Question
Ebola virus disease (EVD) is the disease in humans and other primates that is caused by the Ebola virus. Fruit bats are the reservoir for the virus and are able to spread the disease without being affected. Humans can become infected by contact with fruit bats or with people infected by the virus, their body fluids or equipment used to treat them.
The stacked bar graph shows the epidemiological data for the EVD cases in Conakry, the capital city of Guinea, surrounding suburbs and rural areas in Guinea from the beginning of January 2014 to the end of March 2015.
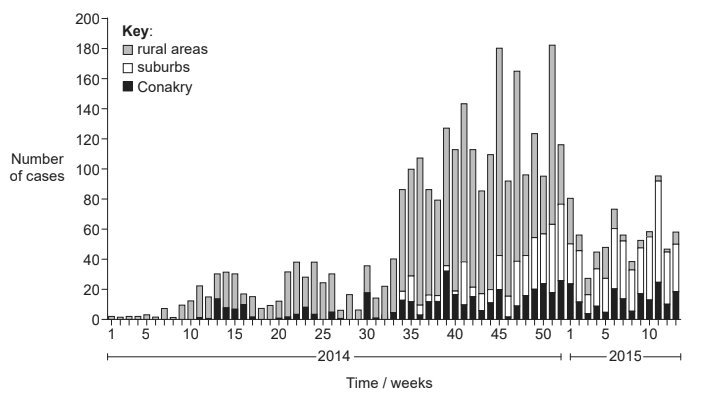
Identify the week and year in which the first cases were recorded in the suburbs. [1]
Week:
Year:
Based on the graph, compare and contrast the progress of the epidemic in the suburbs and rural areas. [3]
Suggest two reasons for the overall decline in the epidemic after week 51. [2]
The table summarizes epidemiological data from Guinea during the Ebola outbreak in 2014. The data are based on figures supplied by Ebola treatment centres. The last column refers to people who died in places other than Ebola treatment centres.
Number of cases
Location
Total
Male
Female
Fatal cases at the Ebola treatment centres
/ %
Fatal cases outside Ebola treatment centres
/ %
Capital city
Conakry
553
307
246
40
18
Suburbs
Coyah
236
112
124
47
19
Forecariah
335
155
180
53
27
Kindia
108
45
63
60
16
Compare and contrast the data for Conakry with the data for the three suburbs. [2]
Suggest reasons for the high percentage of fatal cases at Ebola treatment centres. [3]
An antiviral drug, T-705, was tested in order to establish whether it has potential to treat EVD. The graph shows the data from an in vitro trial of T-705 on cells that had been infected with Ebola virus five days previously. Virus concentration and live cells are shown as a percentage of the control.
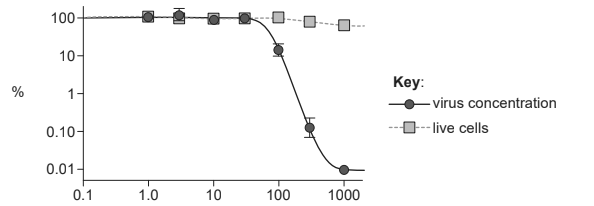
T-705 concentration / μM
Based on these data, outline the evidence that T-705 has potential to be used as a treatment for EVD. [2]
In 2015, an experimental vaccine was trialled in Guinea in an area where new Ebola cases continue to develop. Among the nearly 6000 people who accepted the vaccine, no cases were recorded after vaccination. In comparison, there were 23 cases among those who did not accept the vaccine.
