IB DP Biology- D4.2 Stability and change - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
(B) Removal of apex predators
(C) Reintroduction of keystone species
(D) Restricting size for easier management
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Rewilding focuses on restoring natural processes and reintroducing key species that have been lost from ecosystems. The reintroduction of keystone species is a central strategy in rewilding projects to restore ecological balance.
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
The diagram shows the carbon cycle. Which letter indicates respiration?
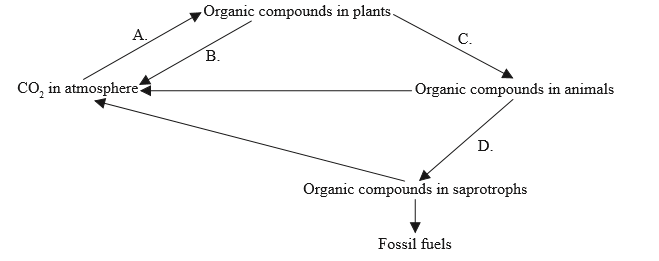
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation:
- In the carbon cycle, respiration is the process in which organisms break down organic compounds (such as glucose) and release carbon dioxide (CO₂) into the atmosphere. This occurs in plants, animals, and decomposers.
- In the diagram, Arrow B shows carbon moving from organic compounds in plants to CO₂ in the atmosphere, which directly represents plant respiration.
- Other organisms also respire, but B is the clearest and most direct example shown.
Answer Evaluation:
A. Incorrect – Represents photosynthesis, where plants absorb CO₂.
B. Correct – Represents respiration, releasing CO₂ into the atmosphere.
C. Incorrect – Represents feeding (carbon transfer from plants to animals).
D. Incorrect – Represents decomposition, not respiration, though microbes respire during decay.
Question
Which processes occur in an ecosystem?
I. Biomass increases in each successive trophic level.
II. Inorganic nutrients are recycled.
III. Chemical energy is stored in carbon compounds.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: C. II and III only
Explanation:
- An ecosystem includes both living organisms and the physical environment, where energy flows and nutrients cycle.
- Inorganic nutrients (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, etc.) are recycled through processes like decomposition and photosynthesis, allowing them to be reused.
- Chemical energy is stored in carbon compounds such as glucose, produced during photosynthesis. This energy is passed through food chains.
- Biomass does not increase at higher trophic levels; it actually decreases because much of the energy is lost as heat, waste, and through respiration.
Answer Evaluation:
A. Incorrect – I is wrong; biomass decreases as trophic level increases.
B. Incorrect – I is wrong; energy is stored but biomass does not increase.
C. Correct – II and III are accurate processes occurring in ecosystems.
D. Incorrect – Includes I, which is not true.
