IB Biology SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction
Topic 6 Weightage : 23%
All Questions for Topic 6.6 – Insulin and Glucagon, Thyroxin, Leptin, Melatonin, Sexual Reproduction, Sex Development, Male Reproductive System, Female Reproductive System, Menstrual Cycle, In Vitro Fertilisation, Homeostasis, Feedback Loops, Endocrine System, Types of Hormones, Gender Issues, Menstrual Events
Question
The graph shows the blood levels of hormones associated with the menstrual cycle.
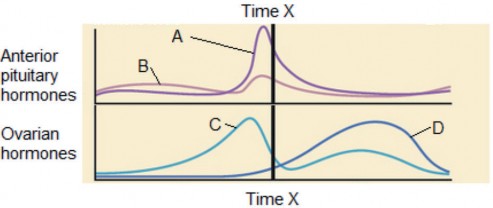
Which line on the graph represents progesterone?
A Line A
B Line B
C Line C
D Line D
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Progesterone is an ovarian hormone. The Luteal phase of the Ovulation Cycle lasts approximately 14 days. In this phase, the dominant hormone of the Follicular Phase estrogen declines and progesterone levels increase. Progesterone levels fluctuate throughout your menstrual cycle. Levels rise after ovulation and continue to rise if pregnancy occurs. In the graph line D is representing Progesterone hormone levels.
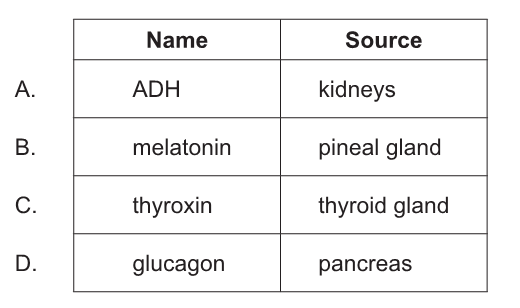
What is the name and source of the hormone that regulates basal metabolic rate?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
The hormone that regulates basal metabolic rate is called thyroid hormone, which is produced by the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck that produces and secretes hormones that regulate metabolism. Thyroid hormone plays a key role in regulating the body’s metabolic rate, which is the rate at which the body burns calories to produce energy. When thyroid hormone levels are low, the body’s metabolic rate slows down, which can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance.
Which hormone inhibits appetite?
A. Epinephrine
B. Leptin
C. Thyroxin
D. Glucagon
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
The hormone that inhibits appetite is called leptin. Leptin is produced by fat cells and acts on the hypothalamus in the brain to regulate appetite and energy balance. When leptin levels are high, it signals to the brain that there is enough energy stored in fat cells and that the body does not need to eat more. This helps to regulate food intake and prevent overeating. However, in some cases, leptin resistance can occur, which can lead to increased appetite and weight gain.
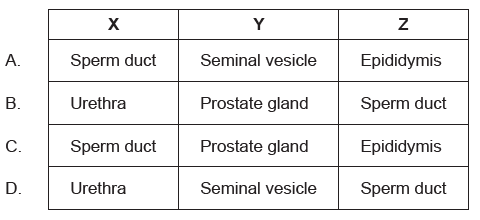
The diagram shows the male reproductive organs in front view.
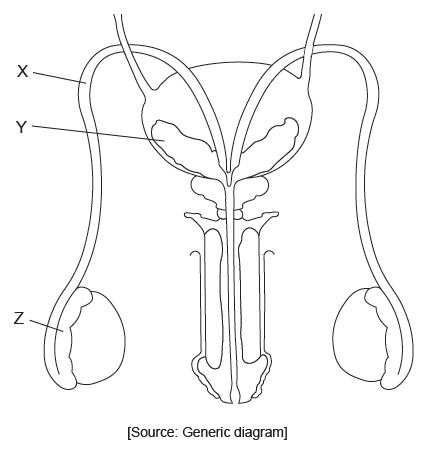
Which structures are indicated by the letters X, Y and Z?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
The male reproductive system contains the external genitals (the penis, testes and the scrotum) and internal parts, including the epididymis, vas deferens, prostate, and seminal vesicles.
