IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 8.3 Photosynthesis
Topic 8 Weightage : 13%
All Questions for Topic 8.3 – Photosynthesis, Light Dependent Reactions, Photophosphorylation, Light Independent Reactions, Calvin Cycle, Chloroplast, Photosynthesis vs Respiration, Accessory Pigments, C3, C4 and CAM Plants, Global Artificial Photosynthesis Project (GAP project)
Question
A summary diagram of photosynthesis is shown. Which molecule represents ATP?
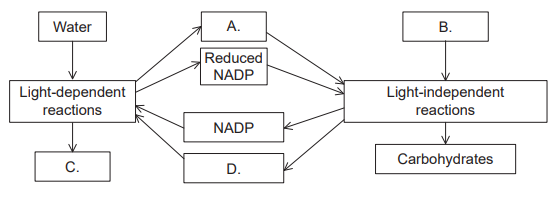
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The molecule that represents ATP in the diagram is labeled “A”. ATP is a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, and it is produced during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. During this process, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and used to generate a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane. This gradient drives the synthesis of ATP by ATP synthase. The ATP molecule is then used to provide energy for the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis, which produce glucose and other organic compounds. Therefore, the molecule labeled “A” in the diagram represents ATP, which is used to provide energy for photosynthesis.
Question
Which process does not take place in the stroma of chloroplasts?
A Synthesis of carbohydrates
B Fixation of carbon
C Reduction of NADP
D Synthesis of ribulose bisphosphate
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The process that does not take place in the stroma of chloroplasts is C) Reduction of NADP.
The reduction of NADP occurs in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts, specifically in the thylakoid lumen. During this process, NADP+ is reduced to NADPH, which is an energy-rich molecule that is used in the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis.
On the other hand, the other processes mentioned in the options (A, B, and D) all take place in the stroma of chloroplasts.
A) Synthesis of carbohydrates: This process occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts, where carbon dioxide is fixed and converted into glucose and other organic compounds.
B) Fixation of carbon: This process also occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts, where carbon dioxide is fixed and converted into organic compounds.
D) Synthesis of ribulose bisphosphate: This process is part of the Calvin cycle, which occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts.
Which process occurs during the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis?
A. ATP, CO2 and H2O are produced.
B. CO2 is used to produce carbohydrates.
C. ATP and O2 are produced.
D. RuBP is phosphorylated.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
The process that occurs during the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis is C) ATP and O2 are produced.
During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and used to generate a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane. This gradient drives the synthesis of ATP by ATP synthase. In addition to ATP, O2 is also produced during the light-dependent reactions as a byproduct of the splitting of water molecules.
On the other hand, the other processes mentioned in the options (A, B, and D) do not occur during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
A) ATP, CO2, and H2O are produced: ATP and H2O are produced during the light-dependent reactions, but CO2 is not produced during this process.
B) CO2 is used to produce carbohydrates: This process occurs during the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis, also known as the Calvin cycle.
D) RuBP is phosphorylated: This process is part of the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis, where RuBP is phosphorylated to produce PGA as part of the carbon fixation process.
Which reaction does not cause a net release of energy?
A. ADP combines with inorganic phosphate to form ATP
B. ATP releases inorganic phosphate to form ADP
C. Loss of hydrogen from reduced NAD
D. Oxidation of reduced FAD
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
The reaction that does not cause a net release of energy is A) ADP combines with inorganic phosphate to form ATP.
The process of ADP combining with inorganic phosphate to form ATP is an endergonic reaction, meaning it requires energy input to occur. In contrast, the other processes mentioned in the options (B, C, and D) all cause a net release of energy.
B) ATP releases inorganic phosphate to form ADP: This process releases energy that can be used by the cell to drive other reactions.
C) Loss of hydrogen from reduced NAD: This process releases energy in the form of electrons, which can be used by the cell to generate ATP.
D) Oxidation of reduced FAD: This process releases energy in the form of electrons, which can be used by the cell to generate ATP.
What is used to reduce NADP in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
A. Conversion of ATP into ADP+Pi
B. Electrons from Photosystem I
C. Protons from the thylakoid space
D. Oxygen released by photolysis of water
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
B) Electrons from Photosystem I.
