IB DP Biology- C4.1 Populations and communities- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
Freshwater mussels are molluscs that inhabit rivers and lakes in many regions worldwide. They filter water to obtain food and in the process remove algae, bacteria and detritus, thereby helping to improve water quality.

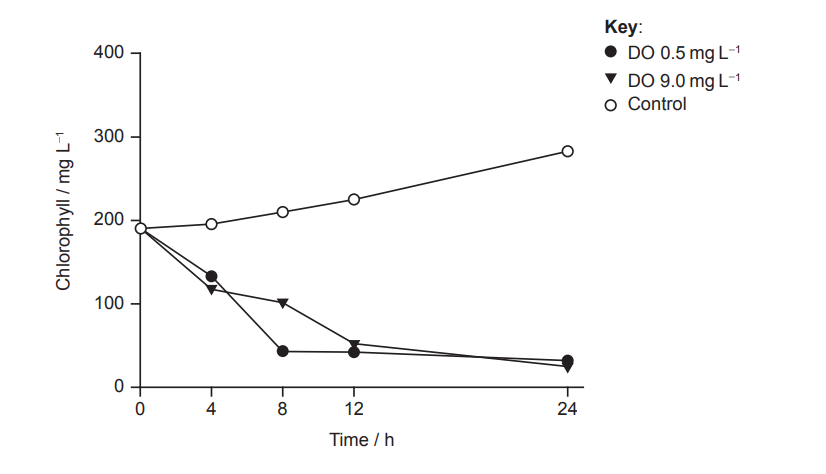
Researchers in South Korea placed mussels (U. douglasiae) into water containing cyanobacteria, a group of photosynthetic bacteria responsible for eutrophication in aquatic environments. The density of cyanobacteria is directly related to the concentration of chlorophyll in the water. The filtration efficiency of mussels can be assessed by observing how chlorophyll concentration changes over different time intervals. The experiments were performed at two different dissolved oxygen levels (DO). In the control experiment, no mussels were introduced and the DO level was \( 9.0 \text{ mg L}^{-1} \).
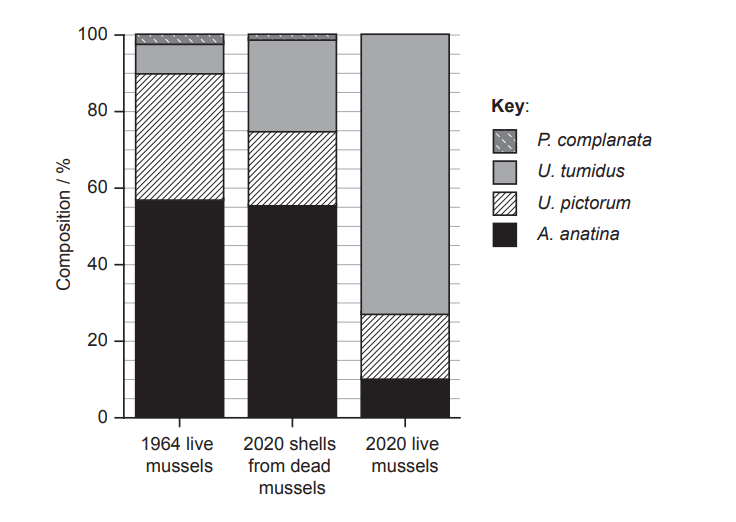
In \( 2020 \), scientists investigated the population density of four mussel species (A. anatina, U. pictorum, U. tumidus, and P. complanata) in the River Thames (United Kingdom). They compared their findings with results collected at the same site in \( 1964 \). The chart illustrates the percentage of each live species found in both years, as well as the percentage of empty shells discovered in \( 2020 \).
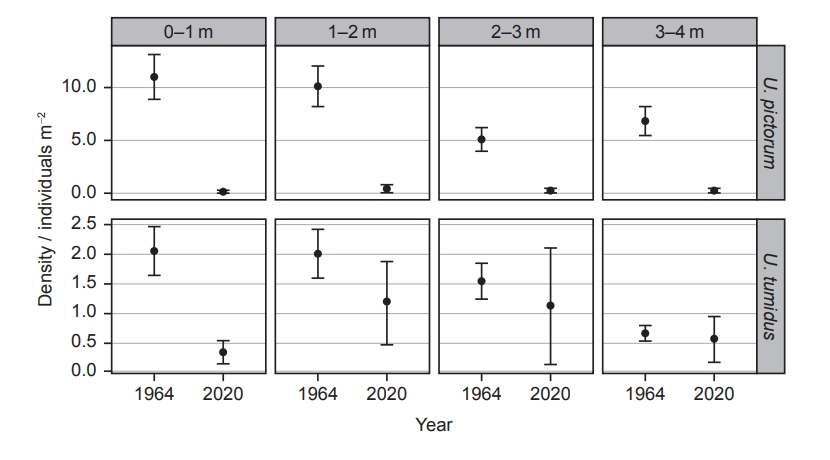
The researchers also examined how mussel density varied at different water depths. The graph below shows the data for U. pictorum and U. tumidus.
Most-appropriate topic codes (CED):
• TOPIC D4.2: Stability and change — part (j)
• TOPIC C4.1: Populations and communities — parts (f), (g)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
Estimated chlorophyll concentration: \( 250 \text{ mg L}^{-1} \) (Acceptable range: \( 240–260 \text{ mg L}^{-1} \)).
(b)
• In the control (no mussels), chlorophyll levels — and therefore cyanobacteria density — increase steadily.
• In the presence of mussels at \( DO = 9.0 \text{ mg L}^{-1} \), chlorophyll concentration decreases due to filtration.
(c)
Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic and would reproduce and grow during the experiment, increasing chlorophyll concentration.
(d)
• Similarity: At both DO levels, mussels reduce chlorophyll concentration.
• Difference: Filtration is initially faster at \( DO = 0.5 \text{ mg L}^{-1} \) but stops after around \( 12 \) hours, whereas filtration continues slowly at \( DO = 9.0 \text{ mg L}^{-1} \).
(e)
Estimated percentage of U. pictorum in \( 1964 \): \( 33\% \) (Based on graph: approximately \( 90\% – 57\% = 33\% \)).
(f)
The shell composition from \( 2020 \) most closely matches the 1964 live species distribution. Reason: The shells have high proportions of A. anatina and U. pictorum, similar to the \( 1964 \) pattern.
(g)
The data does not confirm an increase in the actual population of U. tumidus. Although its percentage increased (from about \( 8\% \) in \( 1964 \) to about \( 74\% \) in \( 2020 \)), the total mussel population may have declined. Thus, the absolute number may be lower.
(h)
Density at \(1–2 \text{ m}\): \( \approx 10.0 \text{ individuals m}^{-2} \)
Density at \(2–3 \text{ m}\): \( \approx 5.0 \text{ individuals m}^{-2} \)
Percentage decrease: \[ \frac{(10.0 – 5.0)}{10.0} \times 100 = 50\% \]
(i)
• Similarity: Both species show a decline in density from \( 1964 \) to \( 2020 \).
• Difference: U. pictorum declines sharply at all depths, approaching zero in \( 2020 \), while U. tumidus only shows a major drop at the shallowest depth.
(j)
The data suggests water quality may have deteriorated. Mussels filter and improve water, and a sharp reduction in mussel density — especially U. pictorum — indicates they may not be surviving due to poorer environmental conditions. Alternatively, a shift in species composition (dominance of U. tumidus) implies changes in water quality that favor certain species over others.