Explain how vaccination can lead to the production of B cells specific to the Ebola virus. [3]
Suggest possible reasons for the difficulty of preventing or controlling a viral epidemic such as the 2014 EVD epidemic in a remote rural region. [2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a week 34 AND 2014 both needed
b
a. start of epidemic/first cases in rural areas
OR
epidemic spread to suburbs later ✔
b. higher maximum number of cases/greater increase in rural areas
OR
converse for suburbs ✔
c. increase came earlier in rural areas «than suburbs»
OR
number of cases peaked earlier in rural areas
OR
more cases in rural areas «than suburbs» in 2014 ✔
d. decrease came earlier in rural areas «than suburbs»
OR
decreasing in rural areas but not in suburbs in 2015/by end of study period
OR
more cases in suburbs than rural areas in 2015 ✔
e. «large» fluctuations in both ✔
c
a. «overall decline due to» fewer cases in rural areas ✔
Answers relating to people who died from the disease or develop immunity to it:
b. fewer cases due to deaths of people who had the disease/people recovering
OR
more people vaccinated/became immune/made antibodies/were not vulnerable toinfection ✔
Answers relating to health care workers or availability of resources:
c. more doctors/nurses/medical equipment/treatment centers/hospitals/spending/aid/NGOs ✔
Answers relating to medical techniques used to tackle the epidemic:
d. better treatments/infection control/hygiene/quarantine/new vaccine/new antiviral drugs ✔
Answers relating to the public and patients:
e. education/better awareness/avoidance of infection/taking precautions/vaccination accepted ✔
Answers relating to reservoirs of infection:
f. fewer infected people «who could spread infection»/fewer bats/less contact with bats ✔
d
differences:
a. Conakry has more cases than any of the suburbs
OR
more cases in total in the suburbs than in Conakry ✔
2 max
b. more male cases in Conakry whereas more female cases in suburbs ✔
c. higher «% of» fatal cases at Ebola treatment centers in suburbs than in Conakry ✔
similarity:
d.in both Conakry and suburbs «% of» fatal cases in treatment centers is higher thanoutside ✔
e
a. most serious cases are in/are taken to treatment centers
OR
treatment centers are set up where there are most cases/most serious cases ✔
3 max
b. long time/distance to travel between contracting disease and arrival at treatment center
OR
travel to treatment center weakens/upsets/harms the patient ✔
c. Ebola is a virulent disease/Ebola virus mutated «to become virulent»
OR
little known about Ebola/new disease so treatments not yet developed ✔
d.no/not enough vaccine/antiviral drug available «in 2014/15»
OR
antibiotics do not work against viral diseases ✔
e. secondary infections/Ebola patients infected with other diseases/other Ebola strains
OR
ineffective hygiene/cleaning/sterilization/use of contaminated equipment/disposal of corpses ✔
f. small number of staff relative to patients/treatment centers overcrowded/swamped with patients
OR
insufficient equipment/supplies for large number of patients/with the rapid rise in patients ✔
g. better reporting at Ebola centers/deaths due to Ebola not reported in rural areas ✔
f
a. cells not killed/few cells killed «even at high concentrations» ✔
b. «T-705» effective/viruses reduced/viruses killed at 100 μM
OR
«T-705» very effective/viruses much reduced/nearly all viruses killed at 1000 μM ✔
c. virus concentration decreases as T-705 concentration increases ✔
d. drug has «high» potential for treatment «at high enough concentration» ✔
g
a. vaccine contains Ebola antigens ✔
b. vaccine «could» contain weakened/attenuated/dead/killed form of «Ebola» virus/virusgenetically modified to express an Ebola/viral protein ✔
c. phagocyte/macrophage engulfs the antigen/presents the antigen to T cell ✔
d. antigen recognized by «specific» T cells/binds to T cells ✔
e. «activated» T cells activate «specific) B cells ✔
f. «activated» B cells make the antibodies «against Ebola» ✔
g. B cells divide forming «clone of» plasma cells/producing more B cells specific to Ebola ✔
h
a. poor transport infrastructure/poor communication/bad roads/difficult access/no maps/supportslow arriving/scattered population ✔
b. poor education/understanding of disease amongst health workers/local population
OR
continued contact with infected people / other example of unsafe actions ✔
c. more sources of infection such as bats/difficult to find sources of infection ✔
d. lack of/limited access to medical care/doctors/health care workers ✔
e. lack of/no access to/unaffordability of treatment centers/medicalsupplies/equipment/antivirals/drugs/vaccine/treatments ✔
f. refusal/reluctance in local population to be vaccinated
OR
difficult to find/reach everyone to vaccinate them/repeat the vaccination ✔
g. migration of people spreads the infection ✔
h. poor sanitation/lack of clean water ✔
Question
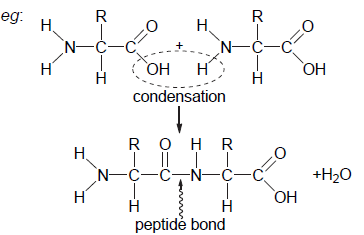
Draw molecular diagrams to show the condensation reaction between two amino acids to form a dipeptide.
Outline the roles of the different binding sites for tRNA on ribosomes during translation.
Explain the production of antibodies.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. each amino acid with a COO–/COOH group at one end AND a NH2/NH3+ at the other
Both needed.
mp a requires the double bond to be shown between the C and O.
b. CH in middle with H or R group attached
c. peptide bond correctly drawn between N and C=0
d. COO–/COOH group at one end of dipeptide AND NH2/NH3+ at other end
Both needed.
e. loss of water
a. A, P and E binding sites are on the large subunit of the ribosome
b. initiation of translation starts with binding of met-tRNA to the start codon
c. large sub-unit binds with «start» tRNA in the P site
d. A binding site holds the tRNA with the next amino acid to be added
e. peptide bond is formed between the amino acids of the A site and the polypeptide at the P site
f. polypeptide is transferred to the tRNA in the A site
g. the tRNA «with polypeptide» in A site then moves to P site
OR
P binding site holds the tRNA attached to the growing polypeptide
h. E binding site «exit» is where the tRNA «from P site without amino acid» leaves the ribosome
Accept annotated diagrams of the sites.
