Question
(a) Distinguish between the structures of DNA and RNA. [3]
(b) Mendel found the same pattern of inheritance in all the crosses that he performed.
Outline, with examples, different types of inheritance that produce non-Mendelian ratios. [4]
(c) Explain the cause of sickle cell anemia and how this disease affects humans. [8]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a
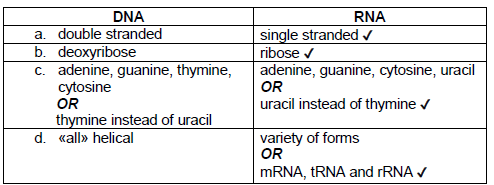
b
a. some traits may involve many genes/be polygenic eg: height, skin colour «correct example required» ✔
b. linked genes/alleles of different genes on same chromosome ✔
c. «small numbers of» recombinant phenotypes due to crossing over «between linked genes» ✔
d. co-dominance of specific alleles/intermediate forms eg: pink flowers «from red and white ones»/blood groups «correct example required» ✔
e. sex-linked effects eg: colour blindness «correct example required» ✔
f. environmental influence on inheritance/epigenetics/methylation ✔
g. any other example of non-Mendelien inheritance with a specific example ✔
c
a. caused by a single nucleotide/base substitution mutation/GAG to GTG ✔
b. «mutation of» a gene of β-globin/a subunit of hemoglobin ✔
c. mRNA copies the mutation of DNA and substitutes an amino acid in hemoglobin «subunit» ✔
d. glutamic acid is substituted by valine ✔
e. sickle cell anemia involves distorted hemoglobin protein/HbS ✔
f. «distorted HbS causes» distortion/sickling/shape change of red blood cells ✔
g. «distorted/sickled red blood cells» block capillaries/blood flow ✔
h. HbS/sickled red blood cells cannot carry enough oxygen «for the body»/leads to fatigue ✔
i. low oxygen concentration seriously affects structure of HbS ✔
j. homozygous «HbS/HbS» state causes severe anemia/death at low oxygen concentrations ✔
k. heterozygous state has less anemia/minor effects/less effect of structure of hemoglobin
OR
heterozygous state only affected at high altitude/extreme exercise/low levels of oxygen ✔
l. «heterozygous state» provides protection against malaria parasite/selective advantage in malaria areas ✔
Question
A wide variety of organic compounds are used by living organisms.
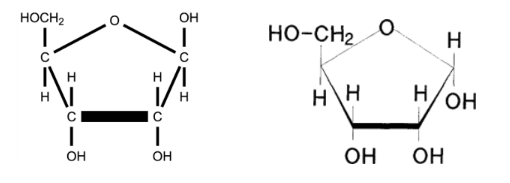
(a) Draw a diagram to show the ring structure of D-ribose. [3]
(b) Describe how ATP is produced by Photosystem II in the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis.[5]
(c) Explain how carbohydrates are transported from plant leaves.[7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
a a. ring with four carbons and one oxygen atom;
b. $\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}$ attached to $\mathrm{C} 4$;
c. $\mathrm{OH}$ and $\mathrm{H}$ attached by single bonds to $\mathrm{C} 1, \mathrm{C} 2$ and $\mathrm{C} 3$ with $\mathrm{OH}$ facing downwards on $\mathrm{C} 2$ and $\mathrm{C} 3$;
b a. light (energy) absorbed by pigments/chlorophyll/photosystems;
b. excited electrons passed to electron carriers/electron transport chain;
c. protons/hydrogen ions pumped into thylakoid (space);
d. proton gradient/high proton concentration generated;
e. protons pass via ATP synthase to the stroma;
f. ATP synthase phosphorylates ADP/ATP synthase converts ADP to ATP;
g. photophosphorylation/chemiosmosis;
h. ATP synthase/electron carriers/proton pumps/photosystems/pigment are in the thylakoid membrane;
c a. translocation/movement by mass flow;
b. in phloem sieve tubes;
c. sieve plates/pores in end walls/lack of organelles allows flow (of sap);
d. carbohydrates (principally) transported as sucrose;
e. (sucrose/glucose/sugar/carbohydrate) loaded (into phloem) by active transport;
f. loading/pumping in (of sugars) by companion cells;
g. high solute concentration generated (at the source);
h. water enters by osmosis (due to the high solute concentration);
i. hydrostatic pressure increased/high hydrostatic pressure generated;
j. pressure gradient causes flow (from source to sink);
k. leaves are a source because carbohydrates are made there;
l. transport to the sink where carbohydrates are used/stored;