In this given diagram, X represents sperm duct or vas deferens, Y represents seminal vesicle and Z represents epididymis.
What happens when human body temperature rises during exercise?
A. The arterioles move closer to the skin.
B. The hypothalamus decreases cell respiration.
C. The skin capillaries close up.
D. The water from sweat evaporates to cool the body.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
When the human body temperature rises during exercise, the water from sweat evaporates to cool the body. This is option D. Sweating is a natural process that helps to regulate body temperature by releasing heat from the body through evaporation. As sweat evaporates from the skin’s surface, it cools the body down, helping to prevent overheating. The hypothalamus plays a key role in regulating body temperature by triggering sweating and other cooling mechanisms in response to changes in temperature. The arterioles move closer to the skin to release heat, and the skin capillaries open up to allow more blood flow to the skin’s surface, which helps to release heat.
Question
The graph shows human body temperature variation in a daily rhythm of 24 hours.
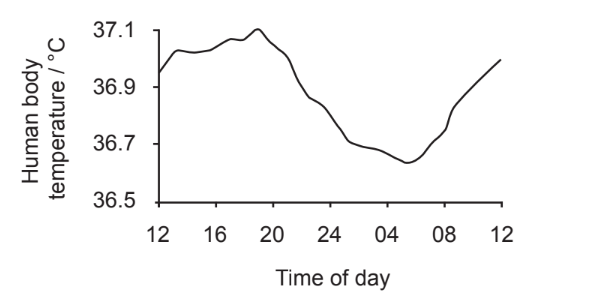
Which hormone controls this variation?
A. Leptin
B. Insulin
C. Glucagon
D. Thyroxin
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Circadian rhythms are physical, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle. These natural processes respond primarily to light and dark and affect most living things, including animals, plants, and microbes. Body temperature varies throughout the day and is lowest in the morning and highest in the afternoon. Human body has a complex thermoregulation mechanism to help keep its temperature within the normal ranges. The thyroid produces hormones that are able to influence how much the blood vessels dilate. In turn, this affects how much heat can escape out the body. This helps to regulate the body temperature.
Question
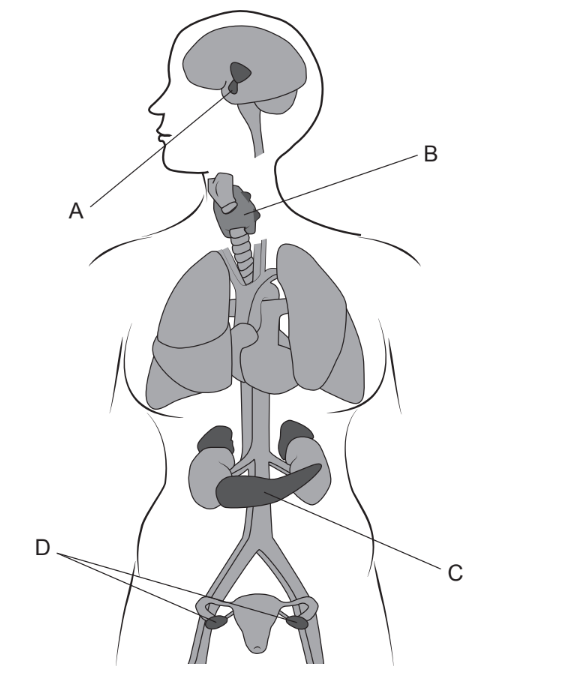
The diagram shows organs that produce hormones in a female human. Which organ is the source of the hormone used in IVF treatment to produce many ova?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
The hormones used are gonadotropins follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinising hormone (LH). Both FSH and LH are secreted by pituitary gland. A hormone made by a part of the brain called the hypothalamus. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone causes the pituitary gland in the brain to make and secrete the hormones luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Naturally as well as in IVF these two hormones are importent for producing ova.
