IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 3.5 Genetic modification and biotechnology
Topic 3 Weightage : 5%
All Questions for Topic 3.5 – polymerase chain reaction, Gel Electrophoresis, DNA Profiling, Gene Transfer, GMO Debate, Clones, Natural Cloning, Artificial Cloning, Stem Cuttings, Vector Delivery, Examples of GMOs, cDNA and Microarrays, Gene Therapy, Gene Silencing
Which is a possible risk associated with a genetic modification of crops?
A. Crop plants will become weaker with time.
B. It can increase mutations in the organisms that consume them.
C. Starch obtained from genetically modified plants will be more difficult to digest.
D. Resistance to herbicide genes can be transferred to weeds.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
One of the possible risks associated with genetic modification of crops is the transfer of resistance to herbicide genes to wheat. This could happen through horizontal gene transfer, which is the movement of genetic material between organisms that are not related by reproduction. Horizontal gene transfer can occur through natural processes such as viral infection, bacterial conjugation, or transposable elements, or through human-mediated processes such as biolistic, electroporation, or microinjection. If resistance to herbicide genes are transferred to wheat, it could result in the emergence of superweeds that are difficult to control and could reduce crop yields and biodiversity.
A DNA profile was made of one individual in a paternity suit. Locus B was used to distinguish between this individual and other individuals. The individual had two alleles of the gene at locus B which are shown below:
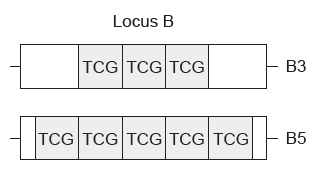
Gel electrophoresis was used to separate and visualize the alleles B3 and B5. The gel, with two bands of DNA, is shown below.
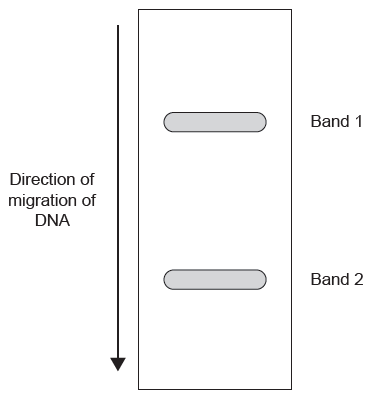
What DNA is in bands 1 and 2?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Which sequence of DNA would be suitable in DNA profiling?
A. —ATTCGTGAATCAGCC–
B. —ATTCGTGAATTTGCC–
C. —ATTCGTGATTGCAGC–
D. –DD
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
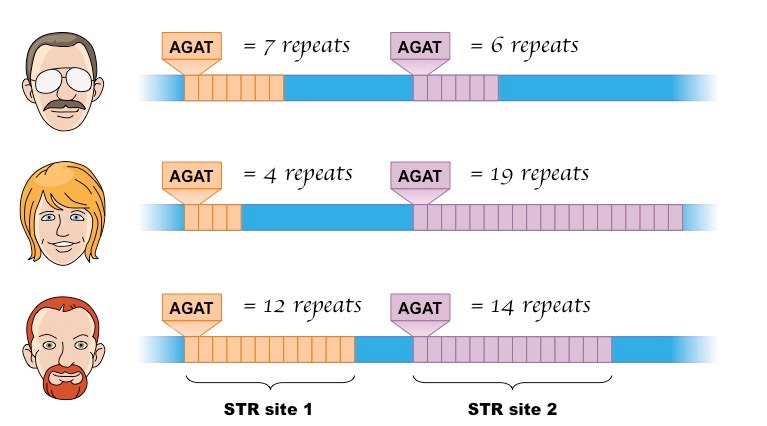
DNA profiling is a technique by which individuals can be identified and compared via their respective DNA profiles.
- Within the non-coding regions of an individual’s genome there exists satellite DNA – long stretches of DNA made up of repeating elements called short tandem repeats (STRs).
- As individuals will likely have different numbers of repeats at a given satellite DNA locus, they will generate unique DNA profiles.
