IBDP Online Test Series By iitianacademy
Comprehensive Test Preparatory package targeted towards IBDP
Question
Outline how the human brain can reorganize itself following a stroke.
State the area of the human brain that may have been damaged when the following symptom is present:
A lack of muscle control on the left side of the body
State the area of the human brain that may have been damaged when the following
symptom is present.
Difficulty in swallowing
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
activities/functions spread across the brain
OR
activities/functions taken over by other areas of the brain
right motor cortex
OR
right cerebral hemisphere
medulla «oblongata»
Question
The images show the early stages and completed outcome of the process of neurulation.
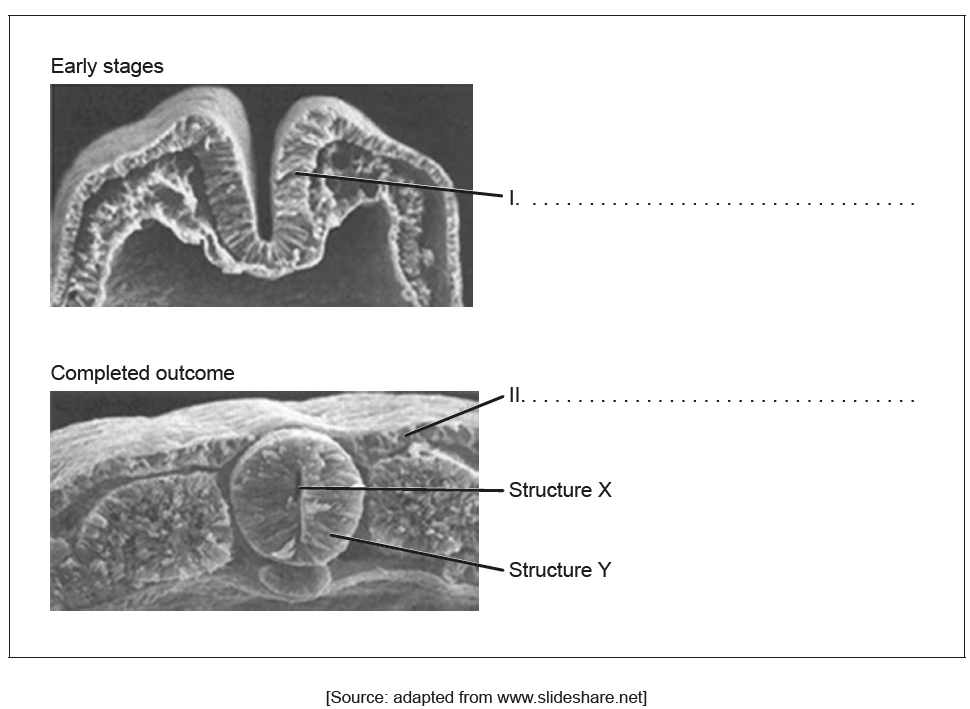
Label the parts I and II on the images.
Structure Y will eventually elongate to form two structures. State the names of these two structures.
1.
2.
State the condition that arises if the closure of structure X is incomplete during embryonic development.
The diagrams show a rat brain and a human brain. They are not drawn to scale.
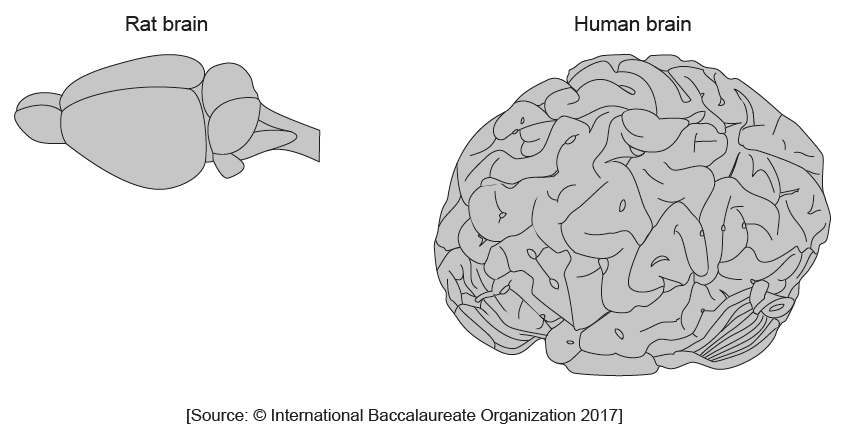
Distinguish between the cerebral cortex of the human brain and of the rat brain.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. I: neural groove/plate/fold
b. II: ectoderm
a. brain
b. spinal cord
spina bifida
a. human cortex larger than rat cortex
b. human cortex proportionally larger than other brain parts than rat cortex OWTTE
c. surface area «of cortex» larger for humans
d. more infolding of the surface of the cerebral cortex in humans
Question
A study examined the effects of four weeks of intensive training in athletes on vertical jumping performance and neuromuscular learning. The graph shows the results for jumping height.
