IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 10.3 Gene pools and speciation
Topic 10 Weightage : 10%
All Questions for Topic 10.3 – Evolution, Allele Distribution, Types of Selection, Isolation Barriers, Speciation, Pace of Speciation, Species Caveats, Allopolyploidy, Extinction, Polymorphisms, Hardy-Weinberg Principle
How do the concepts of gradualism and punctuated equilibrium differ?
A. The timing of evolution
B. The mechanism causing evolution
C. The sequence of evolutionary events
D. The reality of evolution
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Gradualism is a theory that states that evolution occurs slowly and steadily over a long period of time. It suggests that small, incremental changes accumulate over time, leading to the formation of new species. On the other hand, punctuated equilibrium is a theory that suggests that evolution occurs in rapid bursts, followed by long periods of stasis, where there is little or no evolutionary change.
Therefore, the main difference between the two theories is the timing of evolution. Gradualism suggests a slow and steady process, while punctuated equilibrium suggests a more rapid process with long periods of stasis in between.
The graph shows variations in beak size for the bird Geospiza fortis on an island in the Galápagos archipelago.
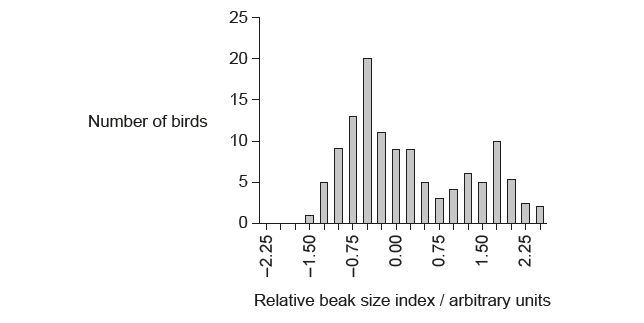
What evidence from the graph indicates that disruptive selection is occurring?
A. An intermediate beak size is less common.
B. Median beak size is the most common.
C. Smaller beaks are favoured.
D. Larger beaks are favoured.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Disruptive selection happens in large populations with lots of pressure for the individuals to find advantages or niches as they compete with each other for food to survive and/or partners to pass on their lineage. Like directional selection, disruptive selection can be influenced by human interaction.
In disruptive selection both extreme traits are favored. Here, both the small and large beaks are favored and the medium beaks are being less common, this is an example of disruptive natural selection.
The genetic determination of dogs’ coats can be quite complex, with many different genes acting at the same time.
• The dominant allele E gives brown tones. The recessive allele e results in red tones.
• The colour intensity is due to another gene. The dominant allele B gives a dark colour, whereas the recessive allele b results in a light colour.
What would be the genotype of a light brown dog produced from a cross between a dark brown dog and a light red dog?
A. EEbb
B. EeBb
C. eeBb
D. Eebb
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
– The dominant allele E gives brown tones. The recessive allele e results in red tones.
– The colour intensity is due to another gene. The dominant allele B gives a dark colour, whereas the recessive allele b results in a light colour.
Two possible combinations form:
BBEE × bbee
BbEe × bbee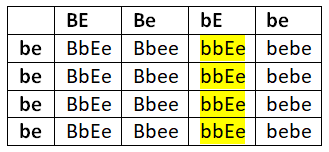
BbEe – dark brown dog
Bbee – Dark red dog
bbEe – light brown dog
Thus, the correct option is D.
What can lead to reproductive isolation after just one generation?
A. Polyploidy
B. Increased mutation rate
C. Changed allele frequencies
D. Independent assortment of chromosomes
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Polyploidy is a type of mutation that results in the doubling of the chromosome number in an organism. This can occur due to various reasons, such as the failure of cell division, the fusion of two gametes, or the hybridization of two different species.
When polyploidy occurs in an organism, it can lead to reproductive isolation after just one generation. This is because the offspring produced by polyploid parents are often sterile or have reduced fertility. Since they cannot produce viable offspring, they are reproductively isolated from both their parents and other individuals of their original species.
Therefore, polyploidy can lead to the formation of new species in a single generation by creating reproductive isolation between the polyploid individuals and their parent population.
Question
Two kinds of wolf spider rub specialized body parts together in order to produce distinct sounds to attract females. Females of both groups will only allow a male of the same kind to mate with them. It has been found through experimentation, however, that offspring can be produced from crossings between the two groups. What can be hypothesized?
I. The groups are reproductively isolated.
II. They could be the same species.
III. This is an example of behavioural isolation.
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and II only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
– The groups are reproductively isolated. Reproductive isolation refers to the situation where different species may live in the same area, but the properties of individuals prevent them from interbreeding. The things which stop species or groups of organisms from reproducing sexually are called isolating mechanisms.
– They could be the same species.
– This is an example of behavioral isolation. Behavioral isolation occurs when mismatches in mating traits (signals and/or preferences) prevent mating between two species/populations.
All three statements can be hypothesized.
Thus, the correct option is D.
