IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 2.6 Structure of DNA and RNA
Topic 2 Weightage : 10%
All Questions for Topic 2.6-Nucleotides, DNA versus RNA, DNA Structure, Watson & Crick, Nitrogenous Bases, Types of RNA
Question
What is common to RNA and DNA?
Thymine
Nitrogenous bases
Histones
Deoxyribose
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
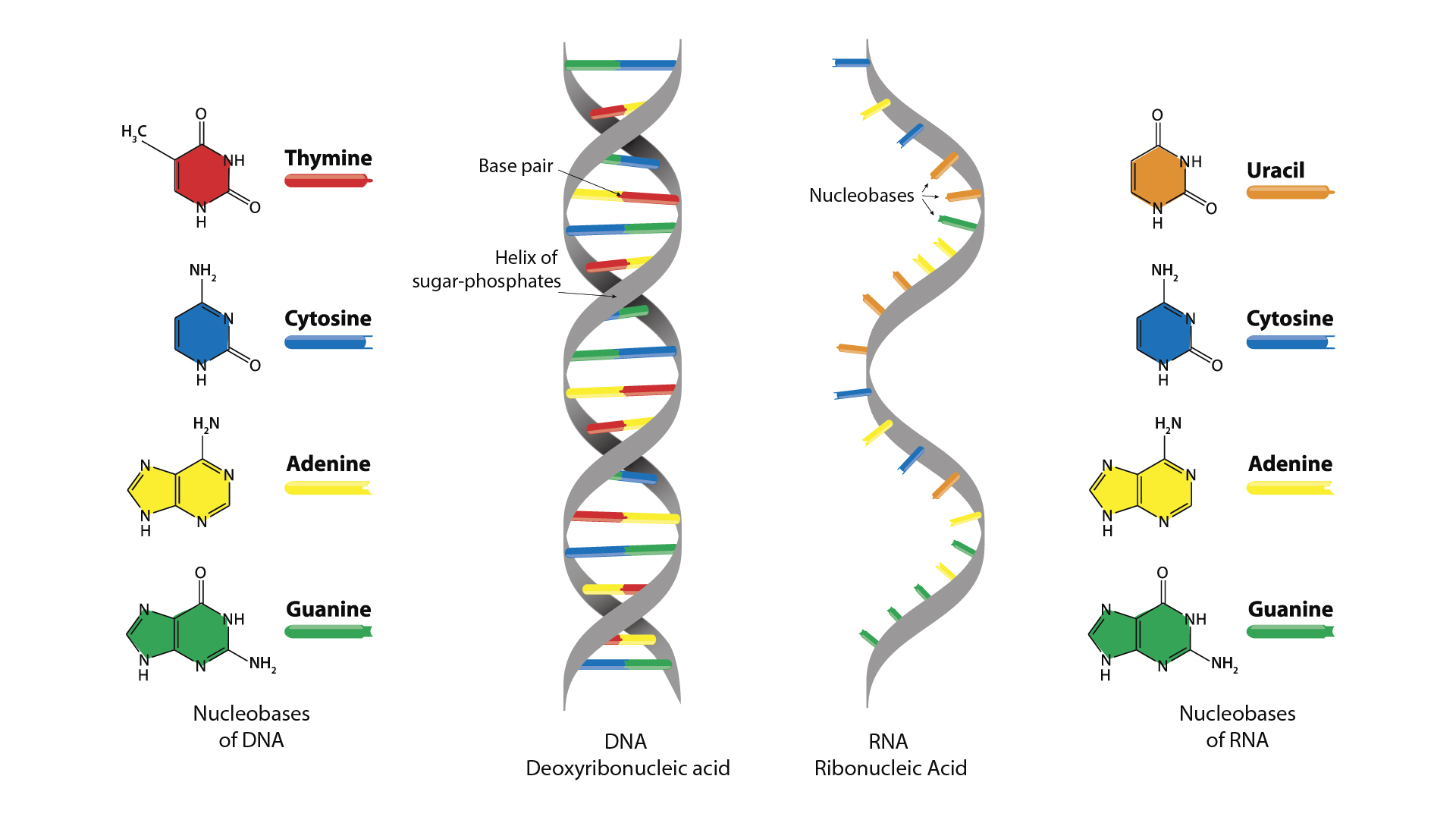
Both RNA and DNA share the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). However, DNA has thymine (T) as the fourth base, while RNA has uracil (U). These bases form complementary pairs that hold the two strands of DNA together or allow RNA to bind to DNA during transcription. The complementary pairs are A-T or A-U and G-C.
Question
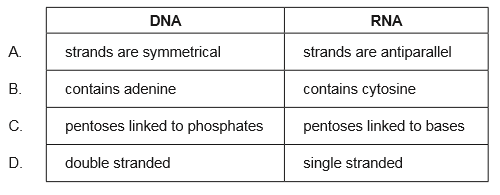
What usually distinguishes DNA from RNA?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D

DNA is structured as a double helix, with two strands of DNA winding around each other, while RNA is structured as a single strand. So DNA has two strands and RNA has one strand.
