IB DP Biology- C2.1 Chemical signaling- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
Most-appropriate topic codes (CED):
• TOPIC C3.1: Integration of body systems — part (c)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
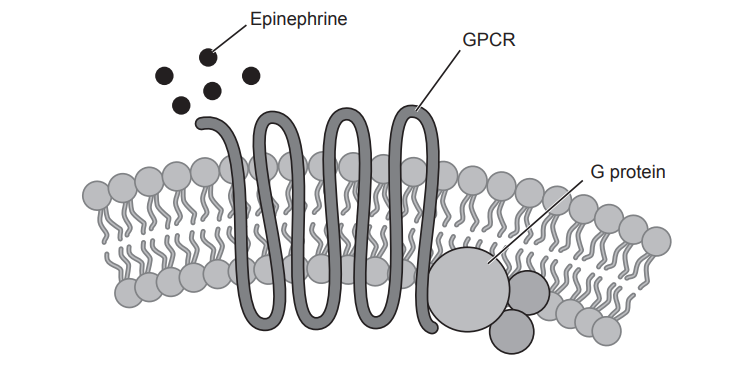
(a)
The ligand is epinephrine (also known as adrenaline).
(b)
Epinephrine binds to its G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) on the cell membrane. This binding activates the attached G protein, which then stimulates a series of intracellular reactions. One major effect is the production of cyclic AMP (cAMP), a second messenger that triggers specific cellular responses, depending on the cell type involved.
(c)
1. Epinephrine increases ventilation rate and causes dilation of the bronchi/bronchioles, allowing more oxygen to enter the bloodstream.
2. It raises heart rate and blood pressure, delivering a greater supply of oxygen-rich blood to active muscles.
Additional acceptable answer: Epinephrine promotes the release of glucose from the liver, boosting ATP production needed for contraction.
