IB DP Biology- C4.1 Populations and communities - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
A capture–mark–release–recapture study was conducted to estimate the population size of common periwinkles (Littorina littorea) on a rocky shore. Researchers used the Lincoln index formula, given by Population size estimate = (M × N) / R. The following data were collected:
| Description | Number |
|---|---|
| Individuals captured and marked initially | 100 |
| Individuals recaptured | 50 |
| Marked individuals recaptured | 10 |
What is the estimated total population size of Littorina littorea based on these results?
A. 160
B. 500
C. 1000
D. 5000
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (B) 500
Question
Limpets are molluscs with conical shells that cling tightly to rocks on seashores. In a study of two species of limpets found on rocks along the Oregon coast, \(30\) randomly placed quadrats were used to determine how often the two species occurred together. The table shows the data that were collected.
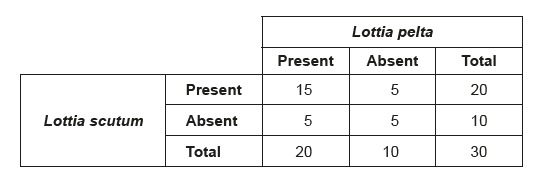
Which statistical method will determine whether these two species occur together by chance or by some kind of interaction?
A. Chi-squared test
B. \(t\)-test
C. Standard deviation
D. Means and ranges
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: A. Chi-squared test
Explanation:
The Chi-squared test \( (\chi^2) \) is appropriate when you are working with categorical data (e.g., presence/absence) and want to test whether two variables are independent or associated.
What the Table Shows:
- You are testing whether the presence of Lottia scutum is independent of the presence of Lottia pelta.
- This is categorical (present/absent) data across two species and \(30\) quadrats.
- A \(\chi^2\) test for independence is ideal here.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect:
| Option | Description | Why It’s Incorrect |
|---|---|---|
| B. \(t\)-test | Compares means of continuous data between two groups. | Here the data are categorical (present/absent), not continuous. |
| C. Standard deviation | A measure of spread for numerical datasets. | Does not test association or independence between variables. |
| D. Means and ranges | Descriptive statistics for continuous data. | Cannot provide a statistical test of independence for categorical variables. |
Question
Which organism can best be described as a saprotroph?
A. A fungus that digests its food externally and absorbs the products of digestion
B. A beetle that feeds by ingesting the dung of other animal species and digesting its food internally
C. A single-celled eukaryote that is able to photosynthesize and consumes smaller organisms by endocytosis
D. A giraffe that feeds by ingesting leaves from an acacia tree
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: A. A fungus that digests its food externally and absorbs the products of digestion
Explanation: 
A saprotroph is an organism that feeds on dead or decaying organic matter by secreting digestive enzymes outside its body (external digestion) and then absorbing the broken-down nutrients. Fungi are classic examples of saprotrophs.
Answer Evaluation:
A. Correct – Fungi are saprotrophs. They release enzymes into the environment to break down complex organic materials (like dead plants), then absorb the simpler nutrients. This is the defining feature of saprotrophic nutrition.
B. Incorrect – The beetle ingests and digests food internally, which is typical of heterotrophic consumers, not saprotrophs.
C. Incorrect – This organism performs both photosynthesis and phagocytosis, making it a mixotroph, not a saprotroph.
D. Incorrect – A giraffe eats plants (autotrophs) and digests them internally. It is a herbivore, not a saprotroph.