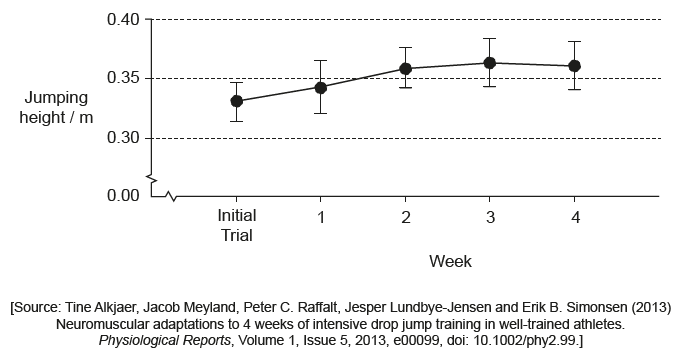
Outline the effect of training on jumping performance.
List the different types of neurons involved in a reflex arc.
Predict whether an animal such as a laboratory rat could be encouraged to learn a new behaviour pattern.
Using an example, describe how innate behaviour may increase the chances of survival of a species.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. jumping performance shows an improvement «during the first two/three weeks»
OR
no/little improvement as error bars all overlap
b. «during the period of this investigation» it reaches a plateau
c. the investigation was over a short time and is not conclusive of the effects of training over a longer period
a. sensory/afferent neuron
b. motor/efferent neuron
c. relay neuron/interneuron
Two correct for [1]
Three correct for [2]
a. operant conditioning/classical conditioning/trial and error experiences
b. behaviour could be modified by positive/negative reinforcement
c. animal makes an association between a particular behaviour and a consequence
Accept reward/punishment and/or examples such as food/electric shock.
a. innate behaviour inherited/develops independently of environment
OR
Changes in innate behaviour depend on change in frequency of alleles that cause the behaviour ✓
b. example of an innate behaviour ✓
c. description of the behaviour ✓
d. outcomes affecting survival
eg
b. synchronized oestrus in female lions
c. female lions can share responsibilities / females can suckle each other’s cubs allowing some mothers to hunt
d. cubs are more likely to survive when they are raised in a group «nursery» rather than by a solitary mother /group of male cubs can leave pride together helping each other
Question
Outline the development of axons in immature neurons.
State one activity controlled by the medulla oblongata.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. axon grows from an «immature» neuron
b. chemical stimuli trigger the growth/direction of axon
c. only one axon develops per neuron
d. some axons extend beyond neural tube to reach other parts of body
gut muscles / heart rate/cardiac centre / vasomotor / breathing/ventilation rate / reflex centre of vomiting/coughing/sneezing/swallowing
Question
Defects in the formation of synapses could be the cause of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease that affects the ability to think and remember clearly. It is more frequent in people older than 65 years of age. The graph shows the changes in synapse number over time. The diagram shows activity-related neural development.
