IB Biology SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 2.8 Cell respiration
Topic 2 Weightage : 20%
All Questions for Topic 2.8– ATP Production, Anaerobic Respiration, Aerobic Respiration, Yeast Fermentation, Respirometry, Energy Sources, Uses of ATP, Anaerobic vs Aerobic
Question
What is a difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration in yeast?
Anaerobic respiration requires enzymes, aerobic respiration does not.
Anaerobic respiration requires glucose, aerobic respiration does not.
Anaerobic respiration produces ethanol, aerobic respiration does not.
Anaerobic respiration does not produce oxygen, aerobic respiration does
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
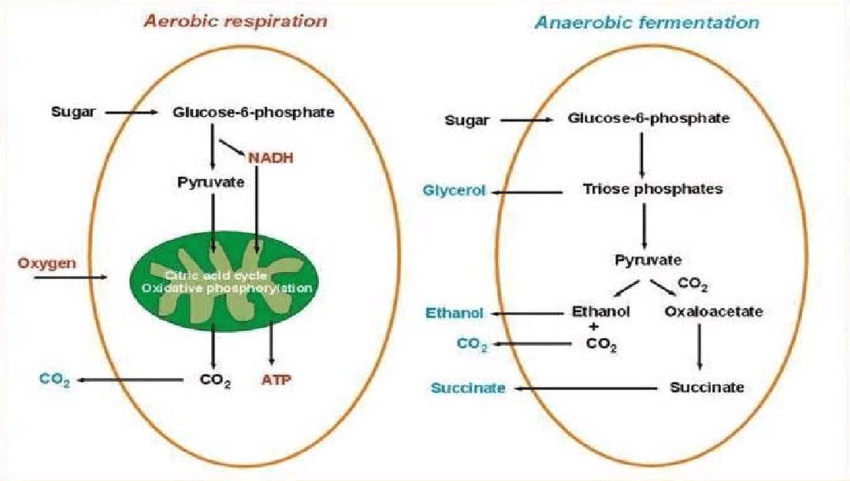
In yeast, both aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration can occur. The main difference between the two is that aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen whereas anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen.
Both processes use glucose as the raw material. However, fermentation produces a much lower amount of ATP than aerobic respiration. Fermentation produces ethanol and carbon dioxide whereas aerobic respiration produces 36-38 ATP, carbon dioxide and water.
The diagram shows anaerobic respiration in yeast cells.
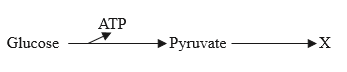
What would be produced at X?
A. ATP
B. Lactate
C. Ethanol and CO2
D. CO2 and H2O
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Yeast can respire anaerobically (without oxygen), breaking down glucose in the absence of oxygen to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process is called fermentation. The process of anaerobic respiration in yeast cells is called fermentation1. During anaerobic respiration process yeast breaks Glucose molecules and produces some amount of energy along with organic alcohol (Ethanol) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Question
The graph shows the results of an experimental investigation that compared the rates at which lactose, glucose and galactose are broken down in the process of anaerobic cellular respiration by the yeast Torulopsis cremoris.
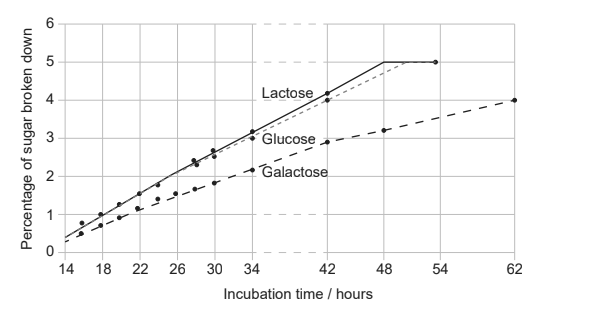
What can be concluded from these results?
Cellular respiration of lactose involves the production of glucose and galactose.
The breakdown of glucose and galactose occurs more slowly in the presence of lactose.
The rate of cellular respiration is greater for glucose than for lactose and galactose.
The percentage of sugar remaining after 42 hours is greater for galactose than glucose.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The glucose and sucrose have a higher rate of CO2 production in yeast due to the yeast being able to break it down into simple sugars, unlike lactose. Another source states that the breakdown of glucose and galactose occurs more slowly in the presence of lactose. The rate of cellular respiration is greater for glucose than for lactose and galactose. The percentage of sugar remaining after 42 hours is greater for galactose than glucose.