Short tandem repeats (STRs) are a type of DNA polymorphism that can be used for DNA profiling. STRs are regions of non-coding DNA that consist of repeated sequences of 1 to 6 base pairs. For example, AGATAGATAGATAGATAGATAGAT is an STR where the nucleotide sequence AGAT is repeated six times. The number of repeats varies among individuals and their alleles, making STRs highly variable and useful for identification purposes. STR analysis is a molecular biology technique that uses polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to amplify specific STR loci and compare them between two or more samples. The length of the PCR product reflects the number of repeats at each locus. The PCR products are then separated and detected by electrophoresis, which produces a pattern of bands or peaks that represents the STR profile of each sample. By comparing the STR profiles of different samples, forensic scientists can determine whether they match or not. STR analysis is widely used in criminal investigations, paternity testing, missing persons cases, and other applications that require human identification.
So in sequence ATTCGTGATTCGTGA, ATTCGTGA is repeating continuously and hence this sequence is suitable of DNA profiling.
Which process can be used to amplify small fragments of DNA?
A. Gel electrophoresis
B. Polymerase chain reaction
C. DNA profiling
D. Electron microscopy
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) are a technique that can be used to amplify small fragments of DNA in a laboratory setting. PCR works by using a DNA polymerase enzyme that can copy a specific region of DNA, known as the target sequence, using short pieces of DNA called primers that bind to the ends of the target sequence. By repeating this process multiple times, PCR can produce millions of copies of the target sequence from a small amount of starting material. PCR is useful for various applications, such as genetic testing, forensic analysis, and molecular biology research.
What is a definition of a clone?
A. A group of cells derived from a single parent cell
B. Differentiated cells that retain the capacity to divide
C. A fetus developed specifically for medical use
D. A group of cells that have lost the ability to differentiate
Answer/Explanation
▶️Markscheme
A
Clone offspring are the result of asexual reproduction, where a single parent cell produces an identical copy of itself. Clone offsprings have the same genetic makeup as their parent and are therefore genetically identical. Clone offspring can occur naturally, such as in bacteria, fungi, plants and some animals, or artificially, such as in cloning techniques used in biotechnology and medicine.
Question
A process for genetically modifying a plant is shown.
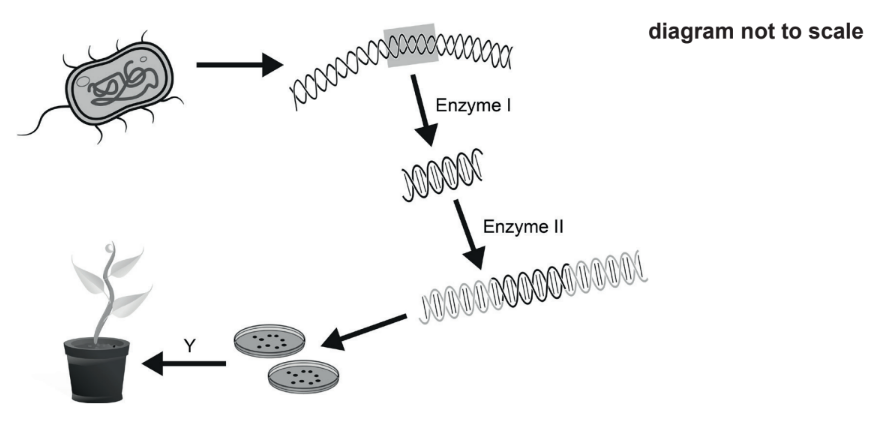
What is the name of enzyme II and the name of process Y?
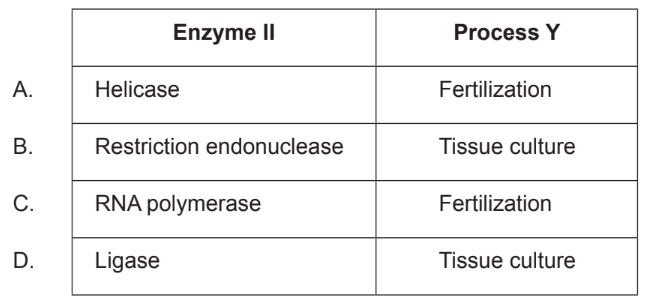
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Ligase is an enzyme that is used to join two DNA fragments together. In tissue culture, ligase is used to insert a gene of interest into a plasmid vector. The plasmid vector is then introduced into the plant cells using a variety of methods such as Agrobacterium-mediated transformation or biolistic transformation.
Question
Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS) are used to test for fetal abnormalities. Which statement is a valid comparison between the two tests?
