IB DP Biology- D1.1 DNA replication- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
Which enzyme is associated with proofreading during DNA replication?
(A) DNA primase
(B) DNA helicase
(C) DNA polymerase III
(D) DNA ligase
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
What is the role of DNA polymerase I in DNA replication?
A. Form replication forks
B. Remove RNA primers
C. Add short length of RNA to template strand of DNA
D. Add DNA nucleotides to the 5 end of the new strand
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: B. Remove RNA primers
Explanation:
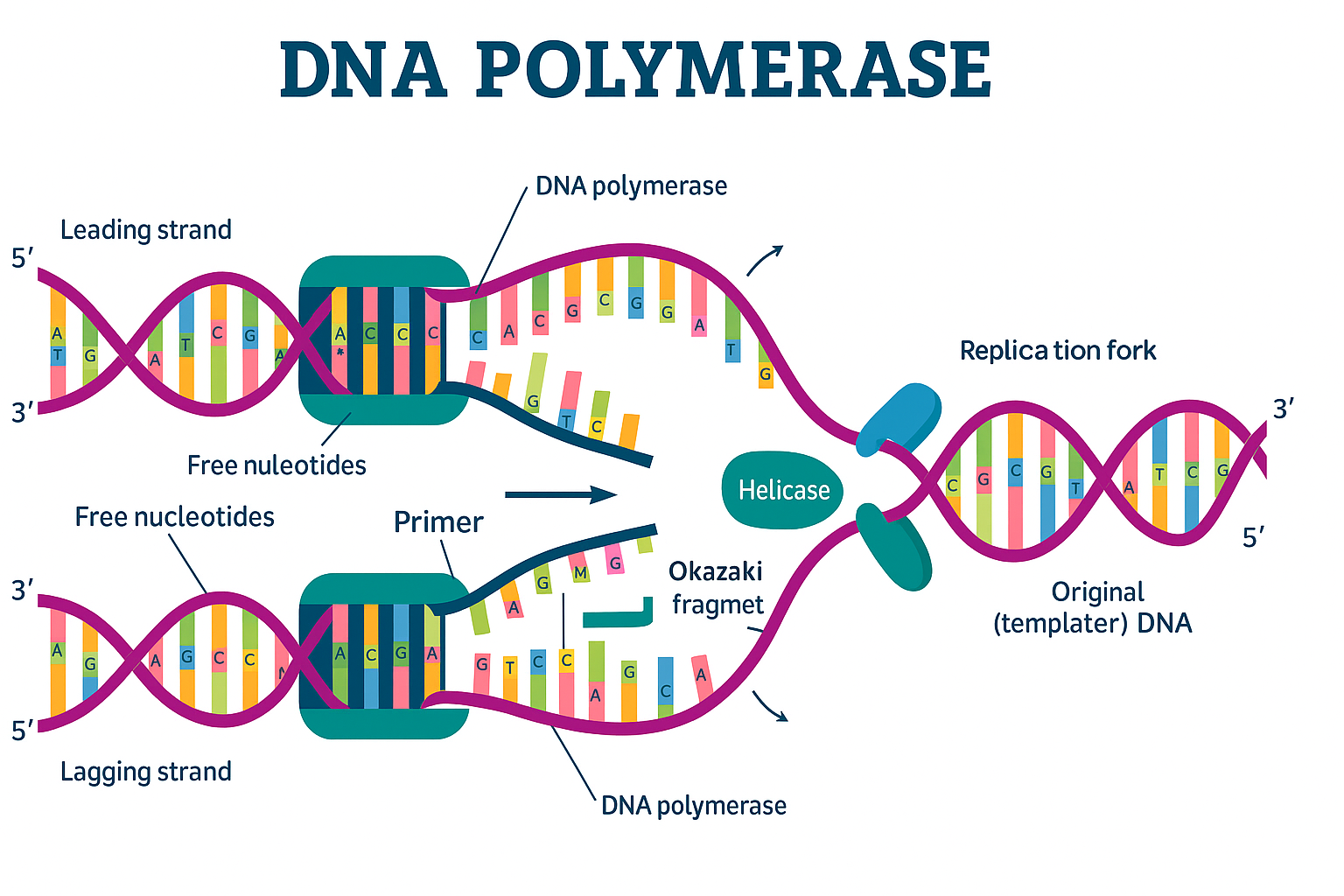
- DNA polymerase I removes the RNA primers laid down by primase and replaces them with DNA nucleotides.
- It also has proofreading and repair functions.
Incorrect options:
A. Form replication forks – This is done by helicase.
C. Add short length of RNA – This is the role of RNA primase.
D. Add DNA to 5′ end – DNA polymerases add nucleotides to the 3′ end, not 5′.
Question
Which are two proteins that assist in the unwinding and separation of DNA strands during replication?
