IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 7.2 Transcription and gene expression
Topic 7 Weightage : 8%
All Questions for Topic 7.2 – Sections of a Gene, Transcription (HL), Messenger RNA, Gene Expression, Epigenetics, Types of RNA, Operons, RNA Interference, Reverse Transcription, Microarrays
Question
What is a feature of transcription in the single-celled organism shown in the electron micrograph?
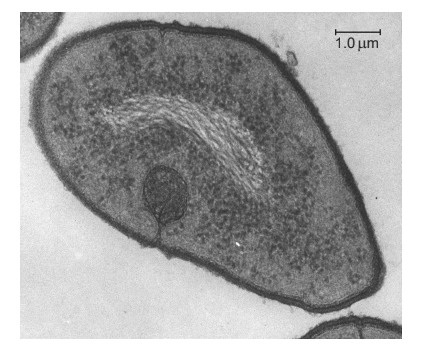
mRNA splicing
Removal of introns
Codon-anticodon binding
Synthesis of RNA in a 5′ to 3′ direction
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Transcription in all organisms involves the synthesis of RNA in a 5′ to 3′ direction. During transcription, RNA polymerase reads the template strand of DNA in a 3′ to 5′ direction and synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule in a 5′ to 3′ direction. This means that the 5′ end of the RNA molecule is synthesized first, followed by the 3′ end. This directionality is important for the correct folding and function of the RNA molecule.
Some regions of DNA do not code for the production of proteins. What are these regions of DNA used as?
A. They have no known function and are recycled to provide nucleotides
B. Gene regulation and coding for production of enzymes used in translation
C. Telomeres and coding for production of tRNA
D. Introns and coding for production of structural proteins
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Some regions of DNA do not code for the production of proteins, but they are still important for the proper functioning of the cell. Telomeres, for example, are repetitive sequences at the ends of chromosomes that protect the genetic material from being lost during replication. tRNA, on the other hand, is a type of RNA molecule that helps to translate the genetic code into proteins. These non-coding regions of DNA are essential for various regulatory functions in the cell.
In which process(es) do nucleosomes play a role in eukaryotes?
I. tRNA activation
II. Transcription regulation
III. DNA supercoiling
A. I only
B. II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and II
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
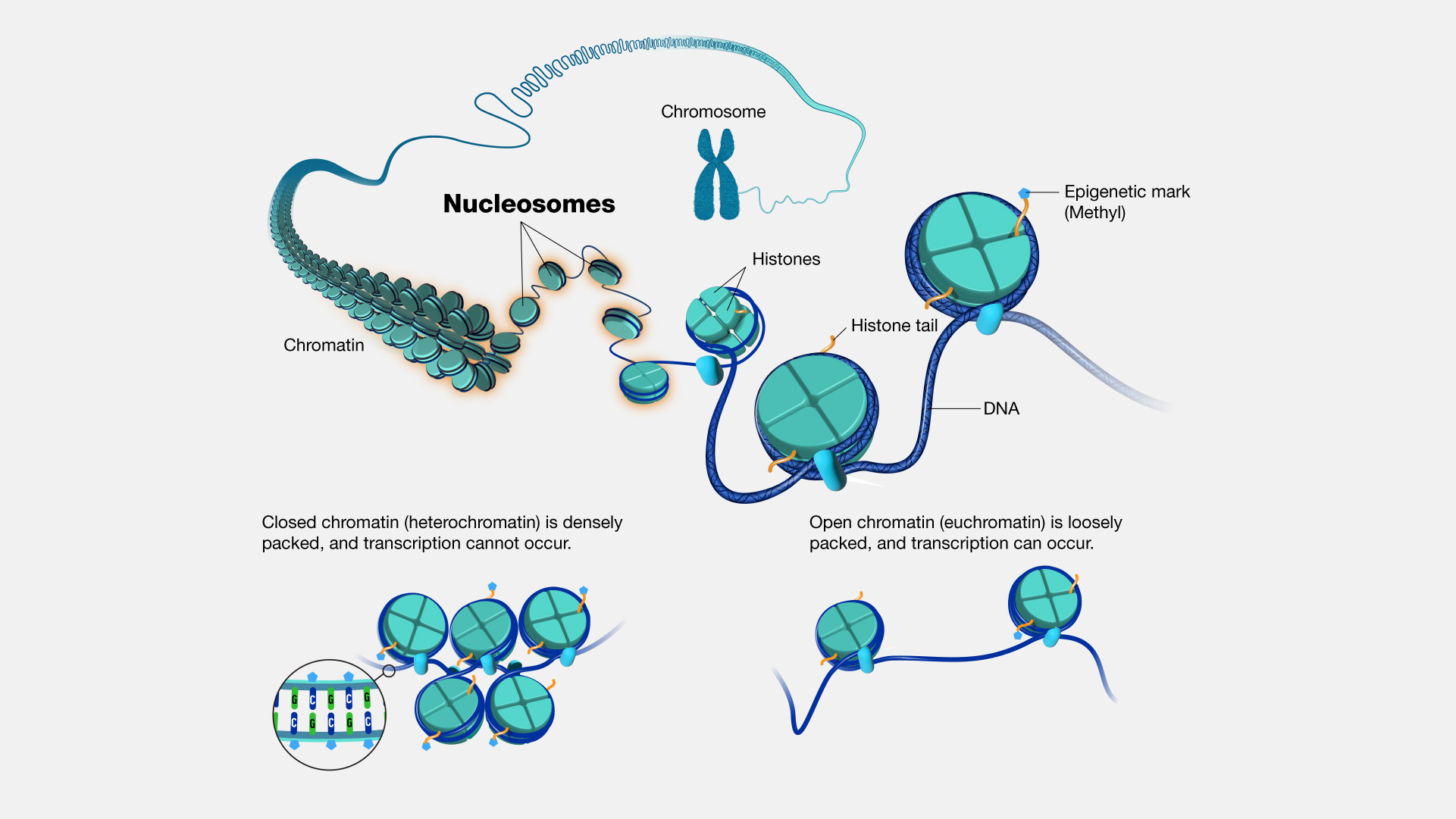
Nucleosomes play a role in transcription regulation and DNA supercoiling in eukaryotes. Therefore, the answer is C. II and III only. Nucleosomes help to regulate gene expression by controlling the accessibility of DNA to transcription factors and RNA polymerase. They also help to package the long DNA molecules into compact chromosomes, which is important for proper cell division. However, nucleosomes are not directly involved in tRNA activation.