A. CVS is performed later in pregnancy but has more risk of miscarriage than amniocentesis.
B. Amniocentesis is performed earlier in pregnancy but has more risk of miscarriage than CVS.
C. CVS is performed earlier in pregnancy but has more risk of miscarriage than amniocentesis.
D. Amniocentesis is performed later in pregnancy but has more risk of miscarriage than CVS.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
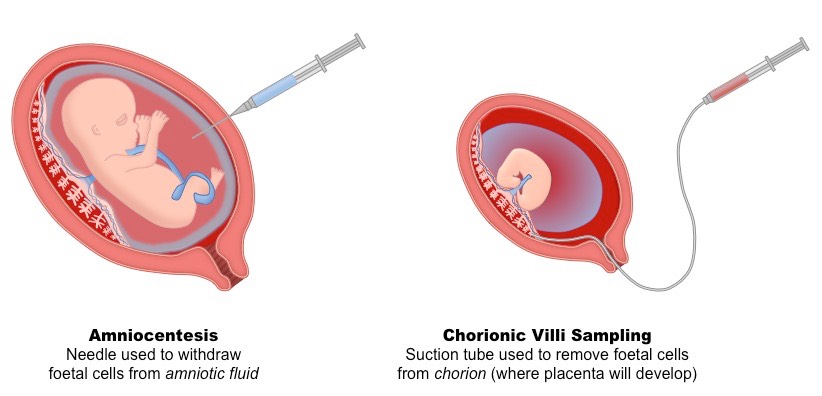
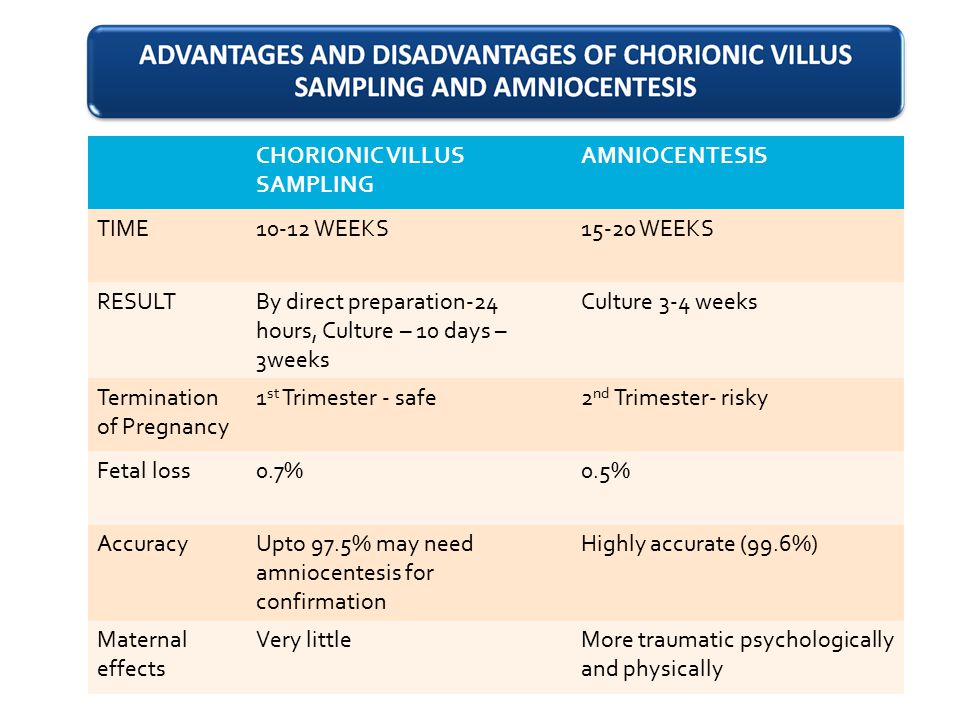
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis are two prenatal tests that can detect genetic disorders in the fetus. However, CVS has some advantages over amniocentesis that make it more effective for some parents. One advantage of CVS is that it can be performed earlier in pregnancy, between 10 and 14 weeks, while amniocentesis can only be done between 15 and 20 weeks. This means that CVS can provide results sooner, which can help parents make informed decisions about their pregnancy and prepare for the birth of their child.
Another advantage of CVS is that it has a lower risk of miscarriage than amniocentesis. Although both risks are low, some parents may prefer to avoid any additional risk to their pregnancy.
However, CVS also has some limitations that should be considered. For example, CVS cannot detect neural tube defects, such as spina bifida, which can be detected by amniocentesis. CVS may also cause bleeding or infection in rare cases. Therefore, parents should discuss the benefits and risks of both tests with their healthcare provider before making a decision.
