IB Biology SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 2.6 Structure of DNA and RNA
Topic 2 Weightage : 20%
All Questions for Topic 2.6-Nucleotides, DNA versus RNA, DNA Structure, Watson & Crick, Nitrogenous Bases, Types of RNA
Question
Which feature is common to both mRNA and DNA?
A Covalent bonds between adjacent nucleotides
B Hydrogen bonds between guanine and cytosine
C Ribose sugar attached to phosphate
D Antiparallel arrangement of polynucleotide strands
▶️Answer/Explanation
In DNA or RNA, adjacent nucleotides are linked by a phosphodiester bond which is a covalent bond formed between the 5’ phosphate group of one nucleotide and the 3’-OH group of another. This arrangement makes an alternating chain of sugar-phosphate backbone.
Question
The hydrolysis of a pure sample of an organic molecule produces a pentose sugar, thymine, guanine and cytosine. What other substances could be expected to be present in the hydrolysed sample?
RNA
Uracil
Phosphate
ATP
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Phosphate is present in hydrolysed nucleic acid because it is used to build the phosphate-sugar backbone, which fixes the nucleotide bases in place. This is achieved by the formation of a phosphodiester bond, in which the phosphate molecule reacts with a hydroxyl group on the ribose sugar forming a bond and releasing water as a byproduct. The negative charge on each phosphate exhibits repulsive forces between each other, so they can be hydrolysed in order to overcome these repulsive forces.
Question
For which discovery about DNA do Watson and Crick receive credit?
A. DNA is the molecule that genes are made of.
B. The amount of adenine equals the amount of thymine in an organism.
C. Phosphate–pentose bonding along the nucleotide backbone is covalent.
D. The shape of DNA is a double helix.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
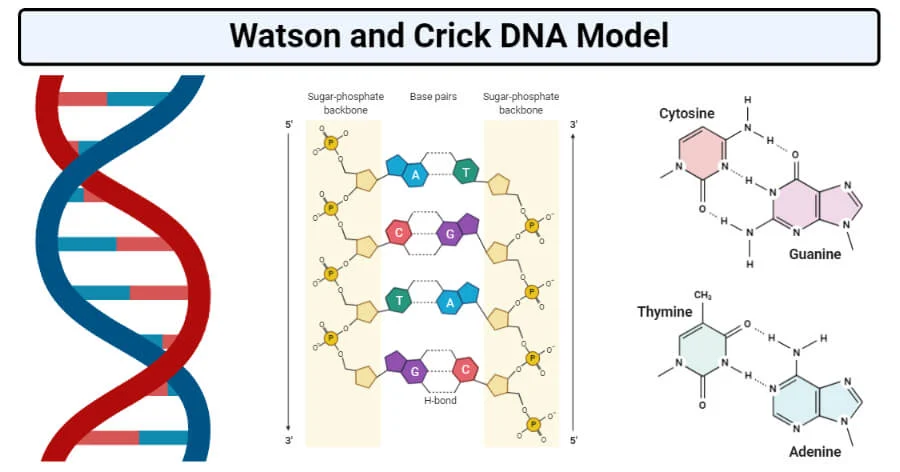
Watson and Crick’s double helical model of DNA was that the DNA molecule exists in the form of a three-dimensional double helix. According to their model, the DNA is a double-stranded helix, which consists of two polynucleotide chains. The two polynucleotide chains are spirally or helically twisted, which gives it a twisted ladder-like look. The precise pairing of nucleotides is a critical aspect of the Watson and Crick model of DNA. Each DNA strand is linear and long and is made up of smaller units known as nucleotides that link together to form a chain.
Question
The diagram shows part of a DNA molecule.
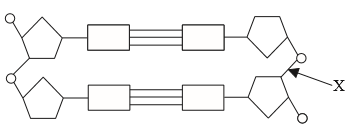
What type of bond does X represent?
A. Covalent bond
B. Hydrogen bond
C. Peptide bond
D. Semi-conservative bond
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Ans:A
“X” marked bond is “phosphodiester bond” that joins one DNA nucleotide to another is a covalent bond. It links the 3’ carbon of the first nucleotide to the 5’ carbon of the second nucleotide.
Question
Cells were grown in heavy nitrogen $\left({ }^{15} \mathrm{~N}\right)$ for many generations and then grown in light nitrogen $\left({ }^{14} \mathrm{~N}\right)$ for two rounds of DNA replication. Which diagram shows the result of the centrifuged DNA?
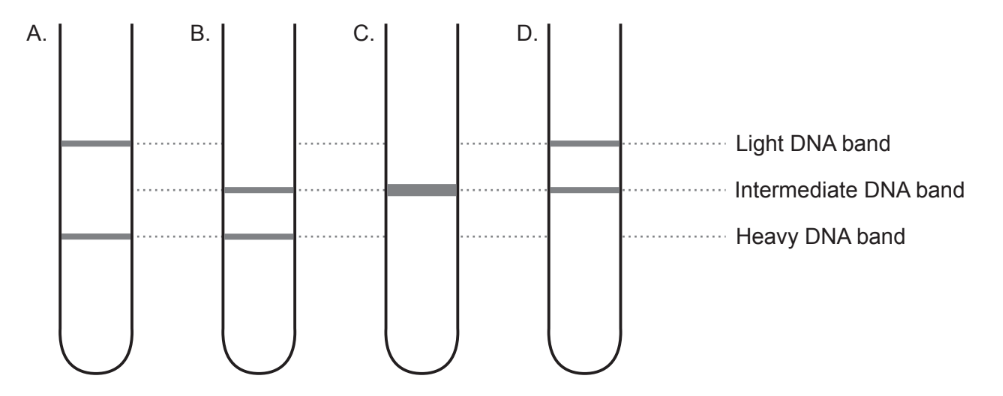
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
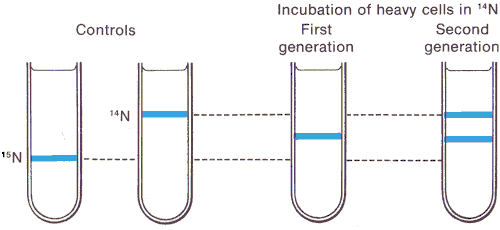
According to Meselson-Stahl experiment, which was an experiment done by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in 1958 to test how DNA replicates. They used different isotopes of nitrogen to label the DNA of bacteria and observed how the DNA changed after several rounds of replication.
According to the semi-conservative model of DNA replication, which was supported by their experiment, each new DNA molecule consists of one old strand and one new strand. Therefore, if the bacteria were grown in heavy nitrogen for many generations and then grown in light nitrogen for many rounds of DNA replication, the configuration of DNA that will appear is a mixture of hybrid DNA (one heavy strand and one light strand) and light DNA (two light strands).
