IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 2.7 DNA replication, transcription and translation
Topic 2 Weightage : 10%
All Questions for Topic 2.7-Semi-Conservative, DNA Replication, polymerase chain reaction, Transcription, Genetic Code, Translation, Universality, Sequence Decoding, Central Dogma, Translation Analogy, Degeneracy, Point Mutations
Question
When does DNA replication occur?
S phase of interphase
Early prophase
G phase of interphase
Late prophasestyle
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
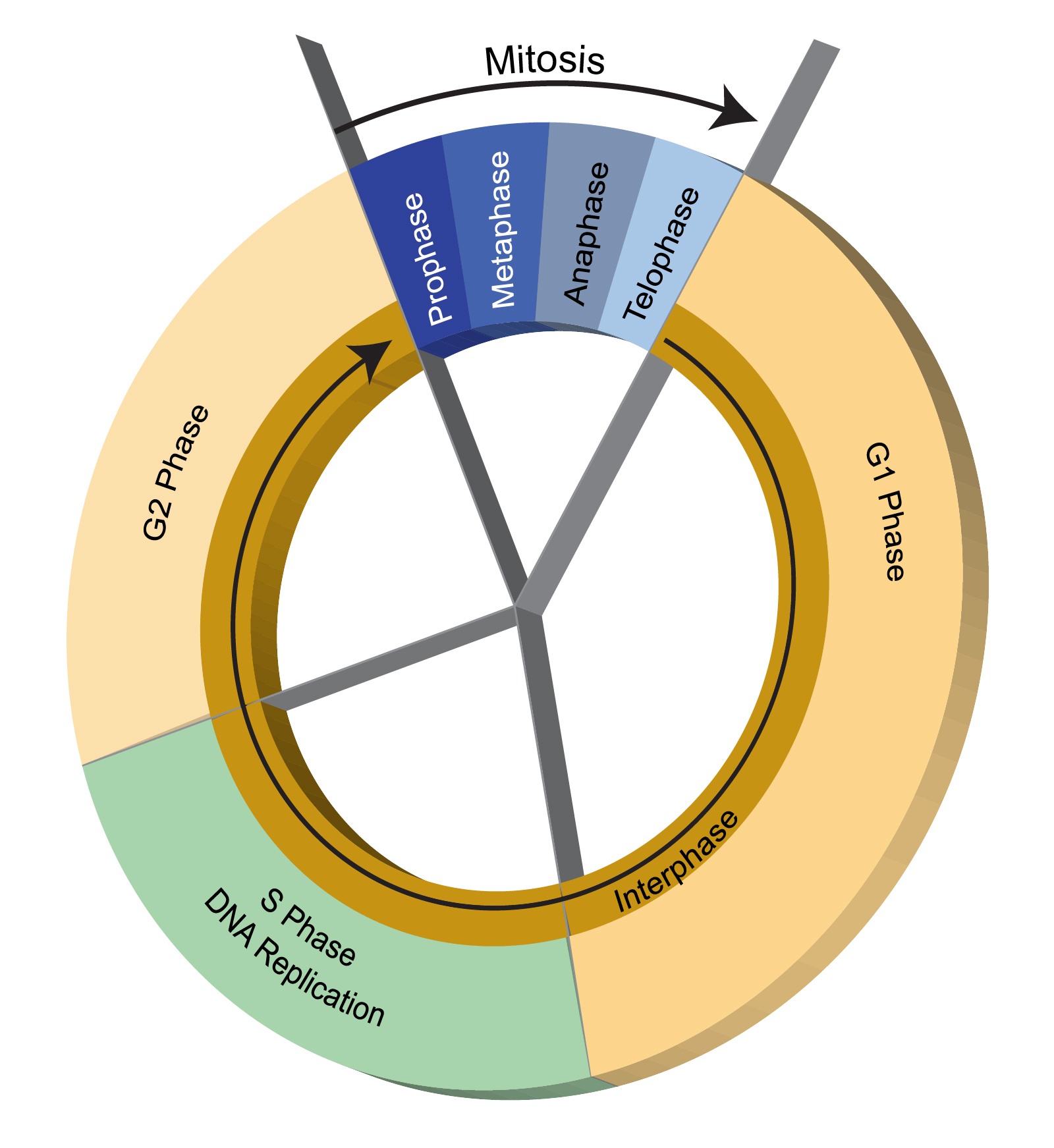
DNA replication occurs during the S-stage of interphase. During interphase, the cell grows and DNA is replicated. Prior to DNA replication, the chromatin loosens giving cell replication machinery access to the DNA strands.
