1.2 The mole concept
Essential Idea:
The mole makes it possible to correlate the number of particles with the mass that can be measured.
Understandings:
- The mole is a fixed number of particles and refers to the amount, n, of substance.
- Masses of atoms are compared on a scale relative to 12C and are expressed as relative atomic mass (Ar) and relative formula/molecular mass (Mr).
- Molar mass (M) has the units g mol-1.
- The empirical formula and molecular formula of a compound give the simplest ratio and the actual number of atoms present in a molecule respectively.
Applications and Skills:
- Calculation of the molar masses of atoms, ions, molecules and formula units.
- Solution of problems involving the relationships between the number of particles, the amount of substance in moles and the mass in grams.
- Interconversion of the percentage composition by mass and the empirical formula.
- Determination of the molecular formula of a compound from its empirical formula and molar mass.
- Obtaining and using experimental data for deriving empirical formulas from reactions involving mass changes.
1.2 The mole concept
- Particles are classified as either: Atoms, ions, molecules or formula units
- To perform chemistry, moles of substance are used, and this allows us to make comparisons between chemical species.
The Mole
- Avogadro’s constant NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1
- Mole: a fixed number of particles and refers to the amount, n, of substance
- Molar mass: mass of 1 mole of a substance (g mol-1)
- Number prefixes which are important to know:
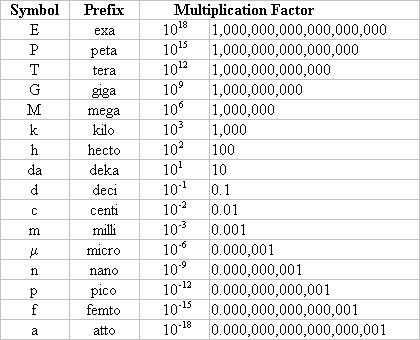
Mole Calculations
Relative atomic mass & molar mass
- Isotopes: Atoms of the same element which have same number of protons
- Isotopes of an element have different mass numbers
- Relative abundance: Measure of percentage of isotopes present in element
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): weighted average of the atomic masses of its isotopes and their relative abundances
- Relative because compared to 1 atom of carbon-12 (12C) which is 12 units
- Relative molecular mass (Mr): Combining individuals Ar values of atoms in molecule or formula unit
Empirical and molecular formula determination
- Empirical formula: simplest whole number ratio of atoms or amount (in mol) of each element present in a compound
- Molecular Formula: the actual number of atoms or amount (in mol) of elements in one structural unit or one mole of the compound
MOLE
It is a unit which represents 6.023 × 1023 particles. The number 6.023 × 1023 is called Avogadro’s number and is represented by N0 or NA. Avogadro’s number of gas molecules occupy a volume of 22400 cm3 at N.T.P. Number of molecules in 1 cm3 of gas at NTP is Loschmidt N0. With value 2.688 × 1019.
ATOMIC MASS
“It is the number of times the atom of the element is heavier than H atom” was the first proposed definition. Later on oxygen was preferred as standard. In 1961 C-12 was chosen as standard and thus “the number of times the atom of an element is heavier than 12th part of C-12 is called atomic mass of the element.
