IBDP Online Test Series By iitianacademy
Comprehensive Test Preparatory package targeted towards IBDP
Question
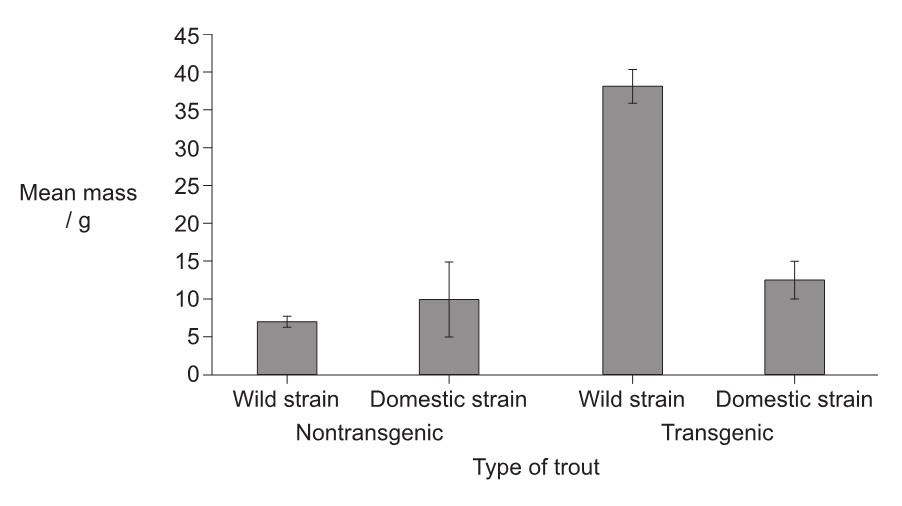
Transgenic rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) were produced from both wild strain and domestic strain trout, using a gene coding for growth hormone from coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). The graph shows the mean mass of the nontransgenic and transgenic trout at 8 months post-fertilization.
[Source: Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature, 409, Growth of domesticated transgenic fish, R H Devlin et al., pp. 781–782, copyright 2001]
Analyse the data for the growth of nontransgenic trout and transgenic trout.
Suggest a reason for the growth differences between the nontransgenic trout and transgenic trout.
Describe the use of marker genes in the development of transgenic organisms such as trout.
Outline the possible environmental impact associated with the accidental release of transgenic trout.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. both transgenic «strains» show more growth/mean mass than nontransgenic
Allow vice versa
b. wild nontransgenic «strain» showed less growth than wild transgenic
Allow vice versa
OR
greatest difference between wild nontransgenic and transgenic «strains»
OR
wild «strain» showed less growth/mean mass in nontransgenic but reverse in transgenic
c. mean mass/growth in domestic nontransgenic «strain» lower than «domestic»
transgenic
d. error bars overlap for domestic nontransgenic and transgenic «strains»
[Max 2 Marks]
gene for growth hormone has been assimilated/is expressed in the transgenic trout
OR
more growth hormone produced/expressed in transgenic trout
a. indicates successful uptake of recombinant DNA
b. identifies transgenic organisms
c. example of a marker gene
eg: antibiotic resistance gene in bacteria
[Max 2 Marks]
a. transgenes may be transferred to other species/organisms
b. may alter ecosystem/food chain
c. may outgrow other species
OR
decrease biodiversity
OR
outcompete nontransgenic individuals/trout
[Max 2 Marks]
Question
The following base sequence represents part of a larger DNA molecule that is going to be analysed for the presence of open reading frames.
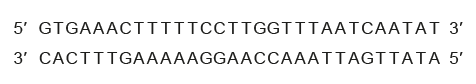
Explain how this DNA can have six possible reading frames.
State the type of codon that helps to identify open reading frames.
Once an open reading frame is identified, explain the steps researchers would follow to determine a potential function for that sequence.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. «three» reading frames can occur in either strand
b. from 5′ « to 3′ »
c. reading frame can start from any of the first three nucleotides
d. from the top strand: GTG or TGA or GAA as first triplet OWTTE
OR
from the bottom strand: ATA or TAT or ATT as first triplet
start codon/AUG
OR
stop codon/UAA/UAG/UGA
a. use a database
b. conduct BLAST search
OR
BLASTn allows DNA sequence alignment
c. «sequence alignment software used» to identify/compare similar sequences in different organisms
d. gene function can be studied using model organisms with similar sequences with known function OWTTE
e. BLASTp allows protein alignment
OR
EST may be used to identify gene activity
f. can change sequence and create “knockout” study organism
g. changes in phenotype due to knockout procedure allow determination of function
h. valid example provided
Question
Outline one example of the use of a marker gene in genetic engineering.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. marker gene inserted into DNA containing target gene
b. recombinant DNA «with marker gene and target gene» inserted into cell/organism
c. named example of marker and target gene eg: ampicillin resistance with BT gene for glyphosate resistance
d. further details of how the marker gene works eg: culture cells in ampicillin and if the cell grows into a callus, uptake has occurred
Question
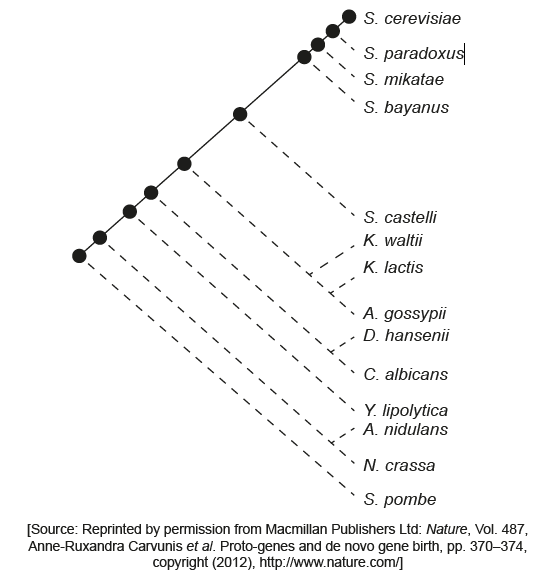
The cladogram is based on a comparison of open reading frames in DNA taken from fungi. It is an example of how open reading frames can be used in phylogenetic studies.
