IB DP Chemistry -Reactivity 2.2 How fast? The rate of chemical change - IB Style Questions For HL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
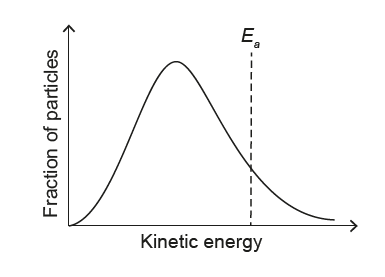
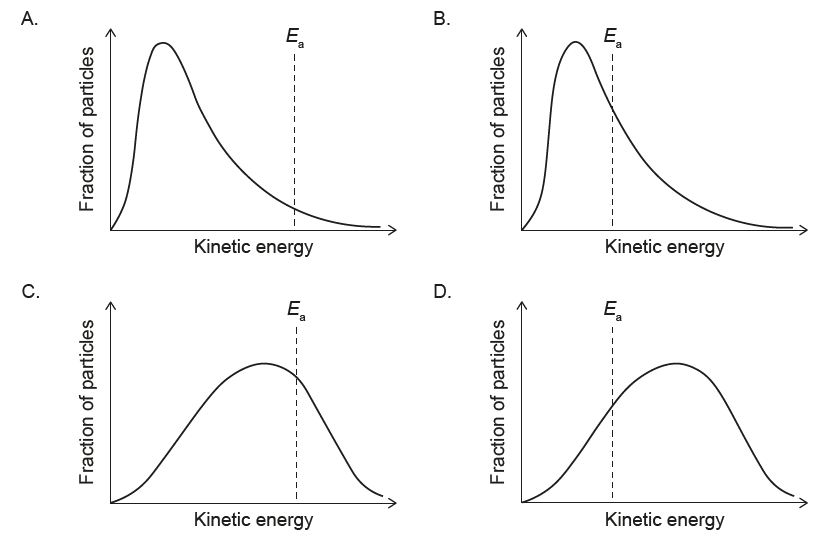
▶️ Answer/Explanation
At lower T:
• Peak shifts to lower energy (left)
• Peak becomes higher and narrower
• Activation energy Ea is independent of T
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
\[ KE = \frac{1}{2}mv^2 \]
(B) decreases by a factor of \(2\)
(C) increases by a factor of \(4\)
(D) decreases by a factor of \(4\)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Markscheme: A
According to kinetic theory, the average kinetic energy of gas particles is directly proportional to the absolute temperature:
\[ KE = \frac{3}{2}kT \]
where:
\(KE\) = average kinetic energy
\(k\) = Boltzmann constant
\(T\) = absolute temperature
If the absolute temperature increases from \(T\) to \(2T\), then:
\[ KE_2 = \frac{3}{2}k(2T) = 2 \left( \frac{3}{2}kT \right) = 2KE_1 \]
So, when the absolute temperature is doubled, the average kinetic energy also doubles.
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
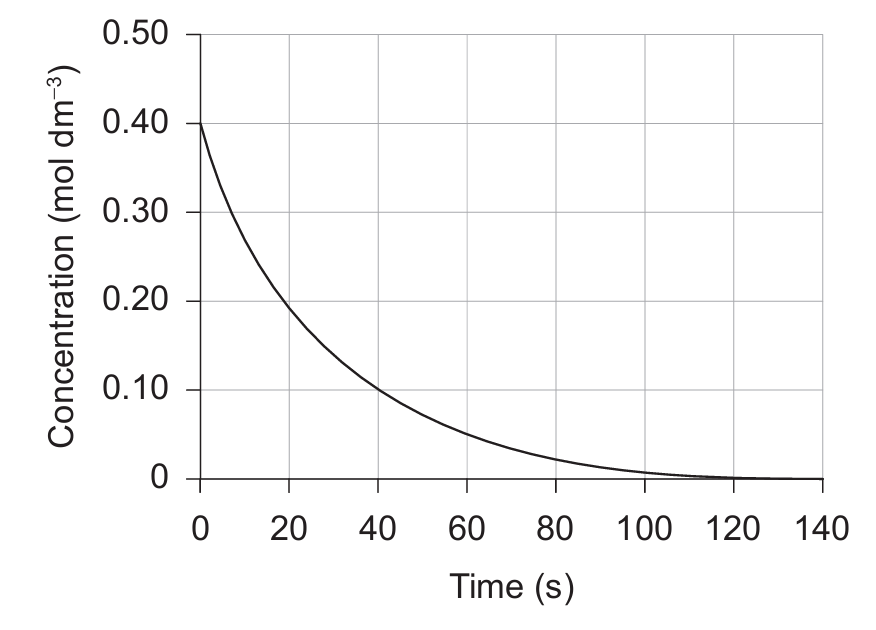
(B) \( \dfrac{0.40 – 0.10}{40 – 0} \)
(C) \( \dfrac{0.40 – 0}{140 – 0} \)
(D) \( \dfrac{0.40 – 0.20}{10 – 0} \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Markscheme: (D)
The rate of reaction can be found using:
\[ \text{rate} = -\frac{\Delta[\text{reactant}]}{\Delta t} \quad \text{or} \quad \text{rate} = \frac{\Delta[\text{product}]}{\Delta t} \]
For the initial rate, we draw a tangent to the graph at \(t = 0\).

From the tangent, the slope can be approximated by:
\[ \frac{0.40 – 0.20}{10 – 0} \quad \text{or} \quad \frac{0.40 – 0.00}{20 – 0} \]
Both expressions simplify to the same initial rate. The closest matching option is:
✅ Answer: (D)