Question
What occurs during DNA replication?
A. DNA polymerase separates the two DNA strands.
B. DNA molecules containing nucleotides from the original molecule are produced.
C. Adenine forms a base pair with either thymine or uracil.
D. New bases attach to the original sugar-phosphate backbone.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
During DNA replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. This is known as semiconservative replication
The process of DNA replication can be summarized as follows:
1. DNA unwinds at the origin of replication.
2. New bases are added to the complementary parental strands. One new strand is made continuously, while the other strand is made in pieces.
3. Primers are removed, new DNA nucleotides are put in place of the primers and the backbone is sealed by DNA ligase.
Most DNA polymerases can “check their work” with each base that they add during DNA replication (copying). This process is called proofreading.
Question
On which molecule is a codon found?
A. DNA
B. mRNA
C. tRNA
D. rRNA
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
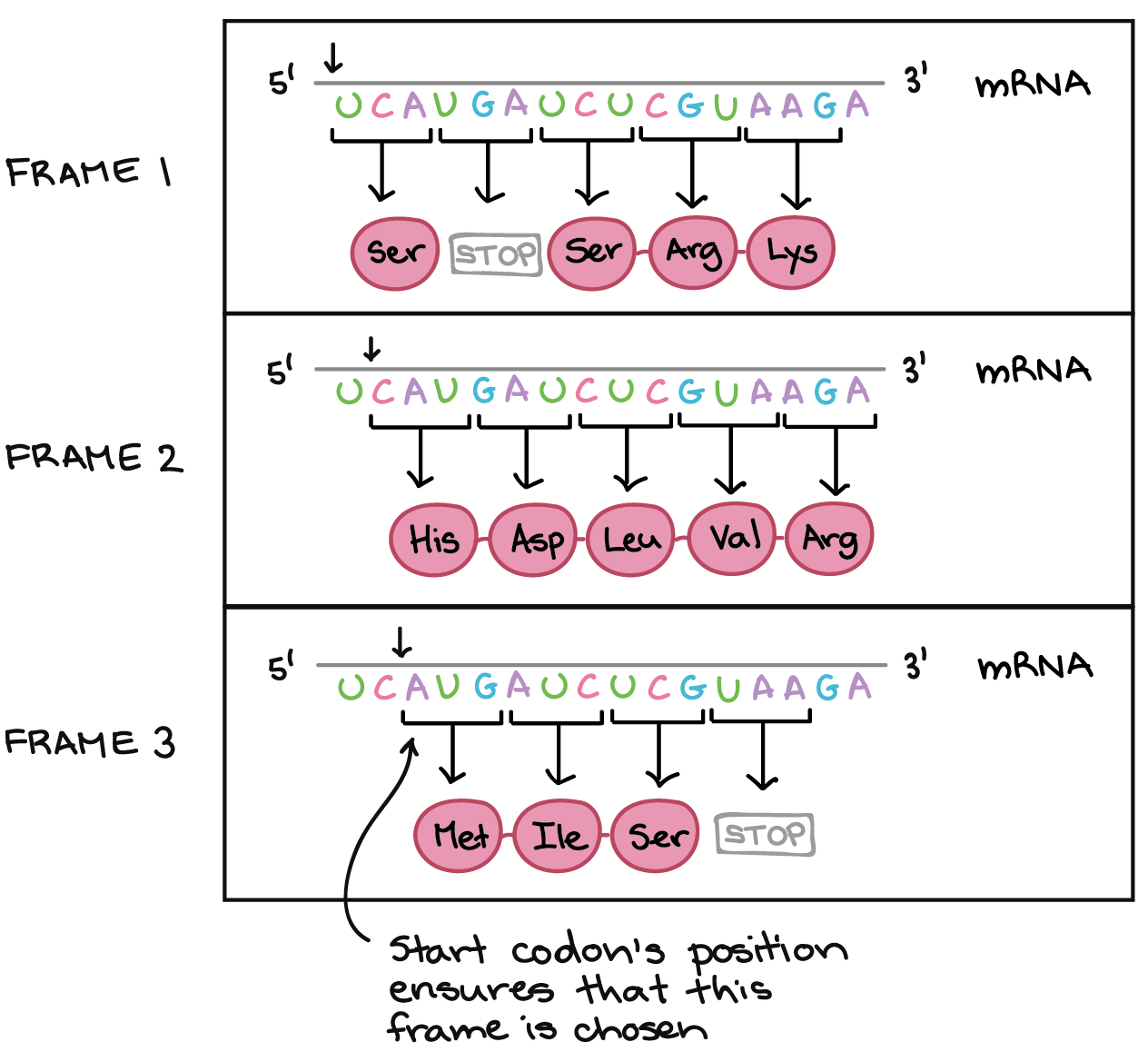
Codons are a sequence of three nucleotides that form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule. They are found on mRNA because they are responsible for coding the sequence of amino acids in a protein. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid or stop signal during protein translation. Cells decode mRNAs by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. In addition, the codon AUG has a special role, serving as the start codon where translation begins
Question
Which sequence represents the order of events in protein synthesis?