Outline how open reading frames are identified in DNA.
Explain what the branching off points represent in the cladogram of these fungi.
There are several methods of introducing DNA into a cell in the laboratory. Outline the introduction of recombinant DNA in plant cell protoplasts.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. identify a start codon and stop codon
b. identify base sequences for a gene/that could code for a polypeptide
c. possible correlation with existing open reading frames in databases
a. represent common ancestors shared by the organisms that emanate from the point
b. indicates time since divergence
c. indicates number of differences in DNA
a. plant cells made into protoplasts by removing their cell wall / use cellulase to produce protoplasts
b. physical methods such as electroporation /microinjection/biolistics
c. chemical methods such as liposomes/calcium chloride/polyethylene glycol «PEG»
d. vectors such as Agrobacterium/tobacco mosaic virus
Question
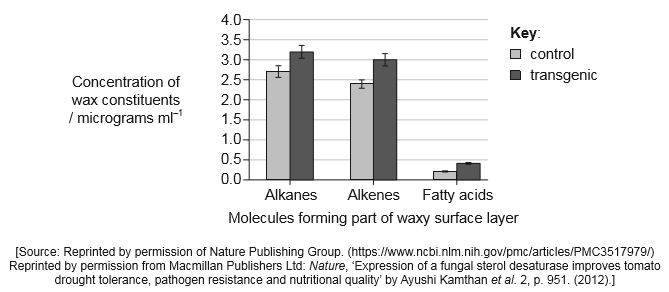
Crop genetic engineering was performed to improve drought tolerance in tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum) by adding a gene from an edible fungus (Flammulina velutipes). The cotyledons of tomato plants were cut and co-cultivated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens containing the transgenic Ti plasmid. Plates containing kanamycin were used to select for transgenic cotyledons. The graph shows concentrations of three constituents of the wax that coats wild type plants (control) and transgenic tomato plants.
Outline the use of kanamycin in the selection of transgenic cotyledons.
State how the sequence of the target gene from the fungus could be identified using a bioinformatics tool.
Suggest whether the results of this experiment show that these transgenic tomato plants are more resistant to drought.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. kanamycin resistance as marker gene
b. when organisms grown in kanamycin, only resistant survive
OR
those that took up resistance/cloned ones survive
database/NCBI search to find target gene/OWTTE
OR
search for target gene in other/related organisms
Allow other named database.
Please check unfamiliar names for authenticity.
a. more wax deposition constituents «in leaves» of transgenic than control plants
b. wax is waterproof
c. less evaporation from «waxy» leaves «protects from drought»
Question
Annual ryegrass (Lolium rigidum) is a weed species that has been successfully controlled by the application of the herbicide glyphosate. The graph shows the number of confirmed cases of glyphosate resistant ryegrass across Australia between 1996−2012.
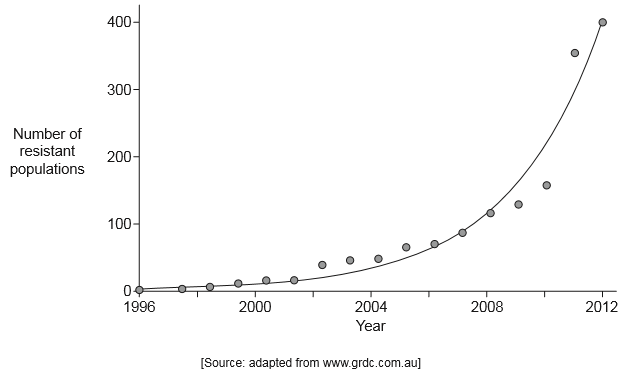
(i) Outline the pattern of change in resistant populations of ryegrass over time in Australia.
(ii) Suggest one reason for the pattern.
State two environmental benefits from the use of genetically modified glyphosate resistant soybeans.
Explain the role of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid in genetic modification.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) Resistance is «exponentially» increasing (OWTTE)
(ii) Increased growth/differential survival of resistant population
OR
Natural selection for glyphosate resistance
Evolution of resistance is possible due to pre-existing variability
«Strong» selective pressure «by application of glyphosate»
Increased crop yields
OR
Reduced demand for more land
Less application of other herbicides «to control weeds»
OR
Glyphosate can replace more toxic/persistent herbicides
Less need for tilling/plowing/ploughing
OR
Less soil erosion
«Less plowing/herbicide application» uses less fuel/less emissions produced
Agrobacterium tumefaciens «Ti» plasmid causes tumours in the plant it infects
Donor gene inserted into Ti plasmid
Along with antibiotic resistance gene
Construct/recombinant Ti plasmid re-inserted into an A. tumefaciens bacterium
Infect leaf with bacterium «and grow on antibiotic medium»
«Some surviving» cells contain the gene/are glyphosate resistant
