IBDP Chemistry Reactivity 2.1 How much? The amount of chemical change HL Paper 2- Exam Style Questions - New Syllabus
Question
Most-appropriate topic codes (IB Chemistry 2025):
• Reactivity 3.1: Proton transfer reactions — parts (a), (b)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
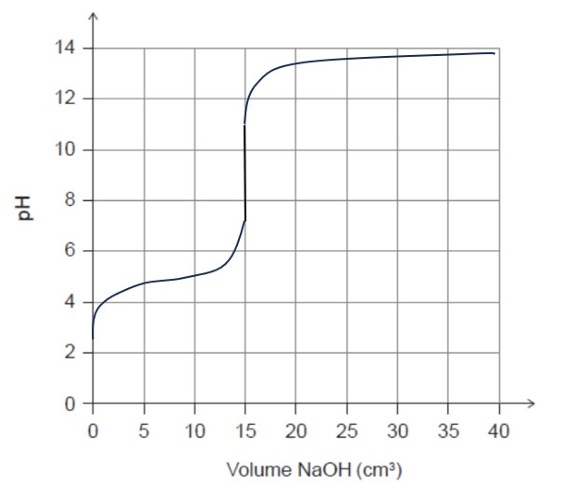
The titration of a weak acid with a strong base produces a curve that shows:
• An initial acidic pH value (approximately \(2\)–\(4\))
• A buffer region with a gradual increase in pH
• An equivalence point above pH \(7\), typically between \(8\) and \(10\), due to the formation of acetate ions
• The equivalence point occurring after \(15.0\ \text{cm}^3\) of \( \text{NaOH(aq)} \) is added
• A sharp rise in pH near the equivalence point
• A final pH approaching \(12\)–\(13\) with excess base
\( \boxed{\text{Weak acid–strong base titration with equivalence point above pH }7} \)
(b)(i)
The most effective buffer is formed when comparable amounts of ethanoic acid and its conjugate base are present.
This is achieved by partially neutralizing \( \text{CH}_3\text{COOH(aq)} \) with \( \text{NaOH(aq)} \) so that the concentrations of \( \text{CH}_3\text{COOH} \) and \( \text{CH}_3\text{COO}^- \) are approximately equal.
\( \boxed{\text{Maximum buffer capacity occurs when } [\text{CH}_3\text{COOH}] \approx [\text{CH}_3\text{COO}^-]} \)
(b)(ii)
Addition of a strong acid:
\( \text{CH}_3\text{COO}^- + \text{H}^+ \rightarrow \text{CH}_3\text{COOH} \)
Addition of a strong base:
\( \text{CH}_3\text{COOH} + \text{OH}^- \rightarrow \text{CH}_3\text{COO}^- + \text{H}_2\text{O} \)
\( \boxed{\text{The buffer minimizes pH change by consuming added } \text{H}^+ \text{ or } \text{OH}^-} \)