IB DP Biology- D1.1 DNA replication - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
Which diagram(s) below best represent the process of semi-conservative DNA replication?
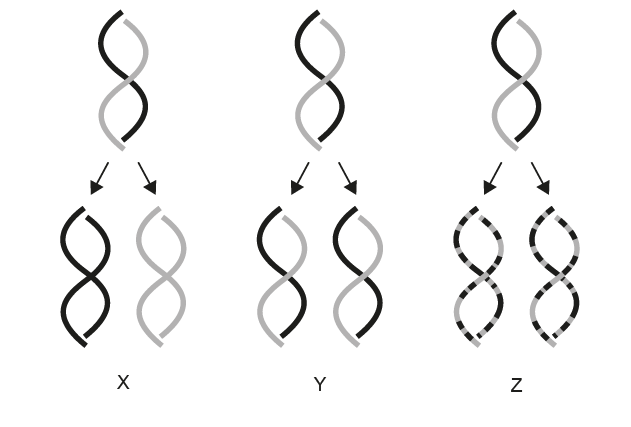
B. Y only
C. Z only
D. X and Y only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
In semi-conservative replication, each new DNA molecule contains one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
Only diagram Y shows this pattern correctly.
✅ Correct Answer: B
Question
Which stage of DNA profiling involves the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
A. During extraction of the DNA sample
B. During replication of the DNA that has been cut with restriction enzymes
C. During electrophoresis to separate the DNA fragments on a gel
D. During incubation with labelled probes
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: B. During replication of the DNA that has been cut with restriction enzymes
Explanation:
DNA profiling is a laboratory technique used to identify individuals by analyzing specific regions of their DNA.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method that creates millions of copies of a targeted DNA segment. In DNA profiling, PCR is used after restriction enzymes have cut the DNA to amplify these fragments, making them easier to detect and analyze during subsequent steps like gel electrophoresis.
Answer Evaluation:
A. Incorrect – Extraction is the process of isolating DNA from cells. PCR is not used during extraction.
B. Correct – PCR amplifies (copies) the DNA fragments after they have been cut with restriction enzymes, allowing further analysis.
C. Incorrect – Electrophoresis is a separation technique based on fragment size; it does not involve replication or amplification.
D. Incorrect – Incubation with labelled probes is used for detecting specific DNA sequences, not for replication.
Question
What is the role of DNA polymerase during DNA replication?
A. It adds nucleotides to the growing strand.
B. It adds nucleotides to the template strand.
C. It builds messenger RNA.
D. It carries out translation.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: A. It adds nucleotides to the growing strand.
Explanation:
DNA polymerase is a key enzyme involved in DNA replication. Its primary function is to add new nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growing strand, using the original DNA strand as a template. This ensures the formation of a complementary and accurate copy of the DNA molecule.
- DNA polymerase does not add nucleotides to the template strand — it reads it and builds the complementary one.
- Building messenger RNA is done by RNA polymerase, not DNA polymerase.
- Translation (protein synthesis) occurs in ribosomes and does not involve DNA polymerase.
Answer Evaluation:
A. Correct – DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the new (growing) strand during replication.
B. Incorrect – The enzyme uses the template strand as a guide; it does not add nucleotides to it.
C. Incorrect – Messenger RNA is synthesized by RNA polymerase, not DNA polymerase.
D. Incorrect – Translation is performed by ribosomes using mRNA, not DNA polymerase.
