IB DP Biology- D2.1 Cell and nuclear division-IB Style Questions For HL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
The image below shows cells in the root tip of an onion (Allium cepa) undergoing cell division by mitosis.
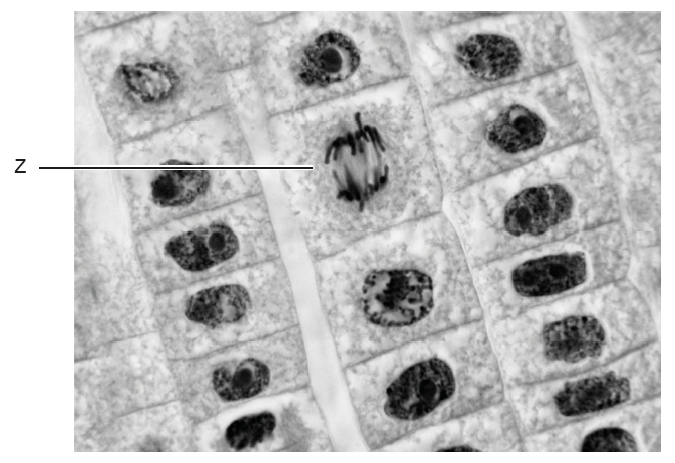
The cell labeled \( Z \) is currently in which stage of mitosis?
A. Interphase
B. Prophase
C. Metaphase
D. Anaphase
▶️ Answer/Explanation
This separation of sister chromatids is characteristic of anaphase, when spindle fibers shorten and move the chromatids apart.
✅ Answer: (D) Anaphase
Question
What would show that a person has developed metastatic cancer?
A. Alveolus cells forming a tumour in the lungs
B. Cancer cells producing the skin pigment melanin in the liver
C. A tumour in the prostate gland increasing levels of prostate-specific antigen
D. Cancerous lymphocytes in blood plasma
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: B. Cancer cells producing the skin pigment melanin in the liver
Explanation:
What is metastasis?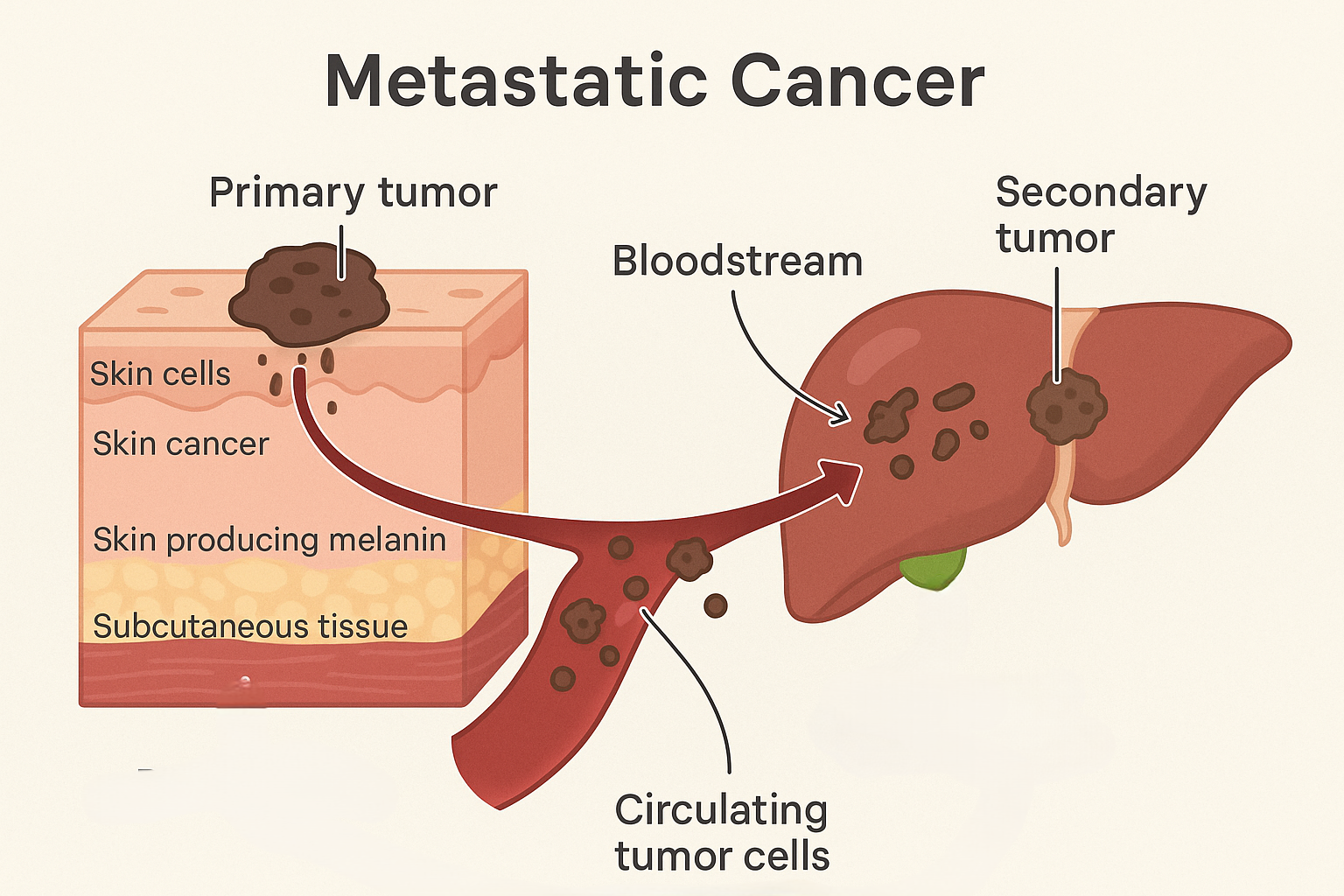
Metastasis is when cancer cells spread from their original site to other parts of the body, often via the blood or lymphatic system. When these cells grow in other tissues or organs, it is considered metastatic cancer.
Now evaluate each option:
A. Incorrect – Alveolus cells forming a tumor in the lungs could just mean lung cancer, but this does not confirm metastasis unless they originated from another tissue.
B. Correct – Melanin is produced by skin cells (melanocytes). If these pigment-producing cancer cells are found in the liver, it means skin cancer has spread, showing metastasis.
C. Incorrect – A tumor in the prostate causing higher PSA levels suggests local prostate cancer, not necessarily metastasis.
D. Incorrect – Lymphocytes are normal parts of blood plasma. Cancerous lymphocytes may indicate leukemia, but unless they originate from another tissue, this isn’t clear evidence of metastasis.
