IB Biology SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 6.1 Digestion and absorption
Topic 6 Weightage : 23%
All Questions for Topic 6.1 – Digestive System, Mechanical Digestion, Chemical Digestion, Small Intestine, Absorption, Starch Digestion, Modelling Digestion, Stages of Digestion, Lipid Digestion, Lipid Absorption, Sections of the Gut
Question
A fluid sample is taken from the digestive tract of a mammal. The sample is basic (alkaline) and able to digest starch and proteins. From which part of the digestive tract was the fluid taken?
A Mouth
B Stomach
C Small intestine
D Gall bladder
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
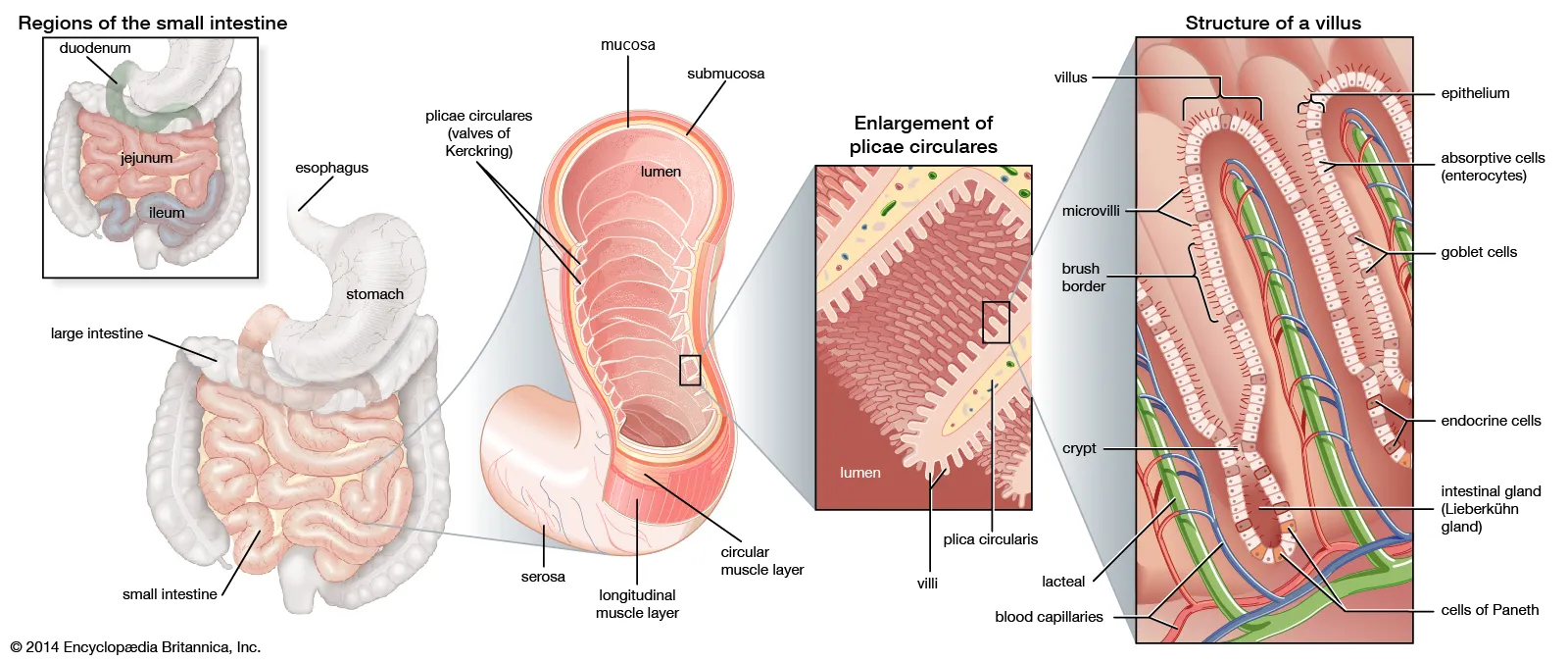
The small intestine is alkaline because it secretes bicarbonate ions that neutralize the acidic chyme coming from the stomach. It also produces several enzymes, such as amylase and protease, which help to digest starch and proteins, respectively. Therefore, the fluid sample that was able to digest starch and proteins and was alkaline was likely taken from the small intestine.
