IB DP Biology- C3.1 Integration of body systems- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
The diagram below shows a vertical (sagittal) section through the human brain.
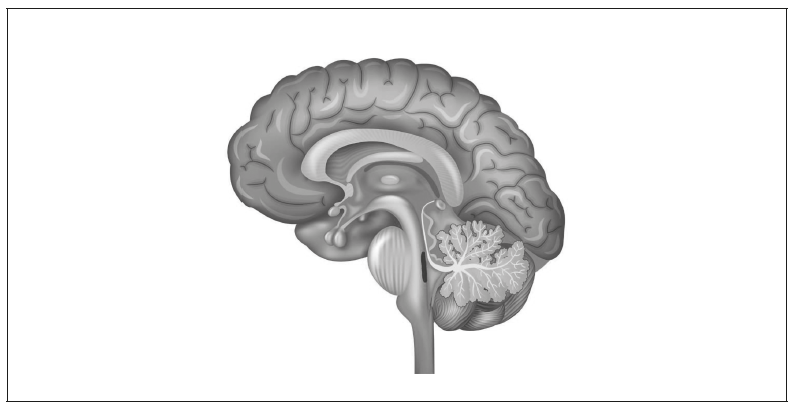
▶️ Answer/Explanation
a.i.
The cerebellum is located at the lower rear portion of the brain, behind the brainstem. It appears as a rounded, folded structure.

a.ii.
The cerebellum helps coordinate voluntary movement and maintain balance, ensuring that muscle activity is smooth and controlled.
b.
One correct label is the pituitary gland or the hypothalamus, both of which produce hormones and are found at the base of the brain.
c.
One method is functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), which detects changes in blood flow to identify which regions of the brain are active during different tasks. Regions that are more active receive more oxygen-rich blood, allowing researchers to identify their functions.
Other acceptable methods include:
- Lesion studies/autopsies: Damage to a specific brain area can reveal its function based on the loss of ability.
- Electrical stimulation during brain surgery: Stimulating regions of the brain and observing the response can indicate their function.
