IB Biology SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 4.3 Carbon Cycling
Topic 4 Weightage : 10%
All Questions for Topic 4.3 – Carbon Cycle, Carbon Compounds, Aquatic Conversions, Methane, Fossil Fuels, Combustion, Carbon Fluxes, Biogeochemical Cycles, Ocean Acidification, Biofuels
The diagram shows the carbon cycle.
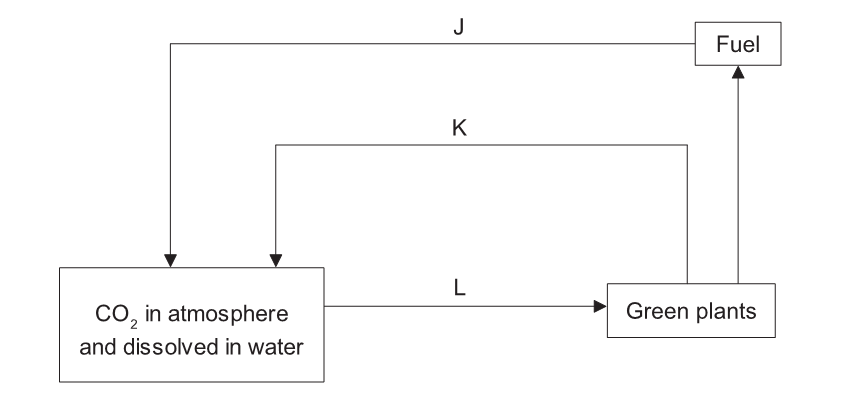
[Source: © International Baccalaureate Organization 2017]
Which two processes correspond to the labelled arrows?
A. K is combustion and L is catabolism.
B. J is anabolism and K is respiration.
C. J is combustion and K is respiration.
D. J is anabolism and L is catabolism.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
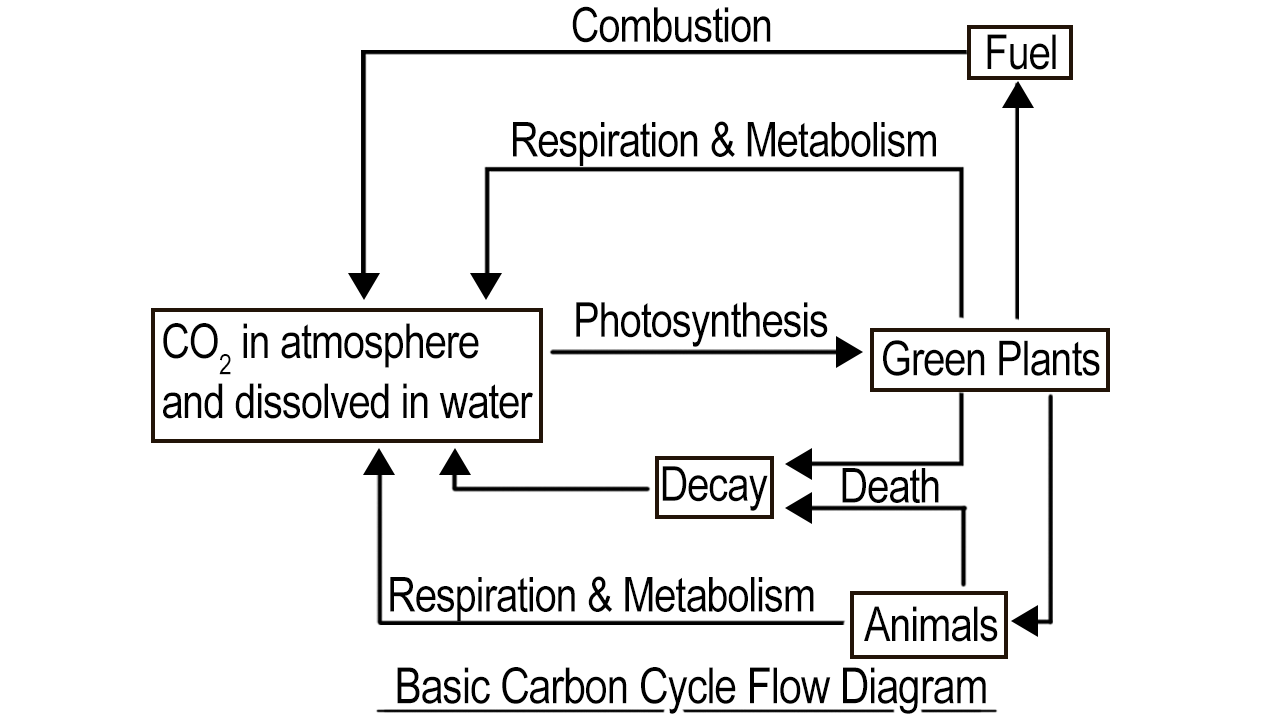
J marked is combustion. Combustion is the process by which carbon compounds, such as fossil fuels, are burned in the presence of oxygen to release energy and produce carbon dioxide and water vapor as waste products. This process is a major contributor to the increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations and is a significant driver of climate change.
K marked is respiration. Respiration is the process by which living organisms break down organic compounds, such as glucose, to release energy for their metabolic processes. During respiration, carbon dioxide is produced as a waste product, which is then released into the atmosphere. This process is a major contributor to the carbon cycle, as it returns carbon from living organisms back to the atmosphere.