Atomic mass = 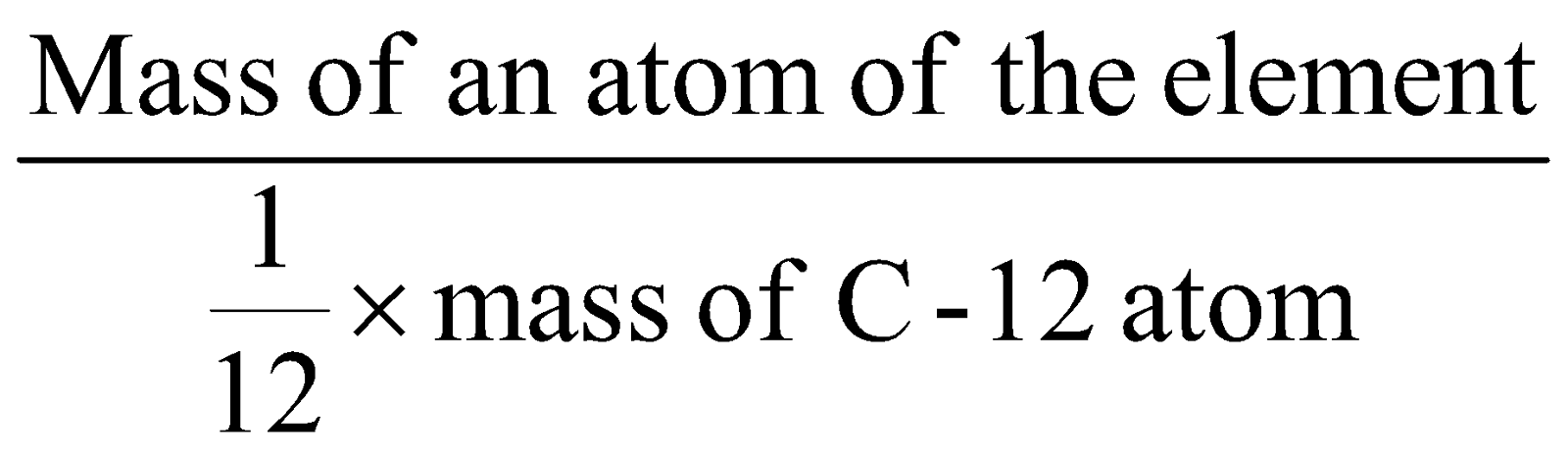
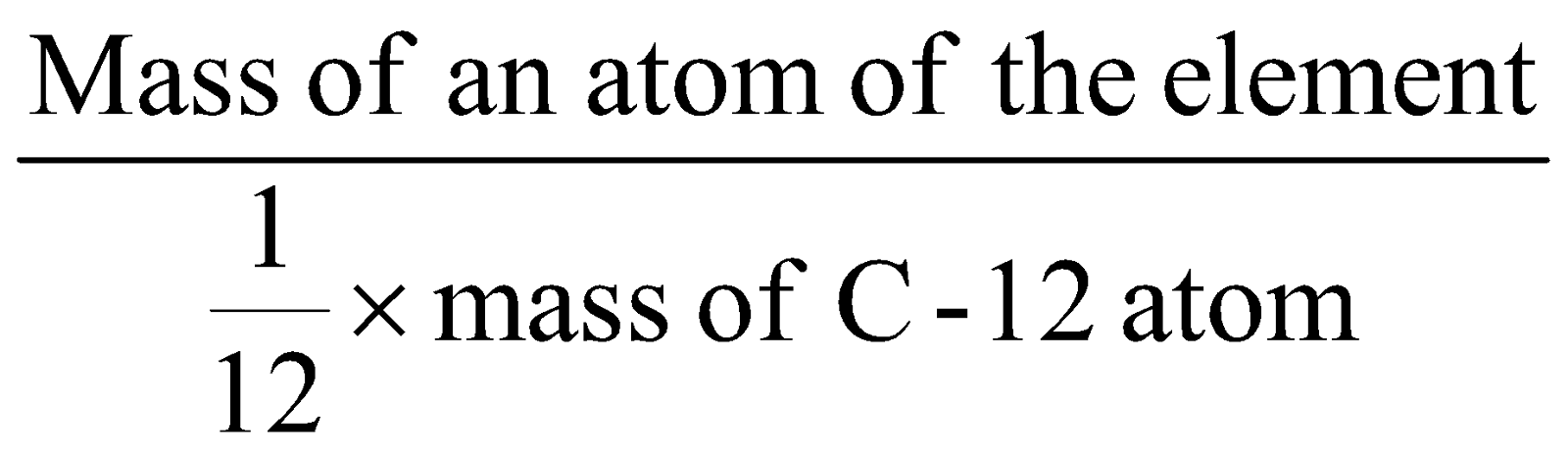
AVERAGE ATOMIC MASS
It is the mass of each isotope determined separately and then combined in ratio of their occurrence. Suppose a and b are two isotopes of an element with their occurence ratio p : q then
Average atomic mass = 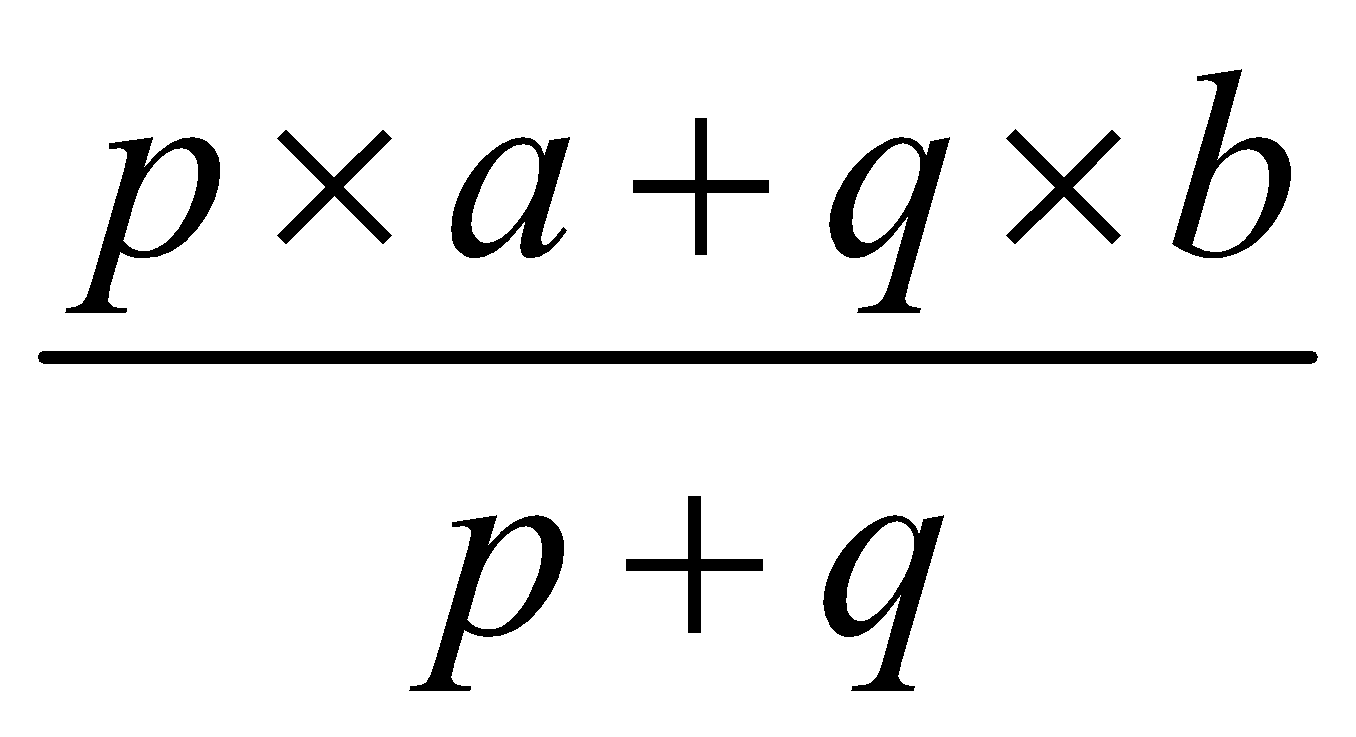
DETERMINATION OF ATOMIC MASS
- Dulong and petit’s rule : It is based on experimental facts. “At ordinary temperature, product of atomic mass and specific heat for solid elements is approximately 6.4 and this product is known as atomic heat of the element”
Atomic mass × specific heat = 6.4
The law is valid for solid elements except Be, B, Si and C.
Correct At. mass = Eq. mass × valency
- Specific heat method : This method is for gases.
