IB DP Biology- C2.2 Neural signaling- IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
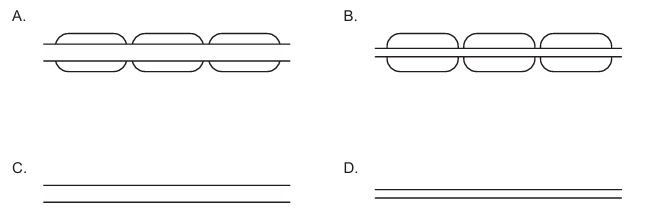
While unmyelinated, small diameter axons typically have the slowest conduction speed, the specific diagrams referenced in the original question must show that the myelinated, large diameter axon has the slowest speed in this particular case, possibly due to other structural factors depicted.
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
Changes in membrane potential during nerve transmission along an axon involve the movement of sodium and potassium ions across the axon membrane.

What explains the membrane potential at Y in the trace?
A. Potassium channels open and allow potassium ions to move to the outside of the axon membrane.
B. Potassium channels allow potassium ions to enter the axon.
C. When the threshold voltage is reached, the sodium pump begins to pump sodium ions to the outside of the axon membrane.
D. Potassium and sodium channels are closed, so there is no movement of ions across the axon membrane.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: A. Potassium channels open and allow potassium ions to move to the outside of the axon membrane.
Explanation:
In the graph, point Y represents the repolarization phase of the action potential, which occurs immediately after the membrane reaches its peak depolarization (approximately +40 mV).
What happens at point Y?
- After the peak of an action potential, voltage-gated sodium (Na⁺) channels close.
- Voltage-gated potassium (K⁺) channels open, allowing K⁺ ions to exit the axon.
- This outward movement of positive K⁺ ions causes the membrane potential to become more negative, returning toward the resting level — this phase is known as repolarization.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. Incorrect – Potassium ions move out of the axon, not in. K⁺ exits through open potassium channels during repolarization.
C. Incorrect – The sodium-potassium pump does help maintain resting potential over time but does not cause the rapid voltage change observed at point Y.
D. Incorrect – At point Y, potassium channels are open while sodium channels are closed; thus, repolarization is occurring, not an absence of ion movement.
Question
The image shows a neuron.

What is the function of X?
A. Increases the speed of transmission along the axon
B. Increases the rate of exchange of sodium and potassium ions
C. Holds bundles of neurons together to form a nerve
D. Determines the direction of the action potential
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: A. Increases the speed of transmission along the axon
Explanation:
In the diagram, label X indicates the myelin sheath, a fatty layer that wraps around the axon in segments, leaving small unmyelinated gaps called the nodes of Ranvier.
Function of the Myelin Sheath (X):
- Acts as an electrical insulator for the axon.
- Enables saltatory conduction, meaning the action potential jumps from one node of Ranvier to the next.
- Greatly increases the speed of electrical impulse transmission along the neuron.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. Incorrect – Ion exchange (Na⁺ and K⁺ movement) occurs at the nodes of Ranvier, not under the myelin sheath.
C. Incorrect – The structure that holds multiple neurons together is connective tissue, not the myelin sheath.
D. Incorrect – The axon hillock determines the direction of the action potential; myelin influences the speed, not the direction.