IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 9.3 Growth in plants
Topic 9 Weightage : 8%
All Questions for Topic 9.3 – Meristems, Apical Growth, Auxin, Tropisms, Micropropagation, Lateral Growth, Plant Hormones
Question
Expansin is a plant protein that loosens connections between cellulose fibres in plant cell walls, allowing growth. In what location would expression of the expansin gene be expected to be increased?
A On the shaded side of a shoot being exposed to light
B On the light side of a shoot being exposed to light
C On the shaded side of a leaf that is transpiring rapidly
D On the light side of a leaf that is transpiring rapidly
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The correct, the answer should be A. The expression of the expansin gene would be expected to be increased on the shaded side of a shoot being exposed to light. When a shoot is exposed to light, the cells on the shaded side undergo more rapid growth than the cells on the light side, which causes the shoot to bend towards the light source. Expansin protein is produced in response to this bending and causes the loosening of connections between cellulose fibers in the cell walls, allowing the cells to elongate and the shoot to grow towards the light source. Therefore, the location where the expression of the expansin gene would be expected to be increased is on the shaded side of the shoot being exposed to light.
What is/are the effect(s) of auxin in plants?
I. Increasing the rate of cell elongation in stems
II. Changing the pattern of gene expression in shoot cells
III. Detecting the direction of light
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
The correct, the answer should be B. The effects of auxin in plants include increasing the rate of cell elongation in stems and changing the pattern of gene expression in shoot cells. Auxin does not directly detect the direction of light, but it can indirectly influence the direction of growth in response to light by promoting cell elongation on the shaded side of the stem or shoot. Therefore, the correct answer is B, I and II only.
What allows most plants to continue producing more roots, leaves or stems throughout their life?
A. Auxin
B. Meristems
C. Phloem
D. Cellulose
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
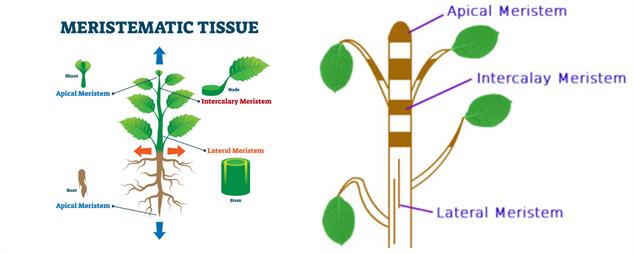
The answer is B. Meristems. Meristems are regions of the plant that contain undifferentiated cells that can divide and differentiate into various types of cells, which can give rise to new tissues and organs. Meristems are responsible for the growth of roots, leaves, and stems, which allows most plants to continue producing more of these structures throughout their life. Auxin is a hormone that regulates the growth and development of plants, but it does not allow most plants to continue producing more roots, leaves or stems throughout their life. Phloem is a tissue that transports organic compounds in plants, and cellulose is a structural polysaccharide that forms the cell walls of plants.
How do auxins cause plant shoots to grow towards light?
A. Increase cell division on the side of the stem near the light source
B. Increase cell division on the side of the stem away from the light source
C. Increase cell elongation on the side of the stem near the light source
D. Increase cell elongation on the side of the stem away from the light source
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
The correct answer is B. Increase cell division on the side of the stem away from the light source. When a plant is exposed to light, auxins move to the shaded side of the stem, where they promote the growth of cells, which causes the cells to elongate and the stem to bend towards the light source. This is known as phototropism. Auxins also inhibit cell growth on the side of the stem that is exposed to light, which causes the stem to bend away from the light source. Therefore, auxins cause plant shoots to grow towards light by increasing cell division on the side of the stem away from the light source.
A man attaches a bird box to the trunk of a dicotyledonous tree. A few years later he returns to the tree and finds that his bird box is still attached and the tree is much taller. How high will his bird box be from the ground?
A. Unchanged as growth from the apical meristem would be above the box.
B. Unchanged as growth from the lateral meristem would be above the box.
C. Higher as growth from the apical meristem would be below the box.
D. Higher as growth from the lateral meristem would be below the box.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
The answer is A. Unchanged as growth from the apical meristem would be above the box. The apical meristem is a region of undifferentiated cells at the tip of the stem of a plant that is responsible for the primary growth of the plant. The apical meristem is responsible for the growth of the stem and the branches, which would occur above the bird box. Therefore, the bird box will remain at the same height from the ground, as the growth from the apical meristem would be above the box. The lateral meristem, on the other hand, is responsible for the secondary growth of the plant, which would not affect the height of the bird box.