L marked is catabolism, which is basically photosynthesis. Catabolism is the process by which living organisms break down complex organic compounds, such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, into simpler molecules, such as carbon dioxide, water, and energy. This process releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to the carbon cycle.
What favours the production of peat?
I. Presence of organic matter
II. Anaerobic conditions
III. Acidic conditions
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
The presence of organic matter, anaerobic conditions, and acidic conditions can all contribute to the formation of peat. Organic matter, such as dead plant material, accumulates in wetland environments, where it is not fully decomposed due to the lack of oxygen and acidic conditions. Over time, the accumulation of this organic matter can form a layer of partially decomposed material known as peat. Anaerobic conditions and acidic conditions slow down the decomposition process, allowing the organic matter to accumulate and form peat.
The diagram shows a version of the carbon cycle. What is indicated by the numbers?
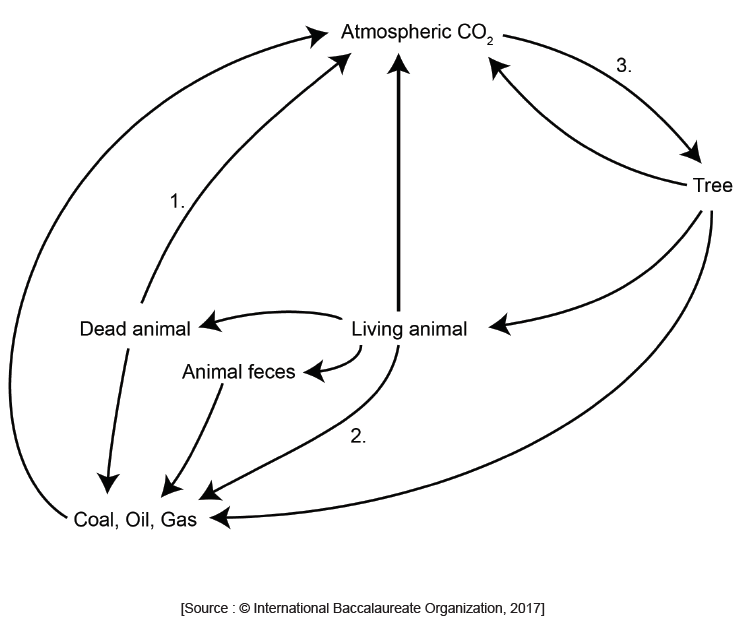
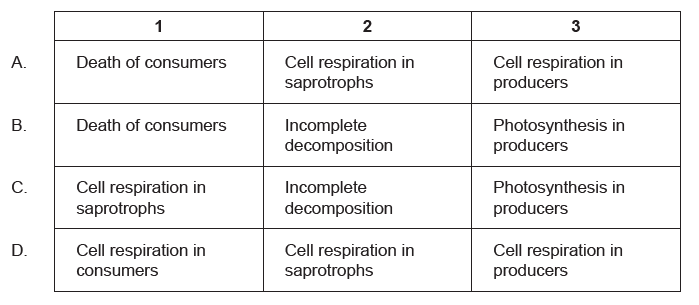
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
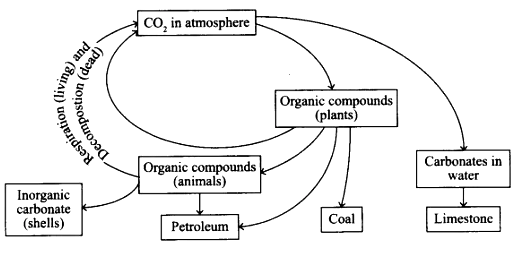

- Saprotrophs, also known as decomposers, play a key role in the carbon cycle by breaking down dead organic matter and returning carbon to the soil. As dead organisms and plant material decompose, saprotrophic microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, break down the complex organic compounds into simpler molecules, such as carbon dioxide and water. This process releases carbon back into the atmosphere and allows it to be recycled into new organic matter. Without saprotrophs, dead organic matter would accumulate and carbon would be sequestered in the soil, reducing the amount of carbon available for new growth.
- The conversion of plants into petroleum is considered incomplete decomposition because the organic matter that makes up petroleum is only partially decomposed. Over millions of years, the remains of dead plants and animals are buried under sediment and subjected to high pressure and temperature. Under these conditions, the organic matter undergoes a chemical transformation, breaking down into simpler hydrocarbons that make up petroleum. However, this process is incomplete, as some of the original organic matter remains in the petroleum. Therefore, petroleum is considered a fossil fuel because it contains partially decomposed organic matter from millions of years ago.
- Catabolism is the process by which living organisms break down complex organic compounds, such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, into simpler molecules, such as carbon dioxide, water, and energy. This process releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to the carbon cycle.
Question
Carbon sinks are any reservoirs that absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Which process increases the size of the carbon sink in oceans?
A. Photosynthesis
B. Respiration
C. Ocean acidification
D. Decomposition
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
The process that increases the size of the carbon sink in oceans is called the biological pump. The biological pump refers to the transfer of carbon from the surface of the ocean to the deep ocean through the action of plankton. Phytoplankton, which are tiny, plant-like organisms, absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis. When they die, their organic matter sinks to the ocean floor, taking the carbon with it. This process removes carbon from the surface of the ocean and stores it in the deep ocean, increasing the size of the carbon sink. Additionally, the sinking organic matter provides a food source for deep-sea organisms, which can also store carbon in their biomass.
IBDP Online Test Series By iitianacademy
Comprehensive Test Preparatory package targeted towards IBDP
