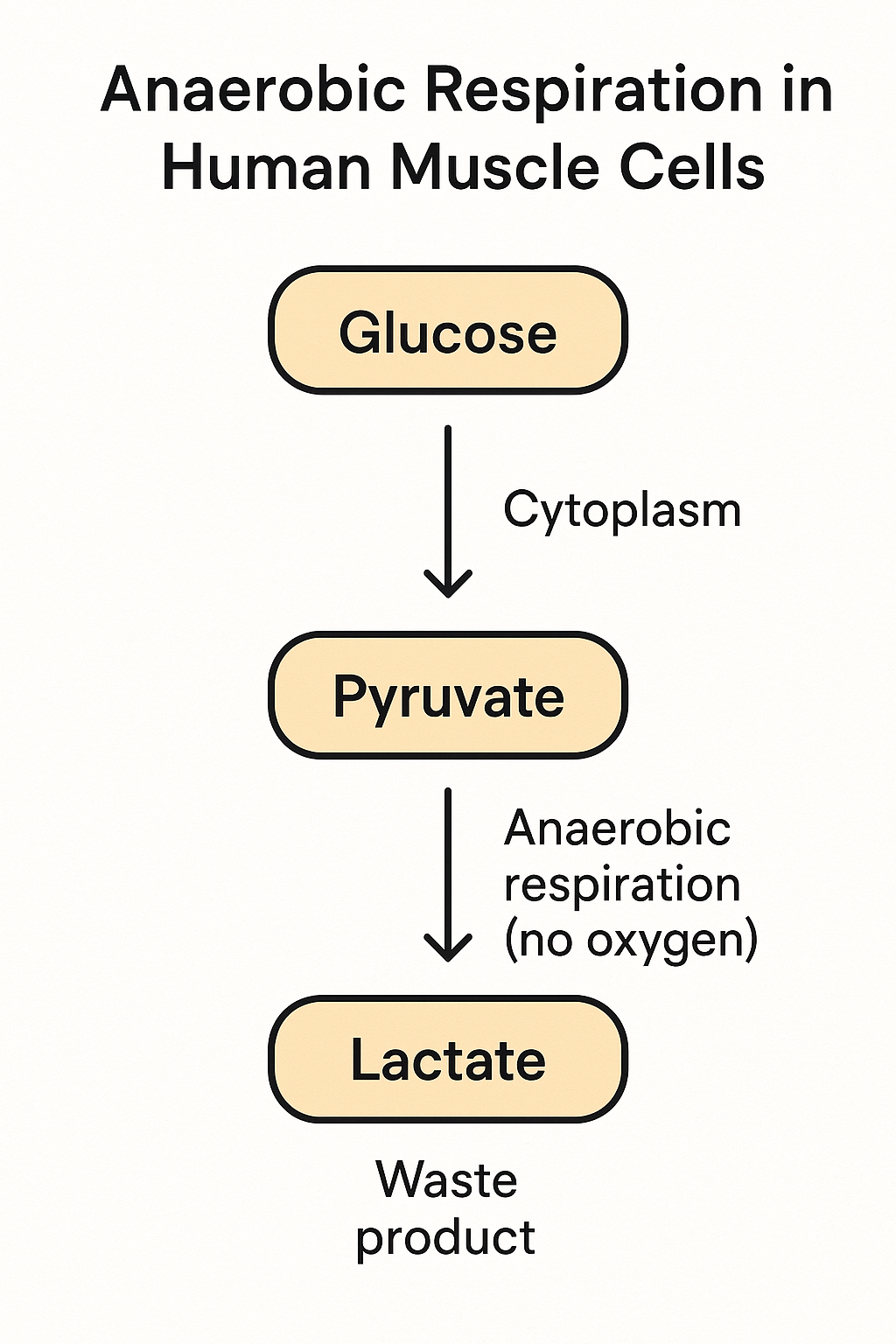
In anaerobic respiration (respiration without oxygen) in humans, the body breaks down glucose to release a small amount of energy. Instead of producing carbon dioxide and water as in aerobic respiration, it forms lactate as the waste product.
This occurs especially during intense exercise when muscles do not receive enough oxygen.
- Glucose → Pyruvate → Lactate
(Pyruvate is converted into lactate when oxygen is unavailable.)
Options Evaluation:
A. Incorrect – Carbon dioxide is produced in aerobic respiration, not anaerobic respiration in humans.
B. Incorrect – Ethanol is produced by anaerobic respiration in yeast, not in humans.
C. Correct – Lactate is the waste product formed during human anaerobic respiration.
D. Incorrect – Pyruvate is an intermediate molecule. In anaerobic conditions, it is converted into lactate, not excreted as a waste product.