A. Helicase and DNA polymerase III
B. DNA gyrase and DNA polymerase I
C. Helicase and DNA primase
D. Single-strand binding protein and DNA gyrase
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: D. Single-strand binding protein and DNA gyrase
Explanation: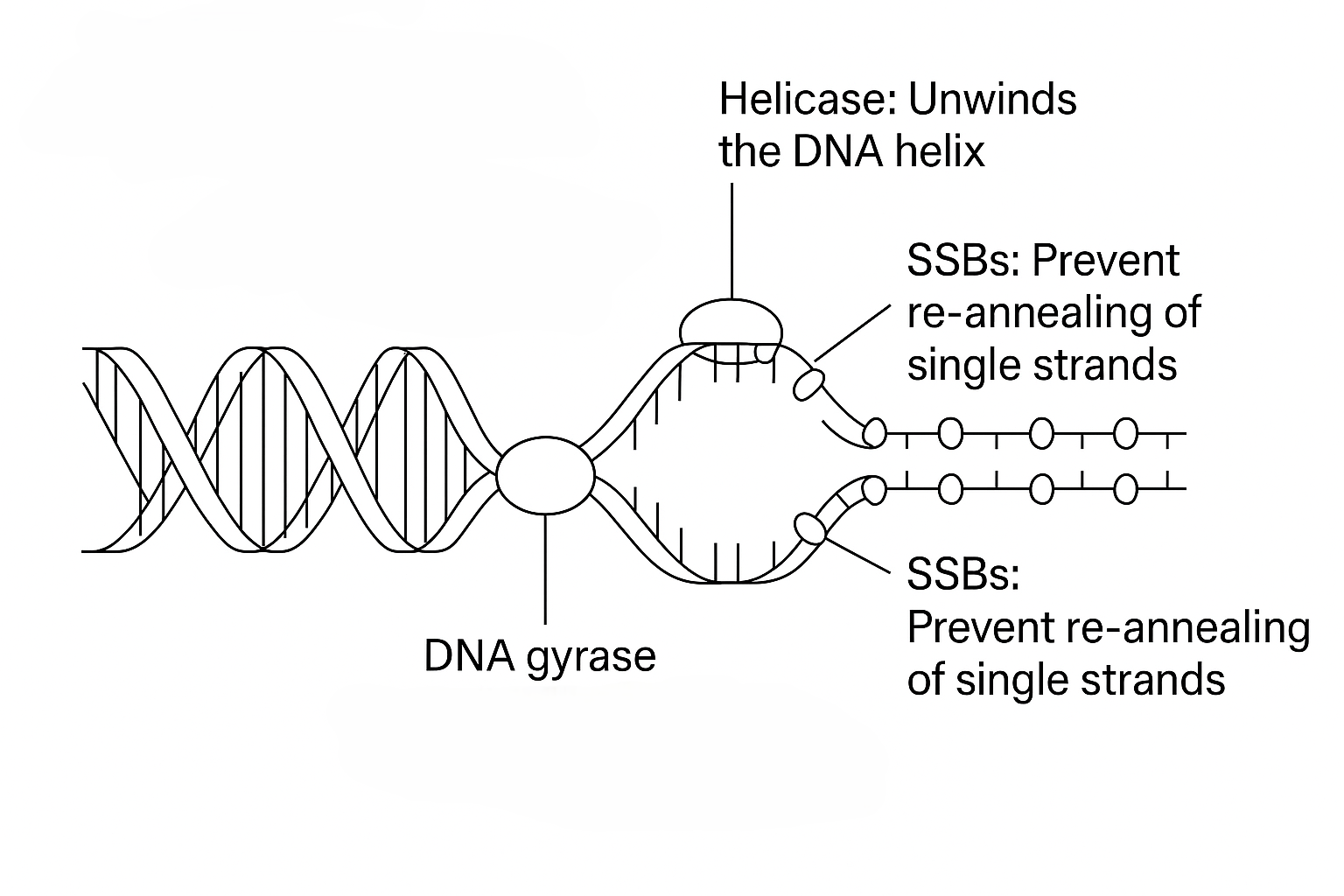
- Helicase unwinds DNA.
- DNA gyrase (topoisomerase) reduces supercoiling during unwinding.
- Single-strand binding proteins (SSBs) keep the strands separated.
Incorrect options:
A. Helicase and DNA polymerase III – Polymerase III extends DNA but doesn’t assist in unwinding.
B. DNA gyrase and DNA polymerase I – Polymerase I removes primers, not involved in unwinding.
C. Helicase and DNA primase – Primase adds primers, doesn’t help unwind DNA.
