IB DP Biology- C3.1 Integration of body systems - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
Which of the following structures functions as the effector in a pain reflex arc?
A. Grey matter
B. Skeletal muscle
C. Motor neuron
D. Pineal gland
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (B) Skeletal muscle
Question
What is a function of the pancreas?
A. To control the rate of metabolism by releasing thyroxine when metabolic rate is low
B. To release glucagon when blood glucose levels are low
C. To release insulin when blood glucose levels are low
D. To secrete an endopeptidase which lowers the blood glucose levels
▶️ Answer/Explanation
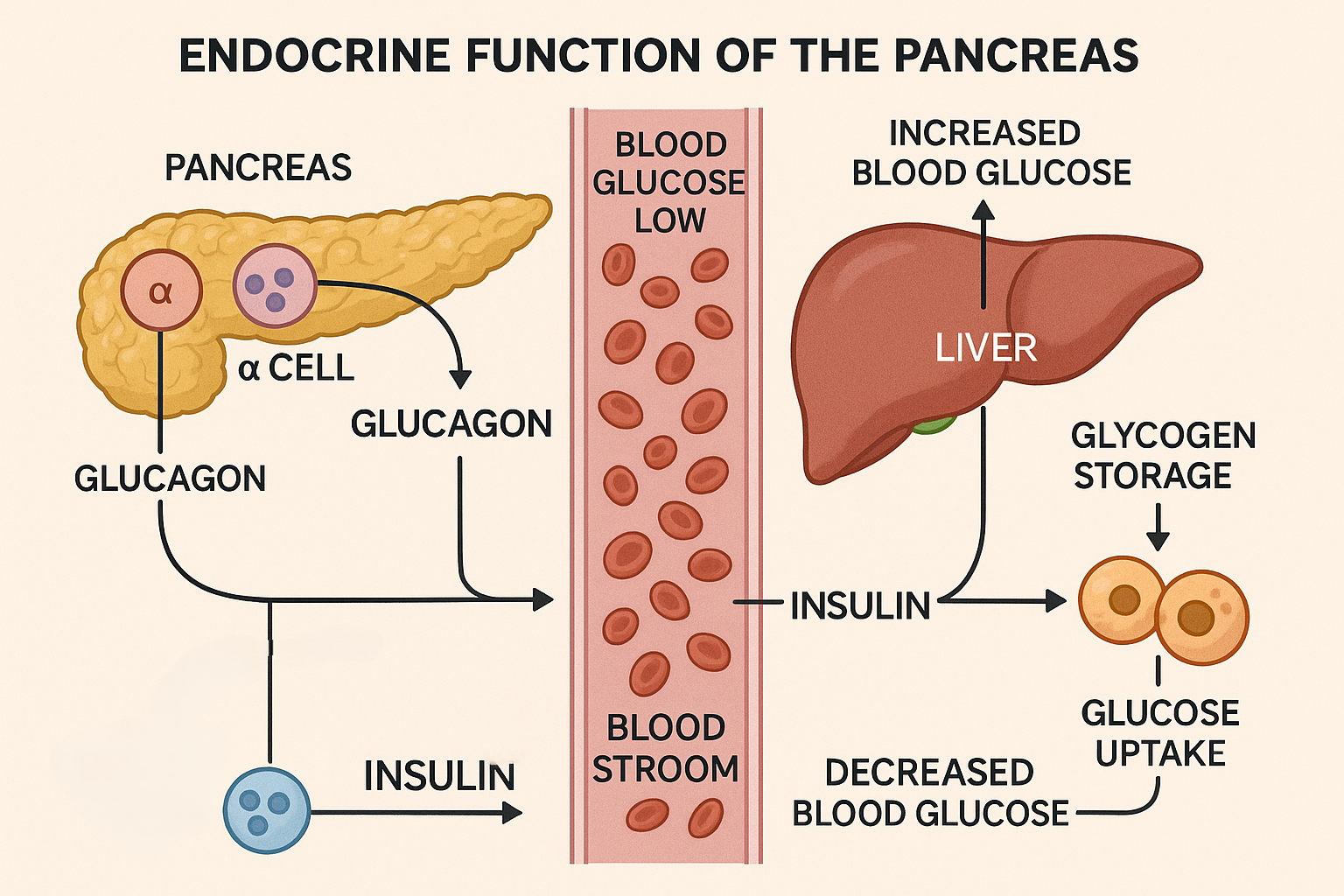 Answer: (B) To release glucagon when blood glucose levels are low
Answer: (B) To release glucagon when blood glucose levels are low
Explanation:
The pancreas helps regulate blood glucose levels by releasing two main hormones:
• When blood glucose is low, the pancreas releases glucagon. Glucagon signals the liver to break down glycogen into glucose and release it into the bloodstream.
• When blood glucose is high, the pancreas releases insulin, which helps cells absorb glucose and reduces blood glucose levels.
Option Evaluation:
A. Incorrect — Thyroxine is produced by the thyroid gland, not the pancreas.
B. Correct — Glucagon is released when blood glucose is low.
C. Incorrect — Insulin is released when blood glucose is high, not low.
D. Incorrect — Endopeptidases digest proteins and do not regulate blood glucose.
✅ Answer: (B)
Question
The diagram shows how heart sounds align with changes in blood pressure during the cardiac cycle.

What can be deduced about the cause of the heart sounds?
A. The \(1^{\text{st}}\) heart sound is caused by the closing of the atrio-ventricular valves
B. The \(2^{\text{nd}}\) heart sound is caused by the opening of the atrio-ventricular valves
C. The \(1^{\text{st}}\) heart sound is caused by the closing of the semi-lunar valves
D. The \(2^{\text{nd}}\) heart sound is caused by the closing of the atrio-ventricular valves
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: (A)
Explanation:
The heart sounds correspond to valve closures in the cardiac cycle:
\(S_1\) (“lub”): occurs at the start of ventricular systole when ventricular pressure exceeds atrial pressure, causing closure of the atrio-ventricular (AV) valves (mitral and tricuspid). This prevents backflow into the atria.
\(S_2\) (“dub”): occurs at the end of ventricular systole when ventricular pressure falls below arterial pressure, causing closure of the semi-lunar valves (aortic and pulmonary).
Option checks:
(B) Incorrect — valve openings are not heard; \(S_2\) is due to semi-lunar closure.
(C) Incorrect — \(S_1\) is AV valve closure, not semi-lunar.
(D) Incorrect — \(S_2\) is semi-lunar valve closure, not AV.
