IB DP Biology- C3.2 Defense against disease - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
Which type of cell belongs to the innate (non-specific) immune system?
A. Phagocytes
B. B-lymphocytes
C. T-lymphocytes
D. Helper T-cells
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (A) Phagocytes
Question
What property of antibiotics makes them effective in the treatment of infectious diseases?
A. They stimulate the production of antibodies.
B. They block metabolic pathways in prokaryotes.
C. They block the metabolic processes in viruses.
D. They inhibit mitosis in eukaryotes.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
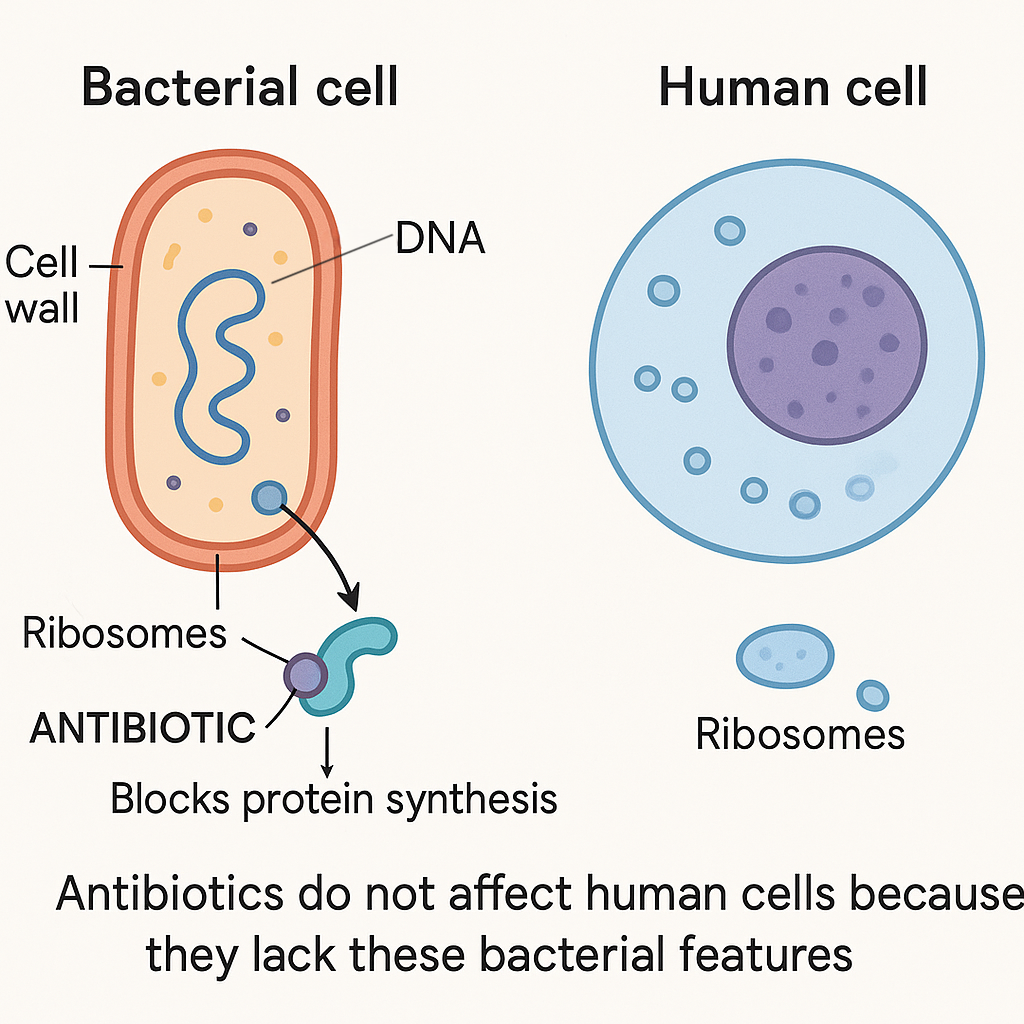 Answer: (B) They block metabolic pathways in prokaryotes.
Answer: (B) They block metabolic pathways in prokaryotes.
Explanation:
Antibiotics are effective because they selectively target metabolic pathways or cell structures that exist in prokaryotic cells (bacteria) but not in human cells. Examples include:
• Inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis
• Blocking bacterial ribosomes to stop protein synthesis
These differences allow antibiotics to kill or stop bacteria without harming human cells.
Option Evaluation:
A. Incorrect — Antibody production is done by the immune system, not antibiotics.
B. Correct — Antibiotics target pathways unique to bacteria.
C. Incorrect — Viruses lack their own metabolic pathways, so antibiotics cannot affect them.
D. Incorrect — Antibiotics do not inhibit mitosis in eukaryotes; that would damage human cells.
✅ Answer: (B)
Question
The diagram shows the major events involved in the formation of a blood clot.
What is Factor Y?
A. Fibrin
B. Prothrombin
C. Fibrinogen
D. Thrombin
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: (D) Thrombin
Explanation:
The diagram represents the blood clotting cascade, in which several clotting factors activate one another in sequence, leading to the formation of a fibrin clot.
Key steps:
• Tissue damage releases clotting factors from platelets and damaged cells.
• These activate an enzymatic cascade involving multiple clotting factors.
• Upstream factors (often labelled W and X) help convert prothrombin into thrombin.
• Factor Y is thrombin, the active enzyme that converts fibrinogen (Factor Z) into fibrin, forming the clot mesh.
Matching each option:
| Option | Substance | Role | Label |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Fibrin | Forms clot mesh | Factor Z |
| B | Prothrombin | Inactive precursor of thrombin | Precursor to Y |
| C | Fibrinogen | Converted into fibrin | Not Y |
| D | Thrombin | Converts fibrinogen to fibrin | Factor Y |
✅ Answer: (D) Thrombin
