IB DP Biology- C3.1 Integration of body systems-IB Style Questions For HL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
Which of the following structures functions as the effector in a pain reflex arc?
A. Grey matter
B. Skeletal muscle
C. Motor neuron
D. Pineal gland
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (B) Skeletal muscle
Question
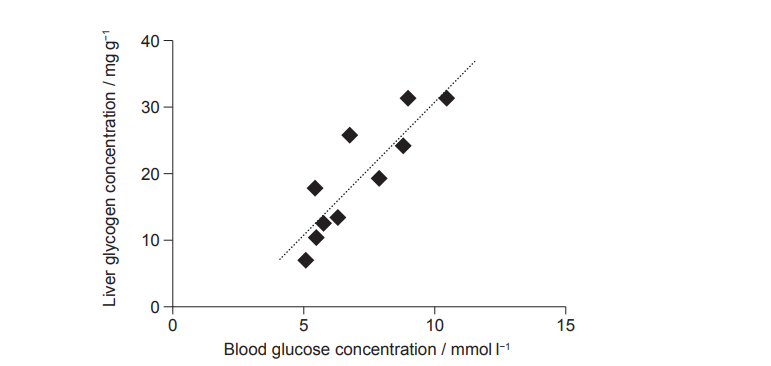
The graph illustrates the relationship between blood glucose levels and liver glycogen concentrations in animals after consuming different glucose meals. Which statement best explains the correlation depicted in the graph?
A. Liver cells store excess blood glucose as glycogen in response to glucagon.
B. Glucagon increases the release of glucose by liver cells to restore concentrations.
C. Insulin decreases respiration rates in liver cells for storage of excess blood glucose.
D. Liver cells respond to insulin by speeding up the conversion of blood glucose into glycogen.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: D. Liver cells respond to insulin by speeding up the conversion of blood glucose into glycogen.
Explanation:
After a meal, blood glucose rises.
The pancreas releases insulin, which signals the liver to store excess glucose as glycogen.
This process lowers blood glucose and increases liver glycogen content.
A is incorrect because glucagon is released when glucose is low, not high.
B refers to glucagon’s opposite function.
C is unrelated; insulin doesn’t directly decrease respiration to store glucose.
Question
Which substances are absorbed by the villi in the small intestine?
A. Glucose, lactose and amino acids
B. Vitamins, polypeptides and fructose
C. Glycerol, fructose and phosphate
D. Fatty acids, maltose and fructose
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: C. Glycerol, fructose and phosphate
The villi absorb:
- Monosaccharides like fructose and glucose
- Fatty acids and glycerol from lipid digestion
- Amino acids from protein digestion
Maltose is typically broken down to glucose before absorption, but may be partially absorbed.
A is incorrect because lactose is not absorbed directly; it’s broken into glucose and galactose.
B is wrong as polypeptides are not absorbed, only amino acids.
C includes phosphate, which is absorbed but not as a major product of digestion like the others.