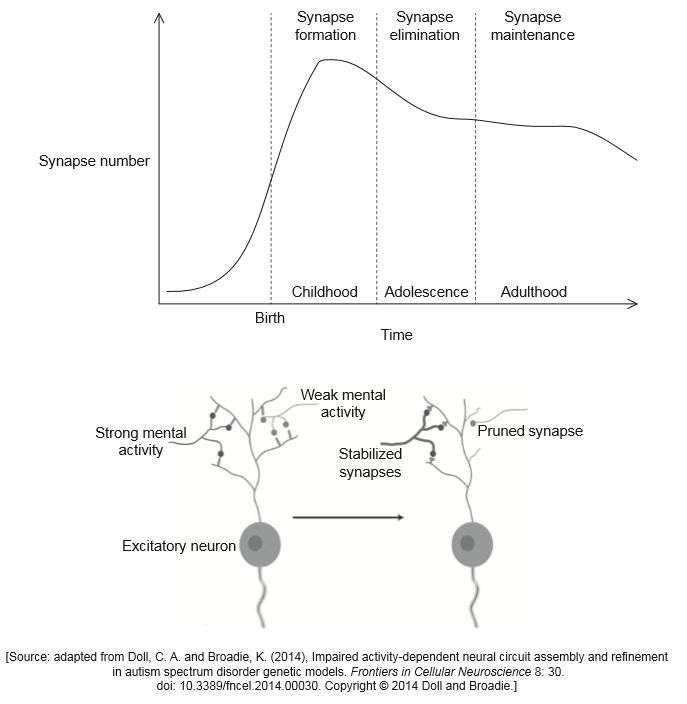
State what happens to unused neurons.
Predict how mental activity might delay the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
Autism appears early in life and affects how a person communicates and relates to others. There is evidence that autism could be caused by a surplus of synapses. Using all of the information provided, suggest two possible causes of a surplus of synapses in people with autism.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
neuron pruning
OR
synapses removed
Do not accept “apoptosis”.
a. more synapses maintained with stimulation/mental activity/OWTTE
b. strong mental activity prevents «neuron» pruning
a. most synapses are formed during childhood/before birth
OR
first years of childhood most important for brain development
b. more synapses «than normal» may be formed «during childhood/before birth in autism»
c. «in autism» pruning of neurons does not occur «causing excess of synapses»
OR
normal synapse elimination does not remove extra synapses
Question
Succinate is industrially produced by continuous fermentation. It is used as a raw material in the production of flavour enhancers, drugs and industrial chemicals. One method of increasing the production of succinate is to genetically modify E. coli to express high levels of formate dehydrogenase (FDH1). This results in the production of higher concentrations of NADH. The engineered pathway is shown as a bold dotted line in the image.
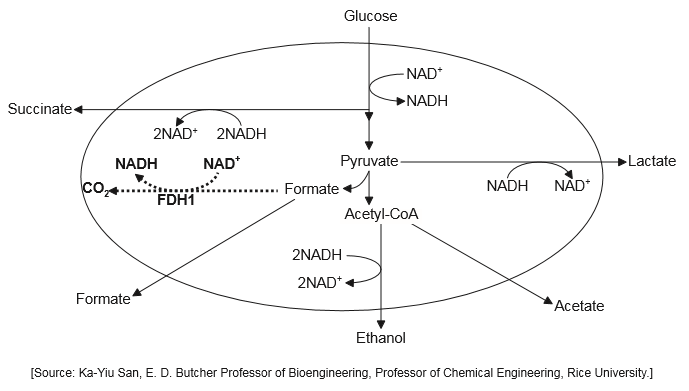
Using the diagram, suggest a reason for high concentrations of NADH favouring the production of succinate.
Predict one metabolite other than succinate that will be produced in greater amounts if the amount of NADH available is increased.
Outline the process of continuous culture fermentation.
Outline one reason this process, to increase the production of succinate, represents pathway engineering.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
NADH is required as a reducing agent/electron donor/hydrogen donor/co-enzyme/limiting factor for the production of succinate
High levels of FDH1 produce greater quantities of NADH which is required for conversion of glucose «via intermediates» to succinate
Lactate/ethanol
CO2 «favoured by high FDH1 levels»
Raw materials are supplied in continuous amounts
Products/wastes are continuously extracted
Conditions are monitored/regulated to keep variables at a steady state
Genetic processes/rate limiting chemicals/regulatory processes are being optimized
Question
With respect to Pavlov’s experiments with dogs, distinguish between the conditioned and unconditioned stimulus.
The bird known as the blackcap (Sylvia atricapilla) traditionally migrates from its summer breeding grounds in Central Europe to Spain and Portugal for the winter. State two adaptive advantages of bird migration.
