IB Biology SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 6.2 The blood system
Topic 6 Weightage : 23%
All Questions for Topic 6.2 – Circulation, Arteries, Capillaries, Veins, Vessel Comparison, Heart Structure, Heart Beat, Heart Rate, Cardiac Cycle, Heart Disease, Blood Composition, Blood Pressure, Electrocardiography
Question
What is a property of arteries?
A Arteries have elastic walls.
B Arteries have valves.
C All arteries carry oxygenated blood.
D Arteries receive blood from the atria
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
A. Arteries have elastic walls.
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart and distribute it throughout the body. One of the key properties of arteries is that they have elastic walls, which allows them to stretch and recoil in response to changes in blood pressure. This elasticity helps to maintain a steady flow of blood through the arteries, even when the heart is not actively pumping.
Valves are structures that are found in veins, not arteries. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart, and they have valves that help to prevent the backflow of blood.
While many arteries do carry oxygenated blood, there are some exceptions. For example, the pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it is oxygenated before being returned to the heart.
Arteries do not receive blood from the atria. The atria are the upper chambers of the heart, and they receive blood from the veins before pumping it into the ventricles, which then pump the blood out through the arteries.
Question
In mammals, mature red blood cells are specialized in that they lack nuclei, mitochondria or ribosomes. Which statement applies to red blood cells?
No chemical reactions take place within their cytoplasm.
They cannot produce new enzymes.
Materials cannot enter red blood cells.
Materials cannot exit red blood cells
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
B. They cannot produce new enzymes.
Mature red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, lack nuclei, mitochondria, and ribosomes. This means that they cannot produce new enzymes or carry out protein synthesis. However, they do contain a variety of enzymes that are necessary for their metabolic functions.
Red blood cells do not have a nucleus, which means they have more space for hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen. The lack of mitochondria means that red blood cells rely solely on anaerobic metabolism to produce ATP, the energy source that powers their functions.
Materials can enter and exit red blood cells, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. Oxygen enters red blood cells through the process of diffusion, where it moves from an area of high concentration (the lungs) to an area of low concentration (the blood). Similarly, carbon dioxide exits red blood cells through the process of diffusion, where it moves from an area of high concentration (the blood) to an area of low concentration (the lungs).
The diagram shows the human heart.
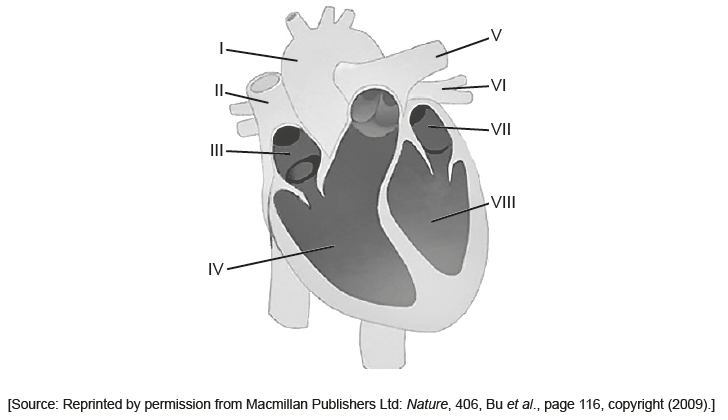
Which shows the sequence of blood flow in the heart?
A. III IV I
B. IV III II
C. VII VIII I
D. VIII VII VI
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Blood comes into the right atrium from the body, moves into the right ventricle and is pushed into the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. After picking up oxygen, the blood travels back to the heart through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, to the left ventricle and out to the body’s tissues through the aorta. So option C seems to be correct.
What is a feature of the left atrium?
A. Epinephrine decreases its rate of contraction.
B. It contracts as the left ventricle contracts.
C. It receives blood from the left pulmonary artery
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
The left atrium is responsible for receiving oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumping it into the left ventricle. As the left ventricle fills up with blood, the pressure within the chamber increases. To prevent this pressure from becoming too high, the left atrium contains a structure called the mitral valve. The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and the left ventricle, and it functions to regulate the flow of blood between the two chambers.
As the left ventricle fills up with blood, the pressure within the chamber pushes against the mitral valve, causing it to close. This closure prevents any blood from flowing back into the left atrium, which would increase the pressure within the atrium. The closure of the mitral valve also helps to decrease the pressure within the left atrium. As the valve closes, the volume of the left atrium decreases, which in turn decreases the pressure within the chamber. This decrease in pressure allows the left atrium to fill up with more oxygen-rich blood from the lungs, which can then be pumped into the left ventricle during the next cardiac cycle.
What helps to keep blood flowing onwards away from the heart in an artery?