Very soon after fertilization, parental epigenetic methylation is reversed in the DNA.
Later, tissue-specific epigenetic modifications are made to the embryonic DNA. The graph follows the degree of methylation from different sources during embryonic development.
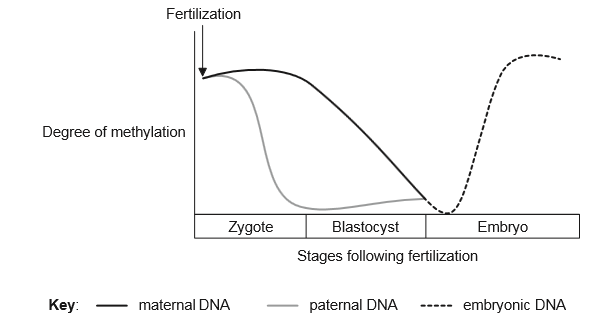
According to the graph, what are the changes in DNA methylation during embryonic development?
A. Only the paternal DNA becomes demethylated.
B. The maternal DNA becomes demethylated first.
C. The methylation patterns of the parents’ DNA are erased before fertilization.
D. The methylation patterns of both parents are erased after fertilization.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
During embryonic development, cells are directed toward their future lineages, and DNA methylation poses a fundamental epigenetic barrier that guides and restricts differentiation and prevents regression into an undifferentiated state.
Shortly after fertilization, the methylation marks inherited from the gametes are erased again (except those at imprinted loci and some retrotransposons), with the paternal genome undergoing active demethylation and the maternal genome undergoing passive demethylation.
In the graph, we can illustration that the methylation patterns of both parents are erased after fertilization.
Thus, the correct option is B.
The antisense strand of a DNA molecule has the sequence TACCCGATC. What would be the resulting mRNA strand sequence?
A. TACCCGATC
B. ATGGGCTAG
C. UACCCGAUC
D. AUGGGCUAG
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
The antisense strand of DNA is complementary to the mRNA sequence, so to determine the mRNA sequence, we need to transcribe the DNA sequence by replacing T with U. Therefore, the resulting mRNA strand sequence would be AUGGGCUAG. So, the answer is D.
Question
The diagram shows a ribosome and associated mRNA.
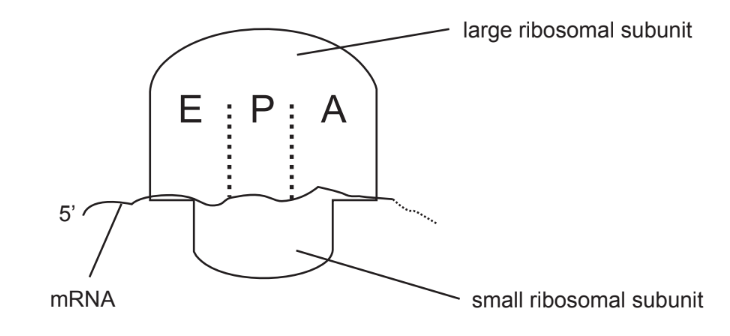
Which of these events occurs first in translation?
A. Small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA.
B. Large ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA.
C. Initiator tRNA enters $\mathrm{E}$ site.
D. Initiator tRNA enters A site.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
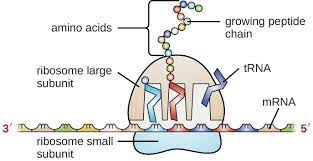
In translation, the first event that occurs is the binding of the small ribosomal subunit to the mRNA molecule. This process is mediated by the ribosome binding site (also known as the Shine-Dalgarno sequence) on the mRNA and the complementary sequence on the ribosomal RNA. Once the small subunit is bound to the mRNA, the initiator tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine can bind to the start codon (AUG) on the mRNA. The large ribosomal subunit then joins the complex, forming the complete ribosome. The ribosome then proceeds to elongate the polypeptide chain by reading the codons on the mRNA and adding the corresponding amino acids.