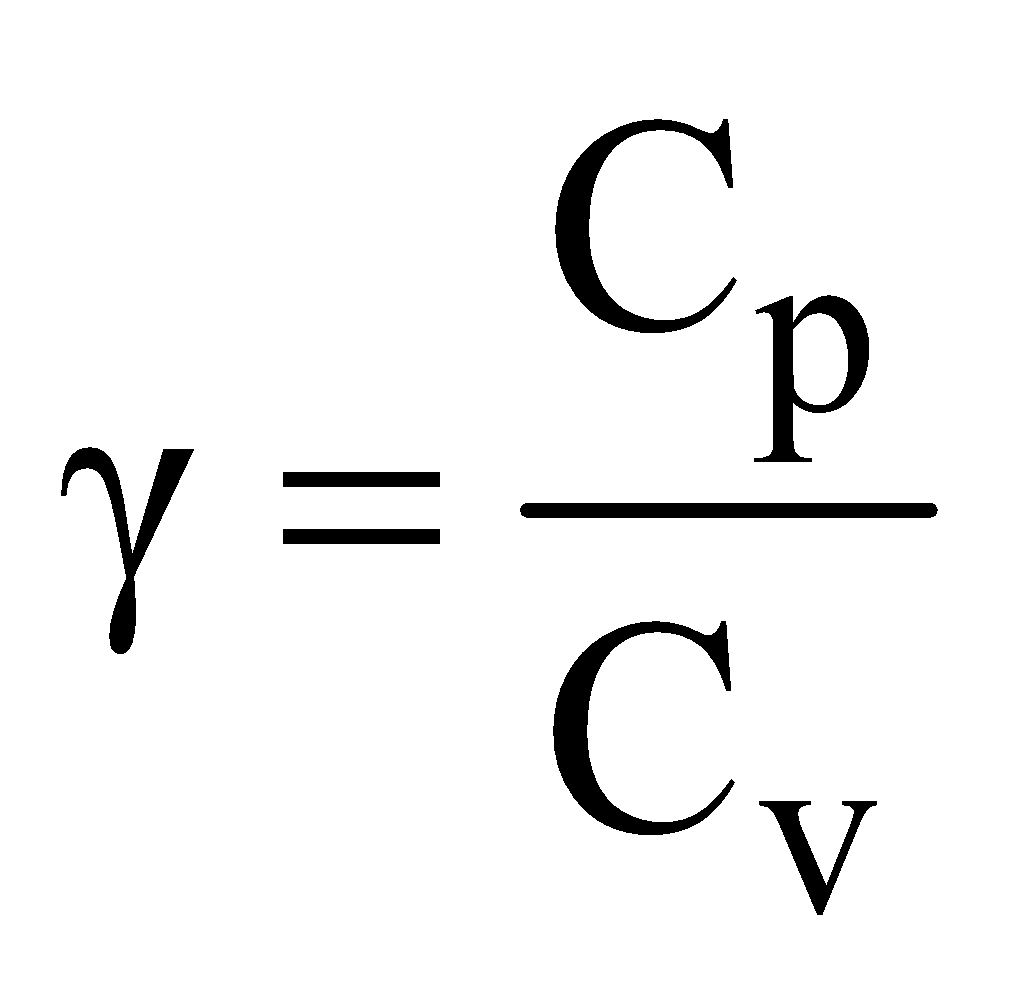 , where Cp = specific heat at constant pressure and Cv = specific heat at constant volume. the ratio g is a constant = 1.66 for monoatomic, 1.40 for diatomic, 1.33 for triatomic gas and atomic mass of gaseous element
, where Cp = specific heat at constant pressure and Cv = specific heat at constant volume. the ratio g is a constant = 1.66 for monoatomic, 1.40 for diatomic, 1.33 for triatomic gas and atomic mass of gaseous element
=.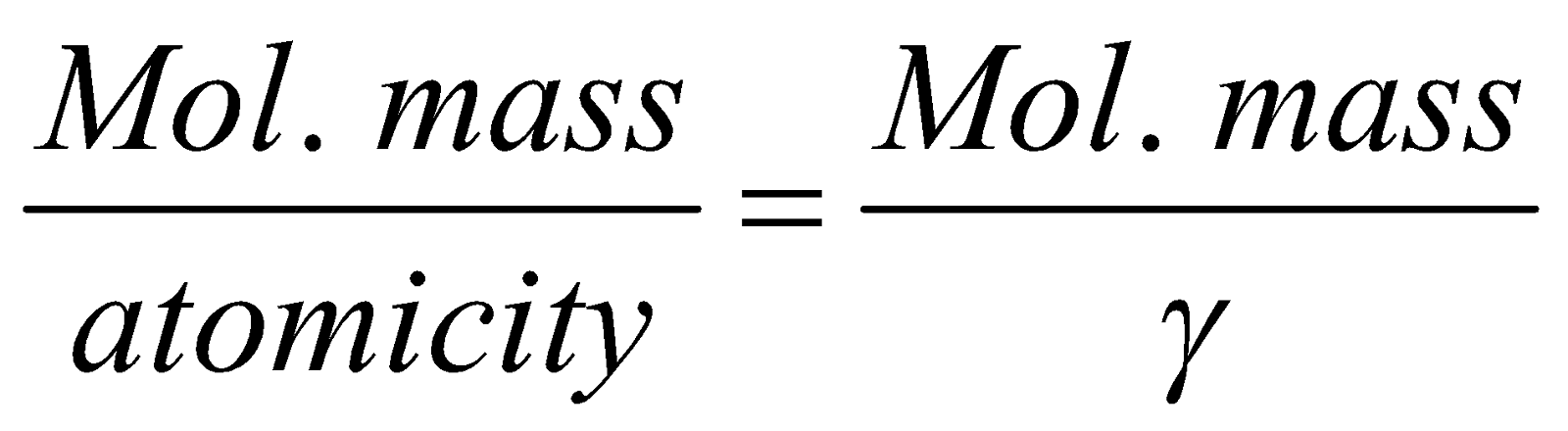
- Chloride formation method : This method converts the element (whose mass is to be determined) into volatile chloride whose vapour density is found by Victor Mayer method.
