Question
(a) Describe what is shown in a cladogram [2]
(b) Outline how variation in organisms of the same species could lead to natural selection [3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans :
a
a similarities/differences between organisms/species/clades
b «probable» evolutionary relationships/closeness/common ancestry/phylogeny
c divergence/splits/speciation/branches/nodes
d relative similarity/differences between base sequence/amino acid sequence
mpa and mpd concern actual characteristics, not evolutionary relationships. mpb concerns such relationships mpc concerns the structure branching of the cladogram
b
a survival of the better adapted/fittest
b more reproduction of better adapted/fittest/individuals with favorable variations
c genes for favorable variations/adaptations passed on to offspring Accept answers in the converse.
d competition for resources/more offspring produced than the environment can support/a struggle for existence
Question
The image shows part of a cladogram.
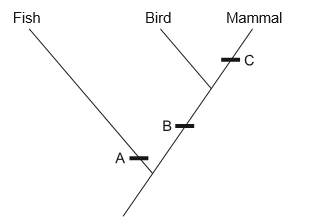
Using the cladogram, identify one diagnostic feature that characterizes the given groups of vertebrates at A, B and C.
A: ……………………………………………………………
B: ……………………………………………………………
C: ……………………………………………………………
Starting from the concept of gene pool, explain briefly how populations of early vertebrates could have evolved into different groups.
Mitochondria are thought to have evolved from prokaryotic cells. Describe two adaptations of the mitochondria, each related to its function.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A: gills or fins or scales or no limbs or external fertilization
B: homeothermic or warm-blooded or endothermic or lungs or tetrapod or four limbs or pentadactyl limbs or internal fertilization
C: hair or fur or mammary glands or milk
Gene pool is all genes/all alleles. Reject all alleles/genes in a species.
Geographic isolation Reject isolation if no type of isolation given.
OR
migration to different areas
OR
temporal isolation
OR
behavioural isolation
Speciation/gene pool split if populations are reproductively isolated/do not interbreed
In different environments there are different selection pressures/opportunities/natural selection/adaptations/niches «to exploit»
Allele frequencies change/diverge Reject gene frequencies.
Double membrane/small intermembrane space/small gap between inner and outer membrane for a gradient «of protons» to develop
Accept only the first two adaptations in the answer.
Cristae/folds in inner membrane/large surface area of inner membrane for ATP synthesis/chemiosmosis/proton pumping/electron transport chains
ATP synthase/stalked particles generates ATP from ADP + phosphate/Pi. Reject ATPase. Allow ATP synthetase.
Electron transport chains for generating a proton gradient/for releasing energy from reduced NAD
Matrix contains enzymes for Krebs cycle/link reaction/oxidation of fats/oxidation of substrates/aerobic respiration
Ribosomes/DNA for protein synthesis/replication