Question
Organisms can be genetically modified to produce the human blood clotting factor IX. What characteristic of the genetic code makes this possible?
A. It is conservative.
B. It is degenerate.
C. It is complementary.
D. It is universal
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
There are different ways to genetically modify an organism to produce human blood clotting factor. One way is to isolate the normal gene for the clotting factor (such as factor VIII or factor IX) from healthy human cells and insert it into the cells of another organism, such as hamsters1 or sheep. The modified cells then use the human gene to make the clotting factor, which can be extracted and purified for medical use. These methods require careful regulation of the expression and dosage of the clotting factor, as well as quality control and safety testing of the final product.
Question
The base sequence of a fragment of DNA is:
ACC GTG CAG GAT
What is the base sequence on the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule transcribed from it?
A. TGG CAC GTC CTA
B. TGG CUC GTC CTU
C. UGG CTC GUC CUT
D. UGG CAC GUC CUA
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
Base pairing is the process of two nucleobases forming hydrogen bonds with each other in a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule, such as DNA or RNA⁴. Base pairing is important for the structure and function of DNA and RNA.
In DNA molecules, the base pairs are:
– Adenine (A) – Thymine (T)
– Cytosine (C) – Guanine (G)
In RNA molecules, the base pairs are:
– Adenine (A) – Uracil (U)
– Cytosine (C) – Guanine (G)
The difference between DNA and RNA base pairing is that DNA uses thymine while RNA uses uracil instead. This is because uracil is more stable than thymine in RNA, which is more prone to degradation by enzymes and chemicals.
Question
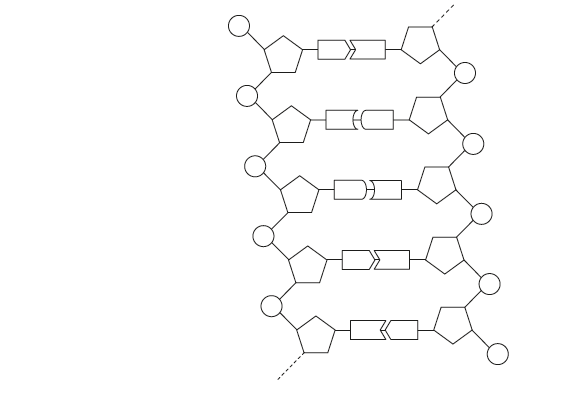
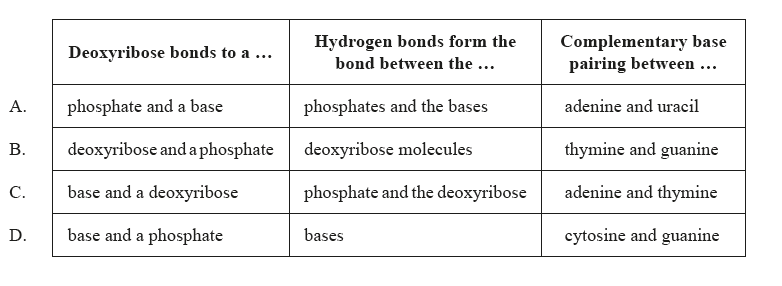
What is correct for the DNA double helix?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
According to the Watson and Crick model, the DNA is a double-stranded helix, which consists of two polynucleotide chains. The two polynucleotide chains are spirally or helically twisted, which gives it a twisted ladder-like look. Each polynucleotide chain is composed of smaller units called nucleotides, which have three components: a phosphate group, a sugar group (deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base. There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The two polynucleotide chains are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. The bases form specific pairs: A with T, and C with G. This is called the base complementary rule. The base pairs are arranged in the center of the helix, while the phosphate and sugar groups form the backbone of each strand. The two strands run in opposite directions, meaning that one strand has its 5′ end (where the phosphate group is attached) facing the 3′ end (where the sugar group is attached) of the other strand. This is called the antiparallel orientation.
Question
The percentage of thymine in the DNA of an organism is approximately 30 %. What is the percentage of guanine?
A. 70 %
B. 30 %
C. 40 %
D. 20 %
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
According to Chargaff’s rule in the DNA of any species and any organism, the amount of guanine should be equal to the amount of cytosine and the amount of adenine should be equal to the amount of thymine. Here, thymine is 30% then adenine will also be 30%. Now in remained 40%, cytosine will be 20% and guanine will also be 20%.
Question
What type of bond is labelled X?