During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and used to generate a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane. This gradient drives the synthesis of ATP by ATP synthase. In addition to ATP, NADP is reduced to NADPH during the light-dependent reactions. The electrons that reduce NADP come from Photosystem I, which receives electrons from the electron transport chain.
On the other hand, the other processes mentioned in the options (A, C, and D) are not involved in the reduction of NADP during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
A) Conversion of ATP into ADP+Pi: This process is involved in the synthesis of ATP during the light-dependent reactions, but it does not directly reduce NADP.
C) Protons from the thylakoid space: Protons from the thylakoid space are involved in the synthesis of ATP during the light-dependent reactions, but they do not directly reduce NADP.
D) Oxygen released by photolysis of water: Oxygen is produced as a byproduct of the light-dependent reactions, but it does not directly reduce NADP.
Which technological advance enabled Calvin to perform his lollipop experiment on the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis in 1949?
A. Methods for tracing radioactive carbon incorporated in molecules produced by the alga Chlorella
B. Development of electron microscopes enabling the molecules produced by the alga Scenedesmus to be viewed
C. Methods for changing the wavelength of light shining on the alga Scenedesmus contained in the lollipop
D. Development of X-ray diffraction techniques enabling the molecules produced by the alga Chlorella to be identified
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
The technological advance that enabled Calvin to perform his lollipop experiment on the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis in 1949 was A) Methods for tracing radioactive carbon incorporated in molecules produced by the alga Chlorella.
The lollipop experiment was a series of experiments conducted by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues in the late 1940s, which helped to elucidate the chemical pathway of the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis, also known as the Calvin cycle. The experiment involved exposing the green alga Chlorella to carbon dioxide labeled with a radioactive isotope of carbon, and then tracing the fate of the labeled carbon as it was incorporated into various organic molecules in the alga. The use of radioactive carbon isotopes allowed the researchers to track the movement of carbon atoms through the Calvin cycle and determine the sequence of chemical reactions involved.
The electron micrograph shows part of a plant cell. Where do the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis take place?
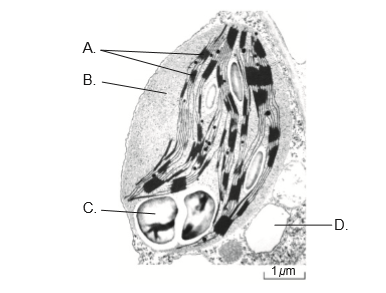
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
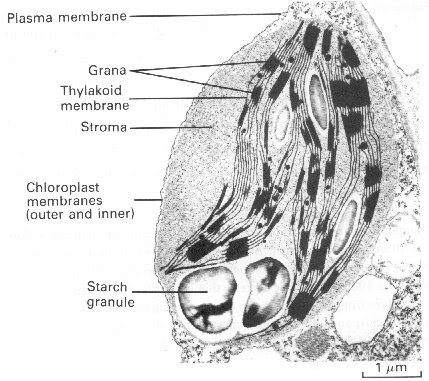
The light-independent reactions of photosynthesis, also known as the Calvin cycle, take place in the stroma of the chloroplasts of a plant cell. The stroma is the fluid-filled space that surrounds the thylakoid membranes, where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place. Therefore, the light-independent reactions do not occur in the thylakoid membranes themselves, but in the fluid-filled stroma that surrounds them.
Question
What occurs in the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis?
A. Glycerate 3-phosphate is reduced to triose phosphate.
B. Ribulose bisphosphate is regenerated using reduced NADP.
C. Ribulose bisphosphate is oxidized to two molecules of glycerate 3-phosphate.
D. Both ATP and NADP are used to produce triose phosphate.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
In the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis, also known as the Calvin cycle, ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) is regenerated using ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. The correct option is B) Ribulose bisphosphate is regenerated using reduced NADP.
During the Calvin cycle, CO2 is fixed into organic molecules, such as glucose, using the energy from ATP and NADPH. The process begins with the enzyme Rubisco catalyzing the reaction between CO2 and RuBP to produce two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA). These molecules are then reduced to form glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) using energy from ATP and NADPH. One G3P molecule can be used to produce glucose, while the other molecules are recycled to regenerate RuBP.
Therefore, options A, C, and D are incorrect as they do not accurately describe the processes that occur in the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis.
