IB Biology SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 6.3 Defence against infectious disease
Topic 6 Weightage : 23%
All Questions for Topic 6.3 – Surface Barriers, Clotting, Phagocytes, Lymphocytes, Antibiotics, Penicillin, HIV Infection, Pathogens, Lines of Defense, Inflammation, Types of Leukocytes, Haemophilia, Immunity Analogy
Question
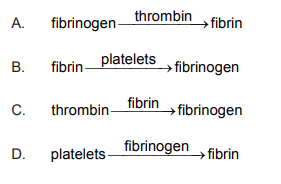
Which reaction occurs in blood clotting?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
In blood clotting, a series of chemical reactions occur that lead to the formation of a clot. The final reaction in the clotting cascade involves the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin by the enzyme thrombin. Fibrin is a protein that forms a mesh-like network of fibers that trap blood cells and platelets to form a clot. This process is essential for stopping bleeding and preventing blood loss in the event of an injury.
What stimulates the production of antibodies?
A. AIDS
B. Antibiotics
C. Anticodons
D. Antigens
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
The production of antibodies is stimulated by antigens. Antigens are foreign substances that enter the body, such as bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms. When an antigen enters the body, it triggers the immune system to produce antibodies that are specific to that antigen. The antibodies then bind to the antigen and help to neutralize or eliminate it from the body.
What can protect the body from blood loss?
A. Antibodies
B. Fibrin
C. Histamines
D. Hemophilia
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Fibrin can protect the body from blood loss. When a blood vessel is injured, a series of chemical reactions occur that lead to the formation of a fibrin clot, which helps to stop the bleeding. Fibrin is a protein that forms a mesh-like network of fibers that trap blood cells and platelets to form a clot. This process is essential for stopping bleeding and preventing blood loss in the event of an injury.
What is a characteristic of antigens?
A. They recognize foreign substances
B. They are produced in bone marrow
C. They cause disease in humans
D. They stimulate the production of antibodies
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
A characteristic of antigens is that they recognize foreign substances. Antigens are molecules that are capable of inducing an immune response in the body, and they do this by recognizing and binding to specific antibodies or immune cells. This recognition is based on the unique molecular structure of the antigen, which is different from that of the body’s own cells. When an antigen binds to an antibody or immune cell, it triggers the immune response and leads to the production of more antibodies or immune cells to fight off the antigen.
Which of the following statements about antibodies is correct?
A. Antibodies are polypeptides.
B. Antibodies are produced by the bone marrow.
C. Antibodies are pathogenic foreign substances.
D. Antibodies kill bacteria but not viruses.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Antibodies are polypeptides. Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are proteins that are produced by B cells in response to the presence of antigens. The antibodies recognize and bind to specific antigens, leading to their elimination from the body. Antibodies are important components of the immune system and play a key role in protecting the body from infection and disease.
Question
Despite continuous scientific research into the control of pathogens, it has proved very difficult to eliminate them. What is/are the reason(s) for this?
I. Development of antibiotic resistance in viruses
II. Development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria
III. Mutations of pathogens
A. II only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
The reasons for the difficulty in eliminating pathogens are II and III only. Development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria and mutations of pathogens are two of the main reasons why it has proved difficult to eliminate pathogens despite continuous scientific research into their control. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria develop the ability to resist the effects of antibiotics, making it more difficult to treat infections. Mutations of pathogens can lead to the development of new strains that are more virulent or resistant to treatment. These factors contribute to the ability of pathogens to persist and spread, making it difficult to control and eliminate them.
