IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 3.3
Topic 3 Weightage : 5%
All Questions for Topic 3.3 – Meiotic Division, Sister Chromatids, Stages of Meiosis, Crossing Over, Random Assortment, Sexual Life Cycle, Genetic Variation, Non-Disjunction, Karyotyping, Drawing Meiosis, Mitosis versus Meiosis, Somatic vs Germline Mutations, Polyploidy
What description is matched with the correct phase in meiosis I?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Ans:C
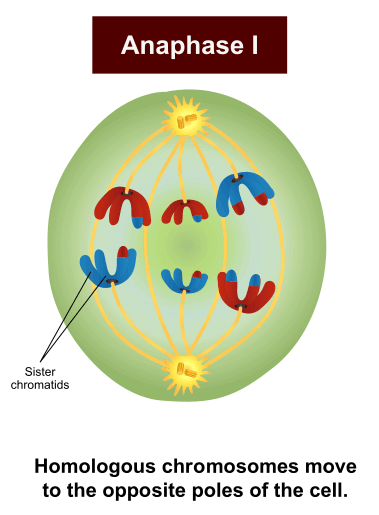
During anaphase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate from each other and migrate to opposite ends of the cell. This mechanism separates homologous chromosomes into two separate groups. Atypical spindle forming and positioning can lead to asymmetrical cell division and the loss or gain of one or more chromosomes to either daughter cell.
What event occurs only in meiosis?
A. Fusion of gametes to promote genetic variation
B. Random separation of chromatids
C. Random separation of homologous chromosomes
D. Replication of chromosomes
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Ans:C
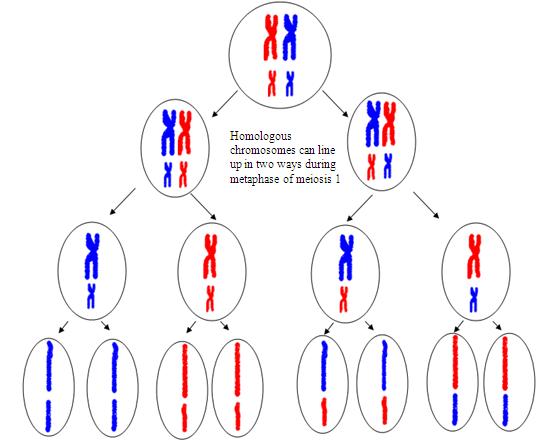
During meiosis, the pairs of homologous chromosome are divided in half to form haploid cells, and this separation, of homologous chromosomes is random. This means that all of the maternal chromosomes will not be separated into one cell, while the all paternal chromosomes are separated into another.
What is the chromosome number in a human gamete with non-disjunction?
A. 46
B. 45
C. 24
D. 23
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Ans:C
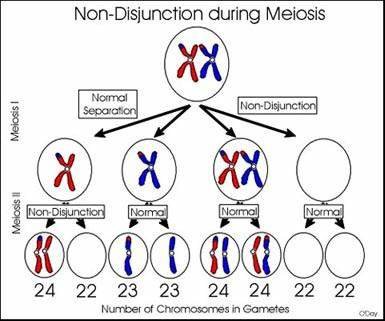
The haploid number for humans is 23, so normally a human gamete would have 23 chromosomes. However, sometimes there is a failure of chromosomes or chromatids to separate properly during cell division, which is called nondisjunction. This can result in gametes with an abnormal number of chromosomes, which is known as aneuploidy. For example, if nondisjunction occurs during meiosis I or meiosis II, a human gamete could end up with 24 or 22 chromosomes instead of 23. This can cause genetic disorders such as Down syndrome (trisomy 21) or Turner syndrome (monosomy X). Therefore, the chromosome number 24 in human gamete is with nondisjunction.
What is meiosis?
