IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 6.3 Defence against infectious disease
Topic 6 Weightage : 20%
All Questions for Topic 6.3 – Surface Barriers, Clotting, Phagocytes, Lymphocytes, Antibiotics, Penicillin, HIV Infection, Pathogens, Lines of Defense, Inflammation, Types of Leukocytes, Haemophilia, Immunity Analogy
The graph is about defence against infectious disease.
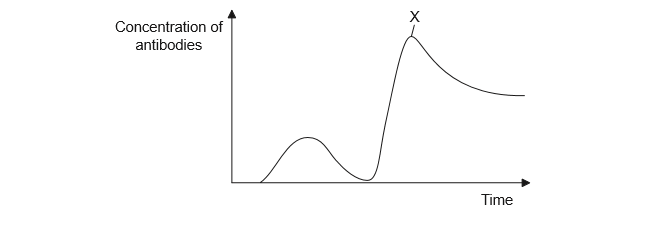
What is likely to be indicated by the letter X?
A. The increase in lymphocytes following HIV infection
B. The peak of the infection
C. The secondary response to a vaccine
D. The first appearance of AIDS symptoms
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Which is the correct statement concerning HIV and AIDS?
A. All HIV patients have AIDS.
B. HIV and AIDS are transmitted on the sex chromosomes.
C. All AIDS patients have HIV.
D. HIV and AIDS neutralize antibodies.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
The correct statement concerning HIV and AIDS is that all AIDS patients have HIV. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS, and people with HIV can develop AIDS if their immune system becomes severely damaged. HIV and AIDS are not transmitted on the sex chromosomes, and they do not neutralize antibodies.
Where are structures I, II and III found in the human body?
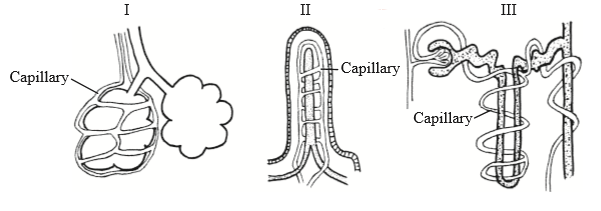
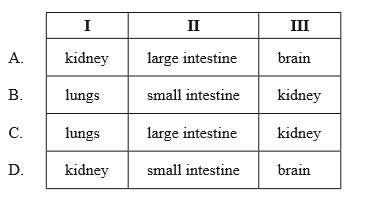
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
I is alveoli. Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged. They are surrounded by capillaries, which allow for efficient gas exchange. The close proximity of the alveoli and capillaries allows for a short diffusion distance, which means that gases can be exchanged quickly and efficiently.
II is villi. Villi are finger-like projections in the small intestine that increase the surface area for nutrient absorption. They are covered in microvilli, which are even smaller projections that further increase surface area. The villi and microvilli are located close to capillaries and lymphatic vessels, which allows for efficient absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream. The close proximity of the villi and capillaries allows for a short diffusion distance, which means that nutrients can be absorbed quickly and efficiently.
III is nephron. The nephron is the basic unit of the kidney that filters waste products from the blood and produces urine. The Loop of Henle is a U-shaped structure in the nephron that helps to concentrate urine by creating a concentration gradient in the kidney. It does this by actively transporting sodium and chloride ions out of the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle, which creates a high concentration of solutes in the surrounding tissue. This concentration gradient allows for the passive diffusion of water out of the descending limb of the Loop of Henle, which helps to concentrate urine.
The Loop of Henle is surrounded by a network of capillaries, which allows for the exchange of water and solutes between the Loop of Henle and the bloodstream. This exchange is important because it helps to maintain the concentration gradient in the kidney, which is necessary for the concentration of urine. The close proximity of the Loop of Henle and capillaries allows for a short diffusion distance, which means that water and solutes can be exchanged quickly and efficiently.
What steps occur in blood clotting?
A. Fibrin is converted to fibrinogen which then alters prothrombin into thrombin.
B. Thrombin is converted to prothrombin which then alters fibrinogen into fibrin.
C. Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin which then alters prothrombin into thrombin.
D. Prothrombin is converted to thrombin which then alters fibrinogen into fibrin.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
The correct answer is D. Prothrombin is converted to thrombin which then alters fibrinogen into fibrin. Blood clotting is a complex process that involves several steps. When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets in the blood are activated and begin to stick together at the site of injury. This forms a platelet plug that helps to stop the bleeding. The damaged tissue then releases a substance called tissue factor, which activates a series of clotting factors in the blood. Prothrombin is one of these clotting factors, and it is converted to thrombin by another clotting factor called Factor Xa. Thrombin then converts fibrinogen, another clotting factor, into fibrin. Fibrin forms a mesh-like structure that reinforces the platelet plug and forms a blood clot.
Which of the following statements about antibodies is correct?
A. Antibodies are polypeptides.
B. Antibodies are produced by the bone marrow.
C. Antibodies are pathogenic foreign substances.
D. Antibodies kill bacteria but not viruses.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Antibodies are polypeptides. Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are proteins that are produced by B cells in response to the presence of antigens. The antibodies recognize and bind to specific antigens, leading to their elimination from the body. Antibodies are important components of the immune system and play a key role in protecting the body from infection and disease.
Question
Despite continuous scientific research into the control of pathogens, it has proved very difficult to eliminate them. What is/are the reason(s) for this?
I. Development of antibiotic resistance in viruses
II. Development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria
III. Mutations of pathogens
A. II only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
The reasons for the difficulty in eliminating pathogens are II and III only. Development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria and mutations of pathogens are two of the main reasons why it has proved difficult to eliminate pathogens despite continuous scientific research into their control. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria develop the ability to resist the effects of antibiotics, making it more difficult to treat infections. Mutations of pathogens can lead to the development of new strains that are more virulent or resistant to treatment. These factors contribute to the ability of pathogens to persist and spread, making it difficult to control and eliminate them.
Question
Some vaccinations, such as the smallpox vaccine, provide lifelong immunity against the disease. For others, such as tetanus, this immunity lasts for a shorter period of time. Why is a tetanus booster vaccination recommended every 10 years?
A. Antibodies that formed after the first vaccination persist in the blood for up to 10 years.
B. Memory cells are not produced after the first vaccination.
C. Only non-specific immunity is stimulated after the first vaccination.
D. Memory cells gradually decline over 10 years.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
The correct answer is D. Memory cells gradually decline over 10 years. A tetanus booster vaccination is recommended every 10 years because the immunity provided by the initial tetanus vaccine gradually decreases over time. Tetanus is caused by a bacterium called Clostridium tetani, which can enter the body through a wound or cut. The tetanus vaccine helps the body produce antibodies that can neutralize the toxin produced by the bacteria. However, over time, the levels of these antibodies can decrease, making a person susceptible to tetanus infection again. Memory cells are produced after the first vaccination, but they gradually decline over time. A tetanus booster vaccine helps to stimulate the immune system to produce more memory cells and antibodies, which can help maintain immunity against tetanus.
