IB DP Biology-D2.1 Cell and nuclear division - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
The image below shows cells in the root tip of an onion (Allium cepa) undergoing cell division by mitosis.
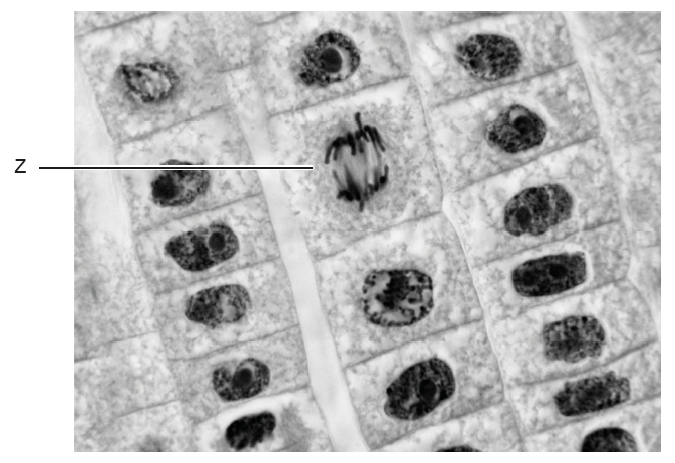
The cell labeled \( Z \) is currently in which stage of mitosis?
A. Interphase
B. Prophase
C. Metaphase
D. Anaphase
▶️ Answer/Explanation
In the micrograph, the chromosomes in cell \( Z \) are being pulled toward opposite poles of the cell.
This separation of sister chromatids is characteristic of anaphase, when spindle fibers shorten and move the chromatids apart.
✅ Answer: (D) Anaphase
This separation of sister chromatids is characteristic of anaphase, when spindle fibers shorten and move the chromatids apart.
✅ Answer: (D) Anaphase
Question
A tissue sample was examined under a microscope to determine the mitotic index. The number of cells in each stage of the cell cycle was counted and recorded in the table.
| Stage of cell cycle | Interphase | Prophase | Metaphase | Anaphase | Telophase | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cells | \(120\) | \(20\) | \(10\) | \(8\) | \(2\) | \(160\) |
What is the mitotic index?
A. \(0.125\)
B. \(0.25\)
C. \(0.75\)
D. \(1.00\)
B. \(0.25\)
C. \(0.75\)
D. \(1.00\)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The mitotic index is the fraction of cells that are in mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase):
\[ \text{Mitotic Index} \;=\; \frac{\text{Number of cells in mitosis}}{\text{Total number of cells}} \] Cells in mitosis here: \(20 + 10 + 8 + 2 = 40\). Total cells: \(160\).
\[ \text{Mitotic Index} \;=\; \frac{40}{160} \;=\; 0.25 \] ✅ Answer: (B) \(0.25\)
\[ \text{Mitotic Index} \;=\; \frac{\text{Number of cells in mitosis}}{\text{Total number of cells}} \] Cells in mitosis here: \(20 + 10 + 8 + 2 = 40\). Total cells: \(160\).
\[ \text{Mitotic Index} \;=\; \frac{40}{160} \;=\; 0.25 \] ✅ Answer: (B) \(0.25\)
Question
A \(2\)-cell sea urchin (Echinoidea) embryo was experimentally separated into its two blastomeres. Each cell proceeded through development and produced an adult sea urchin.
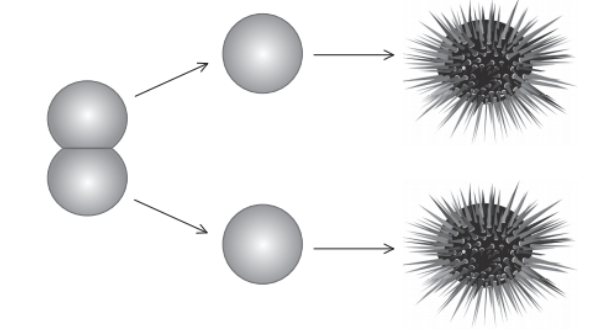
What is the relationship between the two adult sea urchins?
A. They are equivalent to non-identical twins.
B. Half of the genes would be the same.
C. Both adults would have haploid cells.
D. They are clones.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The two adults are clones.
A single zygote first divided by mitosis into \(2\) genetically identical blastomeres. When separated, each cell retained a full diploid genome and developed independently, yielding adults with \(\,100\%\) identical nuclear DNA.
Why others are incorrect
A: Non-identical (fraternal) twins arise from \(2\) different eggs fertilized by \(2\) different sperm → not genetically identical.
B: “Half the genes the same” describes typical siblings; clones share ~\(\,100\%\) of nuclear genes.
C: Adult somatic cells are diploid; only gametes are haploid.
✅ Answer: (D) They are clones.
A single zygote first divided by mitosis into \(2\) genetically identical blastomeres. When separated, each cell retained a full diploid genome and developed independently, yielding adults with \(\,100\%\) identical nuclear DNA.
Why others are incorrect
A: Non-identical (fraternal) twins arise from \(2\) different eggs fertilized by \(2\) different sperm → not genetically identical.
B: “Half the genes the same” describes typical siblings; clones share ~\(\,100\%\) of nuclear genes.
C: Adult somatic cells are diploid; only gametes are haploid.
✅ Answer: (D) They are clones.
