IB DP Chemistry - Reactivity 3.3 Electron sharing reactions - IB Style Questions For HL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
Which option correctly represents heterolytic bond fission?
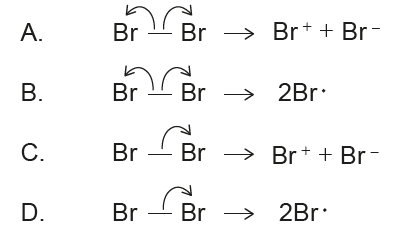
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Detailed solution
Heterolytic fission breaks a covalent bond unevenly, producing a positive and a negative ion.
For Br–Br: \( \text{Br–Br} \rightarrow \text{Br}^+ + \text{Br}^- \).
✅ Answer: (C) .
Question
Which statements about the chlorine free radical are correct?
I. It has 18 electrons.
II. It is an uncharged species.
III. It is formed by homolytic fission.
II. It is an uncharged species.
III. It is formed by homolytic fission.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Detailed solution
Chlorine free radical: \( \text{Cl}\cdot \)
- Statement I: A chlorine atom has 17 electrons, not 18 — so this is false.
- Statement II: A free radical is neutral (uncharged), so this is true.
- Statement III: Chlorine radicals form when \( \text{Cl}_2 \) undergoes homolytic fission, so this is true.
Therefore, only statements II and III are correct.
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
Which of these reactions proceeds by a free radical mechanism in the presence of UV light?
A. \( \text{C}_6\text{H}_6 + \text{Cl}_2 \rightarrow \text{C}_6\text{H}_5\text{Cl} + \text{HCl} \)
B. \( \text{C}_6\text{H}_6 + 3\text{H}_2 \rightarrow \text{C}_6\text{H}_{12} \)
C. \( \text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2 + \text{HBr} \rightarrow \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{Br} \)
D. \( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_3 + \text{Cl}_2 \rightarrow \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{Cl} + \text{HCl} \)
B. \( \text{C}_6\text{H}_6 + 3\text{H}_2 \rightarrow \text{C}_6\text{H}_{12} \)
C. \( \text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2 + \text{HBr} \rightarrow \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{Br} \)
D. \( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_3 + \text{Cl}_2 \rightarrow \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{Cl} + \text{HCl} \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Detailed solution
Free radical substitution occurs when alkanes react with halogens in the presence of UV light. UV light causes homolytic fission of the halogen molecule, forming radicals.
- Option A: Substitution on benzene occurs by electrophilic substitution, not radical substitution.
- Option B: This is hydrogenation of benzene, not a radical reaction.
- Option C: This is electrophilic addition of HBr to an alkene, not a radical mechanism.
- Option D: Reaction of ethane with chlorine under UV light is a classic free radical substitution.
Thus, the reaction that proceeds by a free radical mechanism under UV light is:
\(\boxed{\text{CH}_3\text{CH}_3 + \text{Cl}_2 \rightarrow \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{Cl} + \text{HCl}}\)
✅ Answer: (D)