A. Valves
B. Elastic fibres
C. Contraction of skeletal muscles
D. Having a wide lumen
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Elastic fibers in the artery walls play an essential role in maintaining blood flow away from the heart.
When the heart pumps blood into the arteries, the walls of the arteries stretch to accommodate the increase in blood volume. The elastic fibers in the artery walls allow them to stretch and recoil with each heartbeat, helping to maintain a continuous flow of blood. As the heart relaxes, the elastic fibers in the artery walls recoil, which helps to push blood forward. This recoil action also helps to maintain the pressure within the arteries, which is essential for maintaining blood flow. The elasticity of the artery walls is particularly important in maintaining blood flow during diastole, the period of the cardiac cycle when the heart is relaxed. During diastole, the elastic fibers in the artery walls recoil, which helps to maintain the pressure within the arteries and keep blood flowing forward.
So, the elasticity of the artery walls allows them to stretch and recoil with each heartbeat, helping to maintain a continuous flow of blood and maintain the pressure within the arteries.
In which blood vessel connected to the heart does blood have the lowest carbon dioxide concentration?
A. Pulmonary vein
B. Vena cava
C. Pulmonary artery
D. Coronary vein
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
The blood vessel connected to the heart that has the lowest carbon dioxide concentration is the pulmonary vein.
The pulmonary vein carries oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart, where it is pumped out to the rest of the body. Because the blood in the pulmonary vein has just been oxygenated in the lungs, it has a very low concentration of carbon dioxide.
In contrast, the vena cava carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart, and the pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. These blood vessels have a higher concentration of carbon dioxide than the pulmonary vein.
The coronary vein is responsible for draining blood from the heart muscle itself, and it also has a higher concentration of carbon dioxide than the pulmonary vein.
Question
The diagram shows a staggered transverse section (cut across rather than down) through the heart.
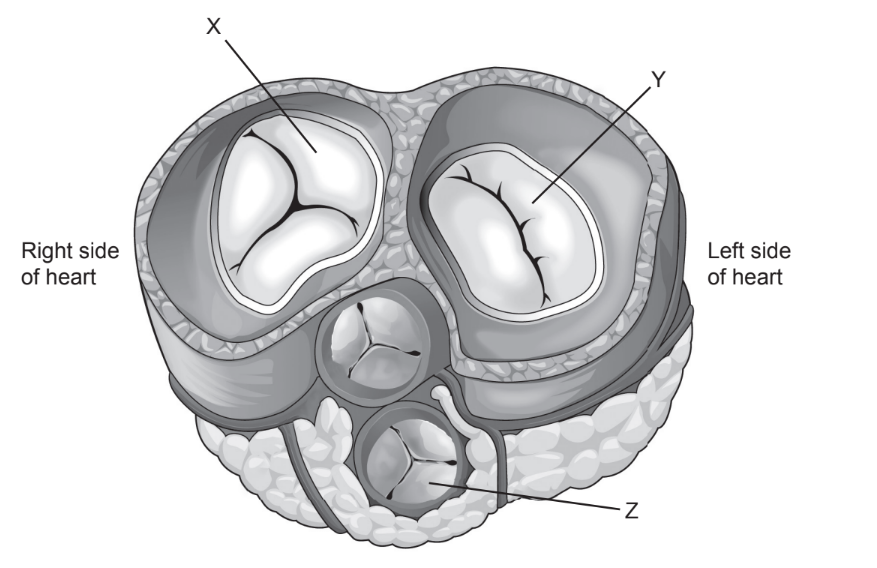
In what state are the valves when the ventricles are contracting?
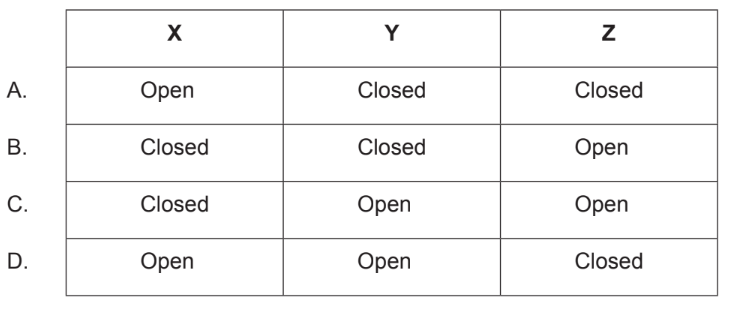
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
In the diagram, X is tricuspid valve, Y is bicuspid valve and Z is aortic valve.
When the left ventricle contracts, the mitral valve closes and the aortic valve opens. This is so blood flows into the aorta and out to the rest of the body. While the left ventricle is relaxing, the right ventricle also relaxes. This causes the pulmonary valve to close and the tricuspid valve to open.
