IB DP Biology- C2.1 Chemical signaling-IB Style Questions For HL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
Which plant hormone promotes a positive feedback loop that accelerates the ripening of fruit?
A. Auxin
B. Cytokinin
C. Epinephrine
D. Ethylene
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ethylene is a gaseous plant hormone that stimulates fruit ripening. As fruits ripen, they release more ethylene, which in turn increases the production of ethylene further — a positive feedback mechanism that ensures rapid and uniform ripening.
✅ Answer: (D) Ethylene
✅ Answer: (D) Ethylene
Question
The hormone leptin has been tested on patients with clinical obesity to try to treat the disease.
From where is leptin secreted, where does it act and what is its function?
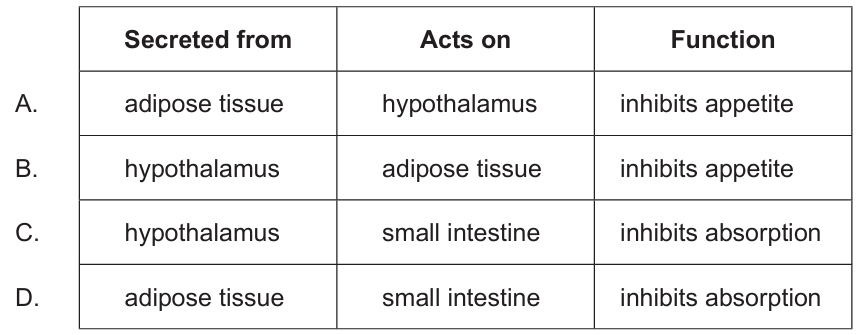
A) Secreted from adipose tissue, Acts on hypothalamus, Inhibits appetite
B) Secreted from hypothalamus, Acts on adipose tissue, Stimulates appetite
C) Secreted from pancreas, Acts on hypothalamus, Stimulates appetite
D) Secreted from intestine, Acts on adipose tissue, Inhibits absorption
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Leptin is produced by adipose (fat) tissue and signals fat storage levels to the brain. It acts on the hypothalamus to suppress appetite and regulate energy balance. The other options incorrectly describe either the source, target, or function of leptin.
