IB DP Biology- C3.1 Integration of body systems - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 2 - FA 2025
Question
The drawing shows a vertical section through the brain.
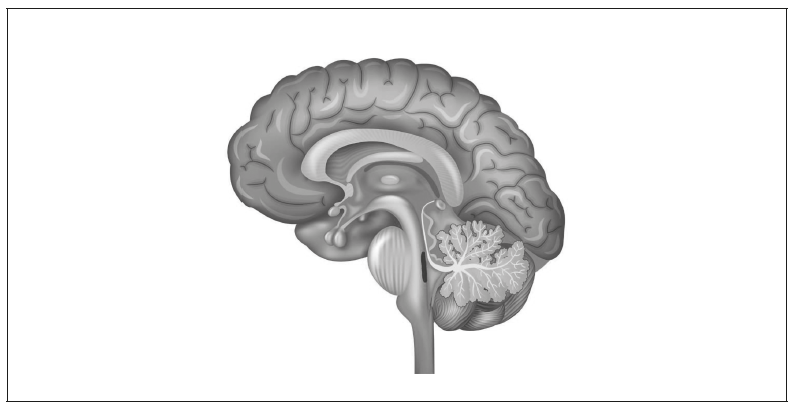
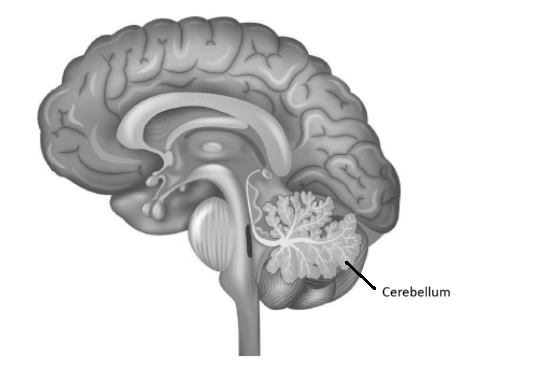
a.i. Label the cerebellum on the diagram.
ii. State a function of the cerebellum.
b. On the diagram, label one named structure that produces hormones.
c. Outline one method that can be used to investigate the function of different parts of the brain.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
a.i.
The cerebellum helps in controlling movement and maintaining balance.
b.
One hormone-producing structure is the pituitary gland, which can be labeled just below the brain, near the middle.
Alternatively, you can label the hypothalamus, just above the pituitary.
c.
One method is fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging). It shows which parts of the brain are active by measuring blood flow.
The cerebellum helps in controlling movement and maintaining balance.
b.
One hormone-producing structure is the pituitary gland, which can be labeled just below the brain, near the middle.
Alternatively, you can label the hypothalamus, just above the pituitary.
c.
One method is fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging). It shows which parts of the brain are active by measuring blood flow.
Another is during brain surgery, doctors sometimes use electrical stimulation to see how different areas affect behavior.
Markscheme:
a.i.
Label to cerebellum:

a.ii.
• Controls/coordinates (motor) movements
• Maintains balance
b.
• Label to pituitary gland
OR
• Label to hypothalamus
c.
Alternative 1:
• fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)
• Scan detects changes in blood flow/oxygenation in blood
OR
• More active parts of brain receive increased blood flow
Alternative 2:
• Lesion studies/autopsy
• Examination of damaged brain areas
OR
• Correlation of damage location with functional loss
Alternative 3:
• Electrical stimulation during neurosurgery
• Observation of behavioral/physiological responses
Note: Description must relate to the specific method named. For fMRI, the “f” must be written as “fMRI”.