a. each antibody corresponds to a specific antigen
b. antibodies are necessary for immunity/resistance to «infectious» disease
c. macrophage/phagocyte ingests/engulfs pathogen
d. macrophage/phagocyte digests pathogen
e. macrophage/phagocyte displays antigen from pathogen
f. antigens of a pathogen correspond to a specific T lymphocytes/cells
OR
T lymphocytes/cells are activated by antigen binding
g. T lymphocytes/cells activate B lymphocytes/cells
h. «B cells» divide by mitosis to form many/clones of plasma cells
i. plasma cells secrete specific antibody
j. some «activated» B lymphocytes/cells act as memory cells
Accept annotated diagrams of the process
Question
Draw a labelled diagram of Escherichia coli as an example of a prokaryote.
Explain the process of transcription in prokaryotes.
Some prokaryotes cause infectious diseases which stimulate the body’s immune system. Outline the principles that form the basis of immunity.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Award [1] for each structure clearly drawn and correctly labeled.
cell wall; (with some thickness)
plasma membrane; (shown as single line or very thin)
cytoplasm;
pilus/pili; (shown as single lines coming from the cell wall)
flagellum/flagella; (thicker and longer than pili and embedded in cell wall)
70S ribosomes; (shown as small dots)
nucleoid / naked DNA;
approximate width 0.5 μm / approximate length 2.0 μm;
Award [3 max] if the bacterium drawn does not have the shape of a bacillus (rounded-corner rectangle with length approximately twice its width).
Award [3 max] if any eukaryotic structures included.
transcription, synthesis of RNA identical to one strand/coding strand of DNA;
antisense stand acts as template/is transcribed;
RNA polymerase attaches to sequence of DNA known as promoter (region);
RNA polymerase separates the two strands of DNA;
(unwinding) exposes (10–20) DNA bases for pairing with RNA nucleotides;
RNA nucleotides matched to complementary bases;
adenine with uracil and cytosine with guanine / uracil replaces thymine;
H bonds between RNA nucleotide and complementary base on DNA strand;
(RNA) nucleoside triphosphates used;
hydrolysis of (two) phosphate molecules provides energy for reaction;
adds nucleotides to the 3′ end of RNA molecule/in 5′ → 3′ direction;
terminator is sequence of DNA signaling end of transcription;
RNA molecule separates completely from DNA;
Award any of the above points for a clearly drawn correctly annotated diagram.
skin and mucous membranes form barriers to pathogens as first line of defence;
macrophage recognizes antigens and ingests pathogen (in blood/body tissues);
presents antigen/MHC on cell surface;
macrophage activates helper T-cells that are complementary to antigen;
complementary B-cell becomes activated/stimulated by T-helper cells;
activated B-cell increases in size and divides by mitosis / creates clone of B-cells;
B-cells differentiate into plasma cells and memory cells; (both needed) plasma cells secrete specific antibodies;
memory cells remain/form basis of long-term immunity;
polyclonal response / multiple B-cells activated by different molecules of antigen;
Award any of the above points for a clearly drawn correctly annotated diagram.
(Plus up to [2] for quality)
Question
Outline the role of the skin in temperature regulation.
Outline the role of hormones in the process of birth in humans
Explain the principles of vaccination.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
heat causes vasodilation of arterioles;
blood closer to surface so heat loss from skin;
heat causes sweating (from sweat glands);
evaporation of sweat leads to cooling;
cold causes vasoconstriction of arterioles;
less blood at surface so less heat loss from skin;
cold leads to less sweating/evaporation of water from skin / hair becomes erect and traps air/goose bumps appear;
temperature receptors in skin transmit impulses to the hypothalamus;
level of progesterone falls before birth;
oxytocin secreted;
from pituitary;
this stimulates contractions of uterus;
uterine contraction/stretching of cervix/vagina stimulates secretion of (more) oxytocin;
form of positive feedback;
vaccine is a modified/weakened/attenuated form of a pathogen / contains antigens from pathogens;
vaccine injected/ingested/introduced to patient;
pathogen/antigens stimulates specific immune response called primary/initial responses;
antigens stimulate macrophages/lymphocytes/T-cells;
which stimulate cloning of B-cells/plasma cells;
including development of memory (B-)cells;
that produce specific antibodies;
(upon second exposure) production of antibodies is much faster;
higher level of antibody production / person has immunity;
called secondary response;
labelled graph showing curve with higher slope/peak for secondary response than primary response;
may need booster shot to maintain immunity;
this is an example of active/artificial immunity;
