IB Biology SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 3.2 Chromosomes
Topic 3 Weightage : 23%
All Questions for Topic 3.2 – Prokaryotic Genetics, Eukaryote Genetics, Identifying Genes, Homologous Pairs, Diploid versus Haploid, Autosome versus Heterosome, Karyograms, Chromosome Size, Chromosome Number, Genome Size, Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic DNA, Chromosome Types, Block Mutations, Sex Determination
Question
What feature of eukaryotic chromosomes distinguishes them from the chromosomes of prokaryotes?
Histone proteins
Circular DNA
Double-stranded DNA molecules
Multiple genes along the length of each chromosome
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
One way to distinguish eukaryotic chromosome from prokaryotic chromosome on the level of histone protein packing is to look at whether the DNA is wrapped around histone proteins or not.
In a eukaryotic cell, DNA wraps around clusters of histone proteins1. However, most prokaryotic cells don’t use histones to help with DNA storage. (Some Archaea do, but they are the exception, rather than the rule.) Like eukaryotic DNA, prokaryotic DNA undergoes supercoiling, but it is not wound around histone clusters first. Prokaryotes tend to compress their DNA using nucleoid-associated-proteins (NAPs) and supercoiling.
Which is a characteristic of the pairs of sister chromatids that are visible during meiosis?
A. They result from the replication of DNA before meiosis.
B. They are only present in meiosis I.
C. They split apart during metaphase I in meiosis.
D. They are only present in meiosis II.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Ans:A
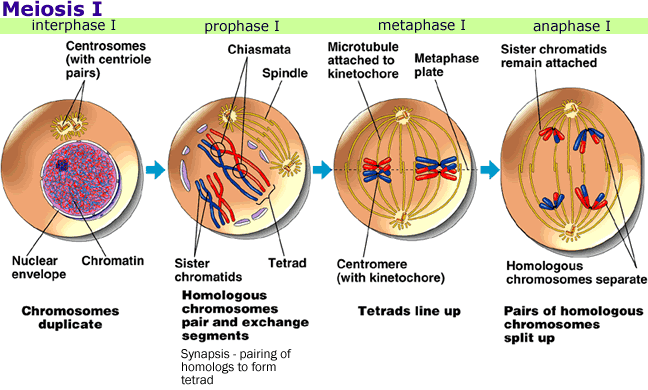
The DNA replicated before meiosis are visible during meiosis because they form sister chromatids, which are the two identical copies of the same chromosome attached by a structure called the centromere. Sister chromatids are separated during meiosis 2nd which produces four haploid cells. DNA replication is necessary before meiosis to ensure that each gamete receives a complete set of chromosomes.
What is a possible source of the chromosomes used for pre-natal karyotype diagnosis?
A. The mother’s lymphocytes
B. The mother’s cheek cells
C. The cells from chorionic villi
D. The fetal hair root cells
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Ans: C
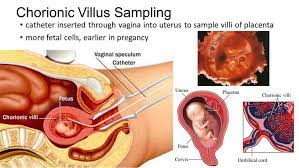
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is used in prenatal diagnosis, enabling to detect fetal genetic abnormalities. Its advantages include the possibility of performing the procedure during the first trimester of pregnancy relatively fast result, risk of miscarriage comparable to that in case of amniocentesis. CVS is a type of prenatal testing that takes a small sample of cells from the placenta, the organ that forms during pregnancy to deliver nourishment to the fetus. The cells are then analyzed for chromosomal abnormalities. CVS can be performed earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis and can detect some genetic disorders that amniocentesis cannot.
What causes the presence of three chromosomes 21 in Down syndrome?
A. Crossing over
B. Allele change
C. Non-disjunction
D. Gene mutation
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Ans: C
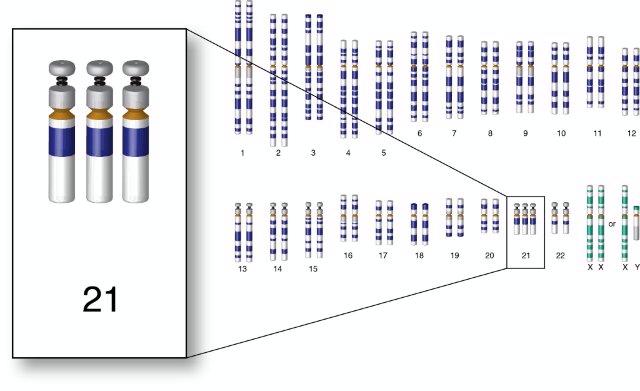
This can happen when there is an error in cell division called nondisjunction. Nondisjunction means that the chromosomes do not separate properly during meiosis, the process that produces eggs and sperm. If an egg or a sperm has an extra chromosome 21 and joins with a normal egg or sperm during fertilization, the resulting embryo will have three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual two. This is called trisomy 21 and it accounts for about 95% of Down syndrome cases¹. Sometimes, only part of chromosome 21 is extra, or the extra chromosome 21 is attached to another chromosome. These are called translocation and mosaic Down syndrome, respectively, and they are less common. The risk of nondisjunction increases with maternal age, especially after age 35. Altered recombination, which means that the exchange of genetic material between chromosomes during meiosis is abnormal, may also increase the risk of nondisjunction.