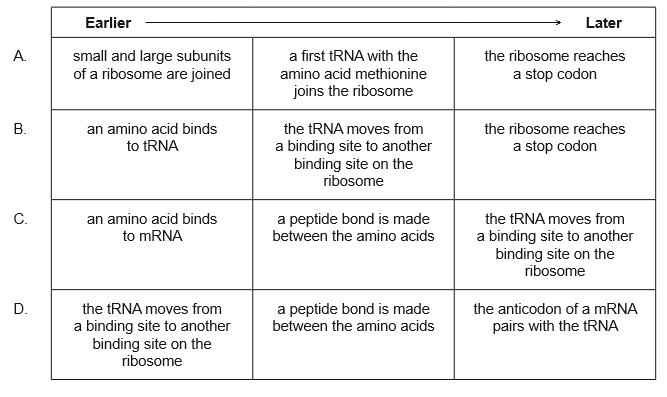
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
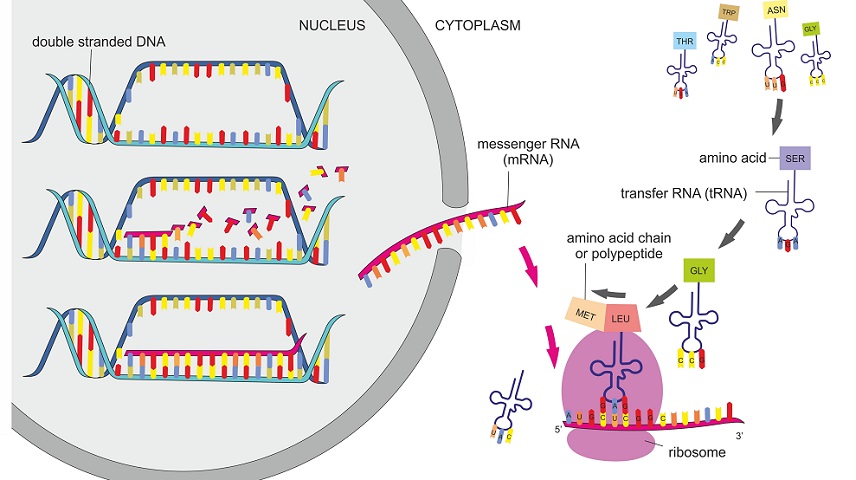
Protein synthesis is the process by which amino acids are linearly arranged into proteins through the involvement of ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, messenger RNA, and various enzymes. The process of protein synthesis is divided into five major steps: activation of amino acids, transfer of amino acids to tRNA, initiation of the polypeptide chain, chain termination and translocation of the protein molecule.
Question
What is the relationship between enzymes and DNA?
A. Enzymes contain the code for DNA.
B. Enzymes act on DNA during translation.
C. Both enzymes and DNA have similar shapes.
D. The structure of enzymes is determined by DNA.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in living organisms. Genes are sections of DNA that code for particular enzymes and proteins. The relationship between enzymes and DNA is that genes code for enzymes. Enzymes are synthesized by ribosomes in cells using the genetic information encoded in DNA. Enzymes play a crucial role in DNA replication, transcription, and translation. For example, DNA polymerases and other enzymes that make copies of DNA during cell division are all proteins.