A. Division of a diploid nucleus to form diploid nuclei
B. Reduction division of a haploid nucleus to form diploid nuclei
C. Reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei
D. Division of a haploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Ans:C
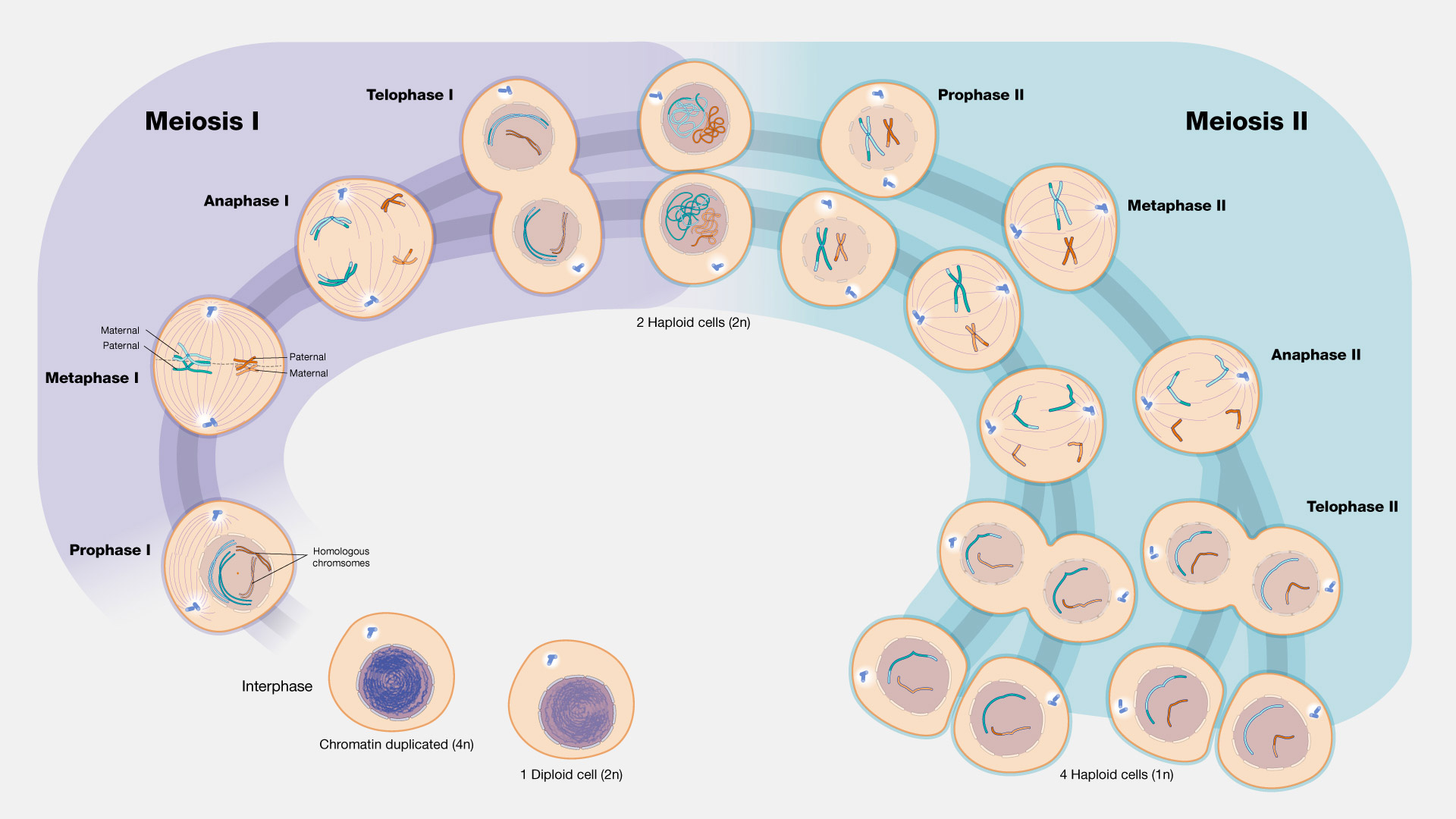
Meiosis is called reductional division because the end result of this special type of cell division is four haploid cells. These can be used as gametes–sperm or egg cells in sexually reproducing organisms. During meiosis I, the chromosome number in the cells reduces resulting in haploid cells. Hence this cell division is known as a reduction division.
What causes genetic variety in the formation of gametes during meiosis?
A. Crossing over in prophase I and random orientation of homologous chromosomes in metaphase I
B. Crossing over in metaphase I and random orientation of homologous chromosomes in metaphase II
C. Linkage of genes in prophase I and crossing over in metaphase I
D. Linkage of genes in metaphase I and random orientation of homologous chromosomes in metaphase II
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
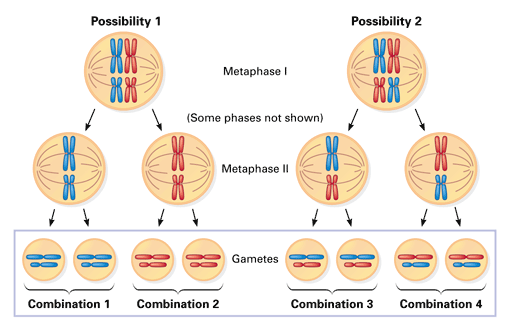
Crossing over in prophase I and random orientation of homologous chromosomes in metaphase I causes genetic variety in the formation of gametes during meiosis. Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between maternal and paternal chromosomes. This exchange results in new combinations of genes on each chromosome. Random orientation of homologous chromosomes in metaphase I is also important for genetic variety as it allows the random uniting of genes at fertilization. This process is called genetic recombination. The transfer of genes that takes place between chromosome pairs in a process known as crossing over also contributes to genetic recombination.
