IB DP Biology- D2.2 Gene expression-IB Style Questions For HL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
Researchers studying twins measured methylation levels of amino acids associated with chromosome 2. Twin 1 showed significantly and consistently higher methylation than twin 2. Which explanation best accounts for this observation?
B. Removal of the histone from the chromosome in twin 2
C. The DNA base sequence of twin 1 was altered
D. Cytosines in promoters of twin 2 are more methylated than in twin 1
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
What is consistently located at the same loci on homologous chromosomes?
A. Alleles with the same function
B. Alleles with identical base sequences
C. Genes with identical base pairs
D. Genes with the same mutations
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: A. Alleles with the same function
Explanation:
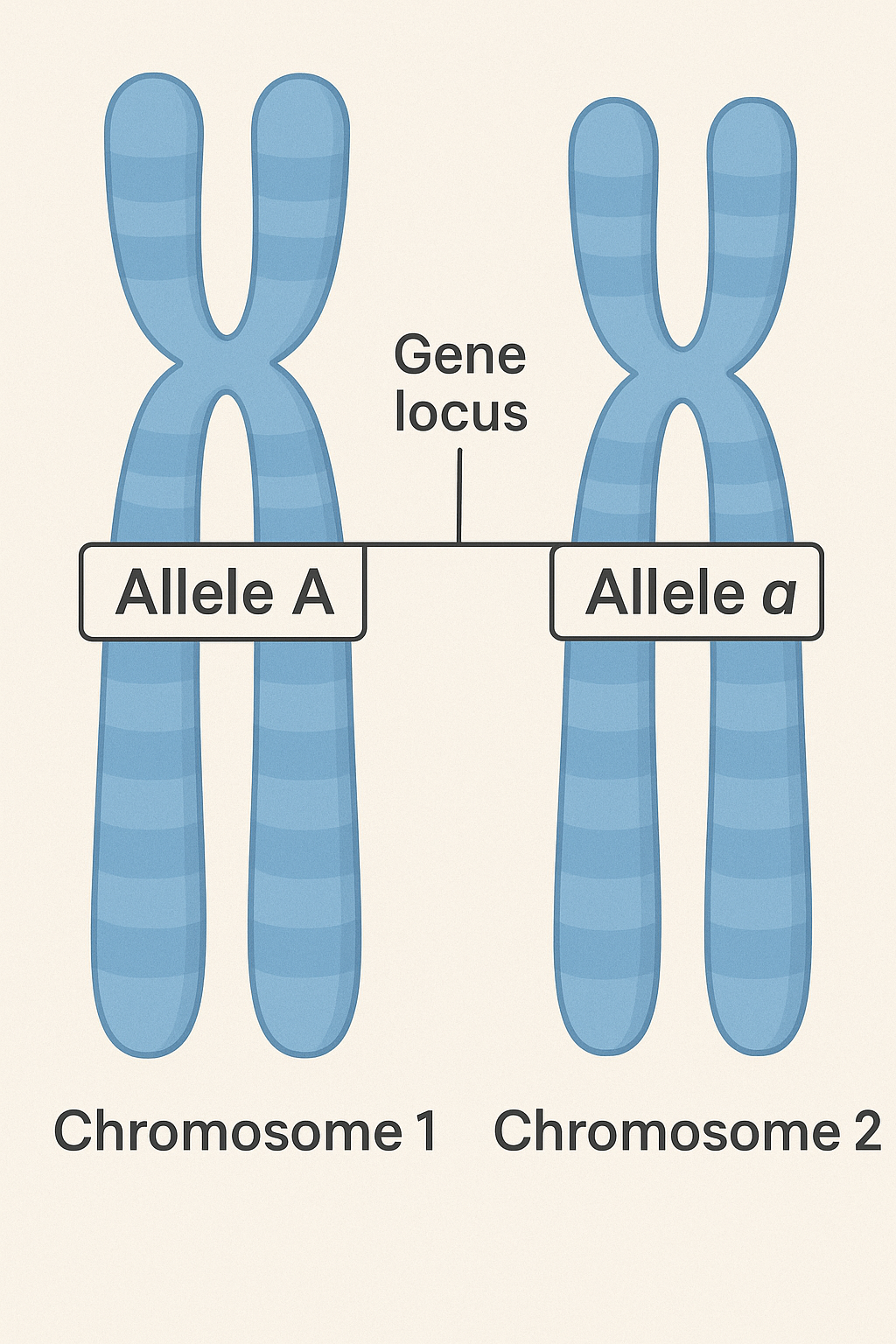
- Homologous chromosomes have genes at the same loci but may carry different alleles of those genes.
- These alleles may have different base sequences but usually code for proteins with the same function (even if one allele is mutated).
- So, while alleles can differ, they generally perform the same biological function at the same loci on homologous chromosomes.
Why other options are incorrect:
B. Alleles with identical base sequences: Alleles can have slight sequence variations.
C. Genes with identical base pairs: Alleles can differ in base pairs due to mutations.
D. Genes with the same mutations: Not all homologous chromosomes carry the same mutation.
Question
What would be an advantage of using embryonic stem cells over adult stem cells in the potential treatment of spinal cord injuries in humans?
A. More cell types can be obtained.
B. Possibilities of rejection are lower.
C. The risk of stem cells forming malignant tumors is lower.
D. Unlimited numbers of cells can be extracted from the umbilical cord.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: A. More cell types can be obtained.
Explanation:
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent, meaning they can develop into almost any cell type. Adult stem cells are multipotent, usually limited to forming certain tissue types.
Let’s analyze the options:
A. Correct – ESCs can become more cell types than adult stem cells, which is especially useful in complex injuries like those in the spinal cord.
B. Incorrect – ESCs are more likely to be rejected by the immune system compared to adult stem cells from the patient.
C. Incorrect – ESCs have a higher risk of forming tumors due to their rapid division and pluripotency.
D. Incorrect – Embryonic stem cells are not extracted from the umbilical cord; that refers to cord blood stem cells, which are distinct.