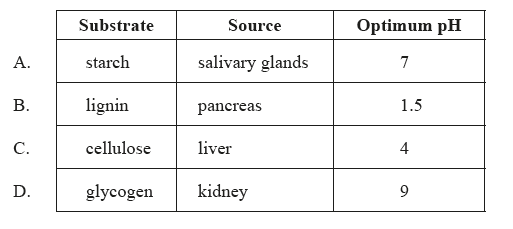
What are features of the enzyme amylase?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Amylase is an enzyme that breaks down starch into simpler sugars, such as glucose. It is found in various organisms, including humans, and is produced in the salivary glands and pancreas. The substrate of amylase is starch, which is a complex carbohydrate made up of glucose molecules linked together.
The optimum pH of amylase depends on the source of the enzyme. For example, human salivary amylase has an optimum pH of around 6.7, while pancreatic amylase has an optimum pH of around 7.5-8.0.
The optimum pH of an enzyme is the pH at which the enzyme works most efficiently. At other pH values, the enzyme’s activity may be reduced. For amylase, the optimum pH is slightly alkaline, which is consistent with the pH of the small intestine.
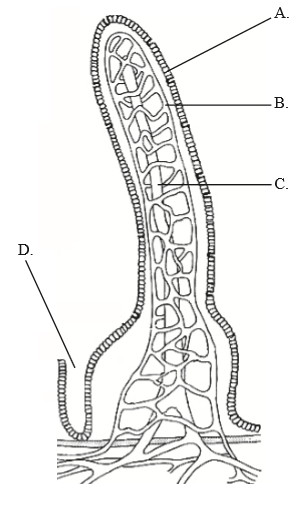
Which label represents the lacteal?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
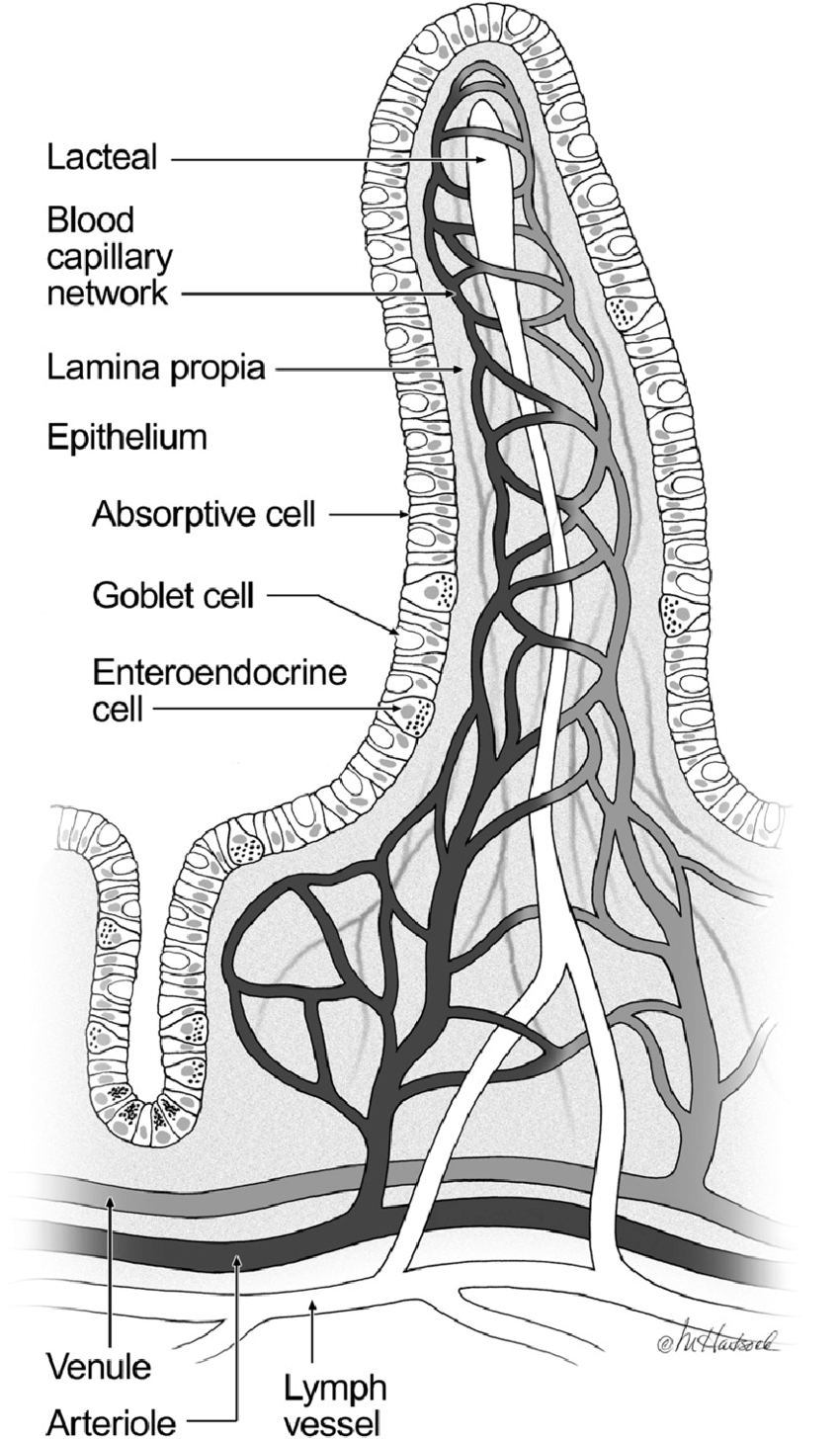 Lacteals are small lymphatic vessels located in the villi of the small intestine. They are responsible for absorbing dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the small intestine and transporting them to the lymphatic system.
Lacteals are small lymphatic vessels located in the villi of the small intestine. They are responsible for absorbing dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the small intestine and transporting them to the lymphatic system.
Celiac disease causes the destruction of the villi cells. Which of the following is most likely to happen to people with celiac disease?
A. Incomplete digestion of fats
B. Poor absorption of calcium
C. Increased levels of glucose in blood
D. Damage in the esophagus caused by increase in acid content of the stomach
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
