Question
Explain the role of cells in the defence against infectious disease.[7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
a.cells of skin provide a physical barrier/produce fatty acids/lactic acid/lysozyme which stops entry of microbes
OR
mucous membranes produce mucus to trap pathogens
OR
stomach cells produce hydrochloric acid which kills microbes;
b.platelets start the clotting process preventing access of pathogens;
c.(two types of) white blood cells fight infections in the body;
d.phagocytes ingest pathogens (by endocytosis/phagocytosis);
e.gives non-specific immunity to diseases / ingest any type of pathogen;
f.production of antibodies by lymphocytes/B cells;
g.in response to particular pathogens/antigens;
h.gives specific immunity;
i.lymphocyte/B cell makes only one type of antibody;
j.plasma cells produce large quantity of (one type of) antibody;
k.some lymphocytes act/remain as memory cells;
l.can quickly reproduce to form a clone of plasma cells if a pathogen carrying a specific antigen is re-encountered;
m.results in faster defence against second exposure to specific antigen/pathogen/disease;
Question
The figure shows a transmission electron micrograph of rotavirus particles. Each rotavirus is about 70 nanometres in diameter.
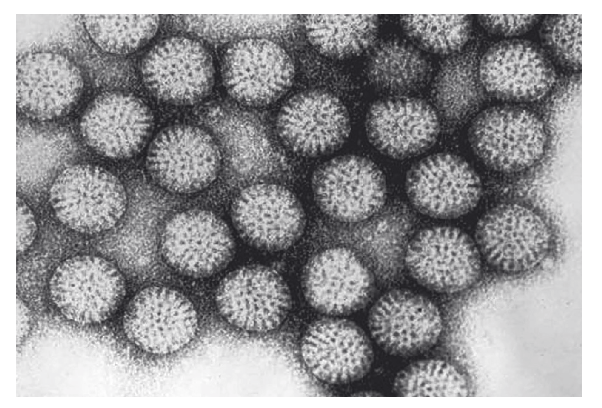
[Source: CDC / Dr. Erskine L. Palmer]
State a reason for using an electron microscope to view this virus rather than a light microscope.
Rotavirus causes diarrhea and vomiting. Explain why viral diseases cannot be treated using antibiotics.
State an application of plasmids in biotechnology.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
electron microscope has greater resolution/magnification
OR
70 nm is too small/viruses are too small to be viewed by a light microscope
a. viruses are not living
b. viruses lack metabolism/lack enzymes «for metabolism»/lack cell walls
c. antibiotics target metabolic «pathways»/cell wall production
[Max 2 Marks]
transfer/vector of genetic material/genes/DNA fragments
OR
to produce insulin/useful protein
Question
Define pathogen.
Explain antibody production.
Explain why antibiotics are effective against bacterial diseases but not against viral diseases.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Organism (or virus) that causes a disease.
a. many types of lymphocytes (B and T) exist;
b. produced/ stored in the lymph nodes;
c. each type recognizes one specific antigen/pathogen;
d. each type responds by dividing to form a clone;
e. (a clone) (B) lymphocyte secretes (specific) antibody against the antigen;
f. antibodies are produced as part of a specific immune response;
g. some reference to plasma/memory cells;
a. antibiotics block metabolic pathways of bacteria / reference to a specific pathway;
b. viruses have no metabolic pathways / viruses reproduce using the host cell’s metabolic pathways;
c. (host cell’s) metabolic pathways are not affected by antibiotics / (antibiotics) do not affect host cells because they are metabolically different from bacteria;
Question
Draw a labelled diagram of a prokaryotic cell.
Bacteria are prokaryotes that sometimes act as pathogens. Describe how the body can defend itself against pathogens.
Explain the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. cell wall – uniformly thick and drawn outside the plasma membrane;
b. plasma membrane – a continuous single line;
c. cytoplasm/cytosol;
d. nucleoid/(naked) DNA – shown as a tangle of thread or irregular shape without a nuclear membrane;
e. (70S) ribosomes – drawn as a small circle or dark dot;
f. pili – hair like structures / flagellum – shown to be longer than any pili;
g. plasmid – circular ring of DNA;
h. capsule – drawn outside the cell wall;
Award [1] for each structure clearly drawn and labelled which conforms to the italicized guidelines given above.
Remember, up to TWO “quality of construction” marks per essay.
a. skin/mucus membranes act as barrier (to pathogens);
b. sebaceous glands secrete lactic acid/fatty acids/sebum / make surface of skin acidic;
c. (skin/stomach) acid prevents growth of many pathogens;
d. lysozyme in mucus can kill bacteria;
e. pathogens caught in sticky mucus and removed from body;
f. inflammatory response/inflammation can cause swelling/redness/fever (to inhibit the pathogen);
g. phagocytes/macrophages/leucocytes/white blood cells (non-specifically) identify (pathogens/bacteria/fungi/viruses) as foreign;
h. (phagocytes macrophages/leucocytes/white blood cells) ingest pathogens;
i. specific lymphocytes recognize one specific antigen;
j. (antigen-specific) lymphocytes clone themselves;
k. lymphocytes/leucocytes produce antibodies;
l. antigen-antibody complex formed and stimulates destruction of pathogen;
a. antibiotics (are chemicals) used to treat bacterial diseases;
b. within populations, bacteria vary in their (genetic) resistance to antibiotics/fitness;
c. resistance arises by (random) gene mutation;
d. when antibiotics are used antibiotic-sensitive bacteria are killed;
e. (natural) selection favours those with resistance;
f. resistant bacteria survive, reproduce and spread the gene / increase allele frequency of resistant bacteria;
g. the more an antibiotic is used, the more bacterial resistance/the larger the population of antibiotic-resistant bacteria;
h. genes can be transferred to other bacteria by plasmids;
i. doctors/vets use different antibiotics but resistance develops to these as well;
j. multiple-antibiotic resistant bacteria evolve/it becomes difficult to treat some infections;
(Plus up to [2] for quality)
Question
The diagrams show a virus and a bacterium.
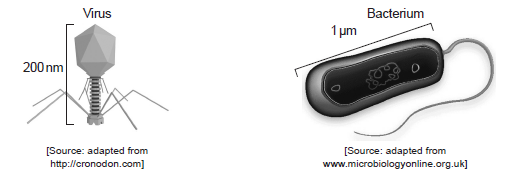
Calculate the magnification of the bacterium.
State the method that bacteria use to divide.
Outline the effectiveness of antibiotics against viruses and bacteria.
Saprotrophic organisms, such as Mucor species, are abundant in soils.
Define saprotrophic organisms.
State one role of saprotrophic organisms in the ecosystem.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
45 000(x) or (x)45000 (accept answers in the range of 44000 to 46 000)
binary fission
effective against bacteria, but not viruses
an organism that secretes enzymes in dead organic matter and absorbs its nutrients/products of digestion
decomposer / recycle nutrients / break down organic material into inorganic material
Do not just accept “recycle” alone.
