IB DP Biology-D1.3 Mutations and gene editing - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
(B) They only occur in germ cells.
(C) The frequency cannot be increased by external factors.
(D) They only occur in certain base sequences of the genome.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Mutations occur randomly throughout the genome and can happen in any cell type. While external factors like radiation and chemicals can increase mutation frequency, the fundamental characteristic is that mutations arise by chance rather than being directed to specific locations or sequences.
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
Which of the following types of information are needed to construct a karyotype?
I. Size of the chromosomes
II. Gene mutations of the chromosomes
III. Age of the individual
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and II only
D. I, II and III
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: A. I only
Explanation:
- A karyotype is a visual display of all the chromosomes in a cell, arranged by size, banding pattern, and centromere position. It is commonly used to detect chromosomal abnormalities such as extra or missing chromosomes (e.g., trisomy 21).
- The size of the chromosomes is essential for pairing and ordering them correctly in a karyotype.
- Gene mutations are changes at the DNA sequence level. They are too small to be seen in a karyotype and require molecular genetic testing.
- The age of the individual is not required to construct a karyotype, although it may be relevant when interpreting certain abnormalities.
Answer Evaluation:
I. Correct – Chromosome size is necessary to assemble a karyotype.
II. Incorrect – Gene mutations cannot be detected using a karyotype.
III. Incorrect – Age is not required to create the karyotype itself.
Question
The flow chart summarizes methods of gene transfer.
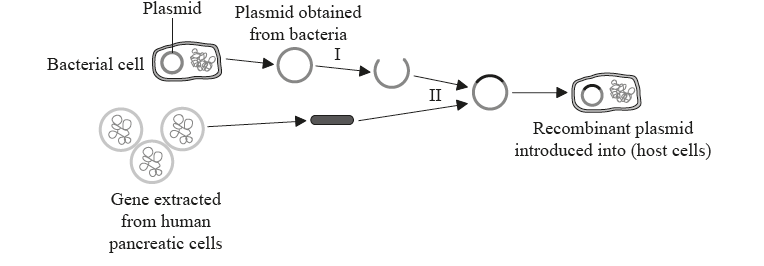
Which enzymes are used in steps I and II?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
Step I: Cutting the plasmid and the human gene
- This step involves cutting both the bacterial plasmid and the target human gene (e.g., insulin gene).
- The enzyme that cuts DNA at specific recognition sequences is a restriction enzyme (restriction endonuclease).
Enzyme used in Step I: Restriction enzyme
Step II: Joining the human gene with the plasmid
- This step involves ligating the human gene into the plasmid to produce recombinant DNA.
- The enzyme that joins DNA fragments together is DNA ligase.
Enzyme used in Step II: DNA ligase