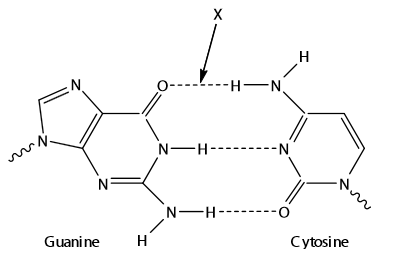
A. Ionic
B. Peptide
C. Covalent
D. Hydrogen
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
Each polynucleotide chain in a DNA is composed of smaller units called nucleotides , which have three components: a phosphate group, a sugar group (deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base. There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The two polynucleotide chains are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. The bases form specific pairs: A with T, and C with G. This is called the base complementary rule. The base pairs are arranged in the center of the helix, while the phosphate and sugar groups form the backbone of each strand. The two strands run in opposite directions, meaning that one strand has its 5′ end (where the phosphate group is attached) facing the 3′ end (where the sugar group is attached) of the other strand. This is called the antiparallel orientation.
Question
In the model of the DNA molecule shown below, which arrows point to covalent bonds?
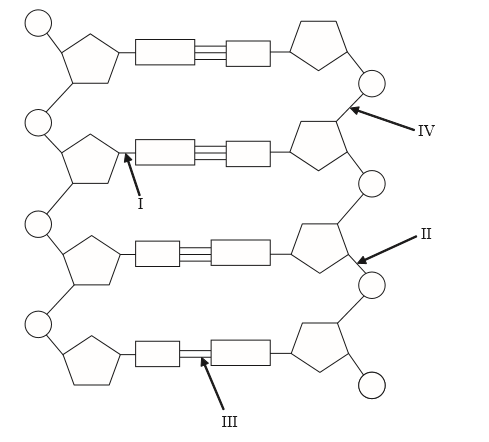
A. I, II and III only
B. II, III and IV only
C. I, III and IV only
D. I, II and IV only
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
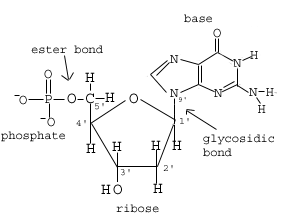
3rd is hydrogen bond.
2nd & 4th are covalent bonds between phosphate and ribose sugar, their name is phosphodiester linkage.
1st is also a type of covalent bond between ribose sugar and N-base, its name is glycosidic linkage.
Question
This question refers to the following DNA diagram.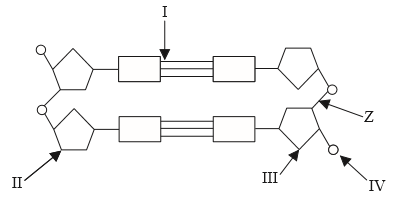
What type of bond does Z represent?
A. Covalent bond
B. Hydrogen bond
C. Peptide bond
D. Semi-conservative bond
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Ans:A

Z marked bond is a covalent bond but its name is phosphodiester bond between phosphate and ribose sugar.
Question
What is the arrangement of the components of nucleotides in a single DNA strand?
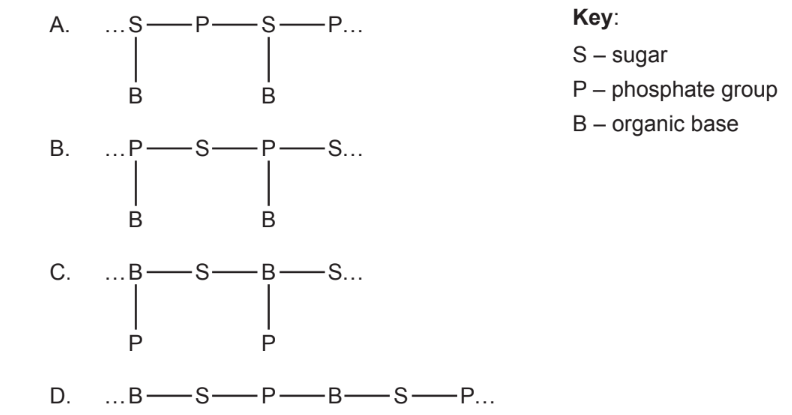
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
According to the Watson and Crick model, the DNA is a double-stranded helix, which consists of two polynucleotide chains. The two polynucleotide chains are spirally or helically twisted, which gives it a twisted ladder-like look. Each polynucleotide chain is composed of smaller units called nucleotides, which have three components: a phosphate group, a sugar group (deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base. There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The two polynucleotide chains are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. The bases form specific pairs: A with T, and C with G. This is called the base complementary rule. The base pairs are arranged in the center of the helix, while the phosphate and sugar groups form the backbone of each strand. The two strands run in opposite directions, meaning that one strand has its 5′ end (where the phosphate group is attached) facing the 3′ end (where the sugar group is attached) of the other strand. This is called the antiparallel orientation. The DNA double helix has a major groove and a minor groove, which are the spaces between the two strands. The major groove is wider than the minor groove, and many proteins that bind to DNA do so through the major groove.