People with celiac disease may experience malabsorption of nutrients due to the destruction of the villi cells. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, such as diarrhea, weight loss, and nutritional deficiencies. The immune system of people with celiac disease reacts to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, causing inflammation and damage to the villi. Celiac disease can cause poor absorption of calcium because the damage to the villi in the small intestine can reduce the surface area available for nutrient absorption. Calcium is absorbed in the small intestine through active transport and passive diffusion, and the villi play a crucial role in this process by increasing the surface area available for absorption. When the villi are damaged in celiac disease, the absorption of calcium may be impaired. Additionally, people with celiac disease may have lower levels of vitamin D, which is essential for calcium absorption, due to malabsorption caused by the damage to the villi.
Questions 9 and 10 refer to the following diagram of the human digestive system.
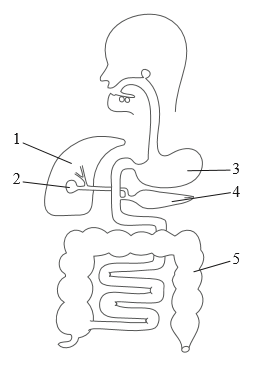
Which structure produces lipase?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 5
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
The pancreas produces lipase, which is an enzyme that breaks down fats into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the small intestine. The pancreas secretes lipase into the small intestine through the pancreatic duct.
Question
The digestive system hydrolyses macromolecules into monomers for absorption. Which chemical(s) produced by humans can perform hydrolysis?
I. Cellulase
II. Glycogen
III. Amylase
A. I and III only
B. II and III only
C. III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Amylase is a chemical produced by humans that can perform hydrolysis. It is an enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates, such as starch and glycogen, into smaller molecules, such as glucose. Cellulase is an enzyme that breaks down cellulose, which is a carbohydrate found in plant cell walls, but it is not produced by humans. Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate that is stored in the liver and muscles of animals, including humans. It is broken down by enzymes, including amylase, into glucose for energy.