Outline one way in which synchronized oestrus in female lions increases the chances of survival and reproduction of offspring.
Outline one way in which neurons can be altered by memory and learning.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Unconditioned stimulus triggers a response automatically/innately
Sight/smell of food «naturally» triggers salivation in dogs
Conditioned stimulus is a previously neutral stimulus «eg: sound of bell»
that becomes associated with the unconditioned stimulus «and is learned»
Triggers a conditioned response, salivation with sound before food
Award [2 max] if no reference to Pavlov’s investigation.
Food is more abundant
Temperature is more tolerable
More suitable habitat
Alternative 1
Females have their cubs/are lactating at same time
Can suckle/care for each other’s cubs while others hunt
Cubs are more likely to survive when they are raised in a nursery rather than by a solitary mother
Alternative 2
A group of male cubs, of same age, leave the pride at the same time
So can compete for dominance of another pride more effectively
Involve changes in neurons caused by slow-acting neurotransmitters
Neurons make new connections/increase number of synapses
«Short-term» memory depends on change in strength of existing neuronal connections
Long-term potentiation «LTP» is a lasting increase in strength of synaptic transmission
More receptors added to enhance synaptic transmission
Question
Synaptic density is the number of synapses per unit volume. The graph shows the synaptic density for a 28-week-old fetus, and from birth to age 70.
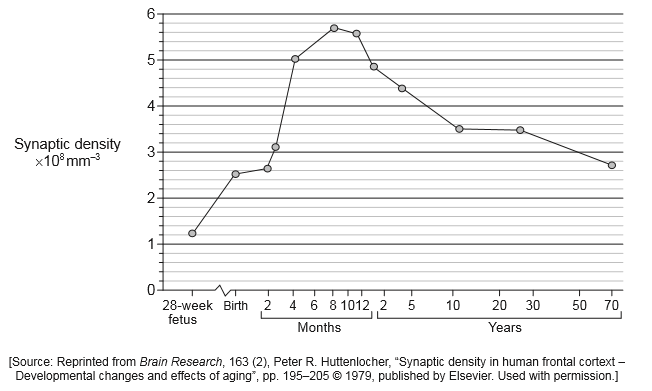
(i) Determine the age when synaptic density is highest.
(ii) Explain how synaptic density decreases after the age determined in (a)(i).
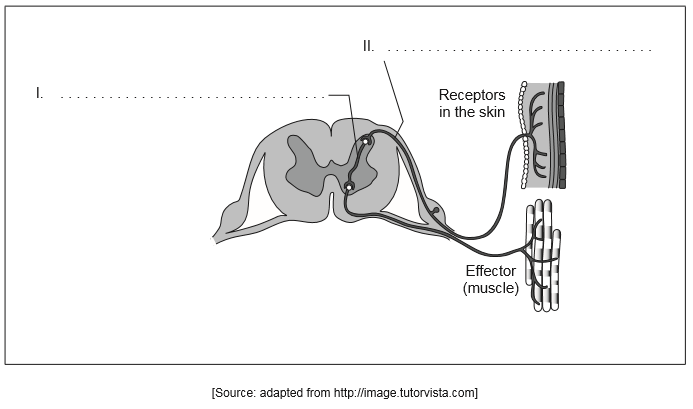
Label the diagram of the reflex arc with the names of the neurons indicated.
Draw an arrow on the diagram of the reflex arc to show the direction of impulses.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) 8 months
(ii) Neural pruning
OR
loss of neurons
Through apoptosis/programmed cell death
Loss of dendrites/axon branches/synapse elimination
Due to lack of use
«In older age» damage to brain/strokes/chemical abuse
I: interneuron/relay neuron
II: sensory neuron
Arrow drawn on diagram to show correct direction of impulse
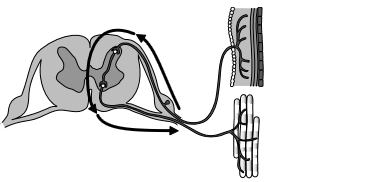
Arrow can also be a single loop through interneuron showing complete pathway or two arrows to and from interneuron.