Molecular mass = 2 × V.D.
- Vapour density method is suitable for elements having volatile chlorides.
Atomic mass = Eq. mass of metal × valency.
- Mitscherlich’s law of isomorphism : It states that isomorphous substances have similar chemical constitution. Isomorphous substances form crystals of same shape and valencies of elements forming isomorphous salts are also same. eg: ZnSO4. 7H2O, MgSO4.7H2O and FeSO4.7H2O are isomorphous.
GRAM ATOMIC MASS (GAM)
Is the mass of an atom expressed in gms.
No. of Gm-atoms of element = 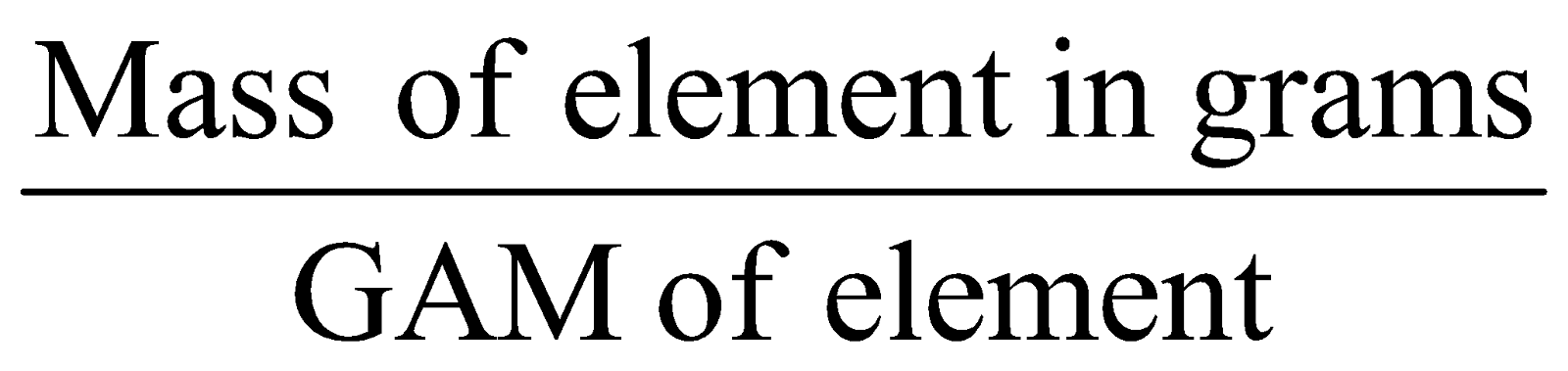
MOLECULAR MASS :
It is the average relative mass of the molecule as compared with mass of C-12 atom.
Molecular mass = 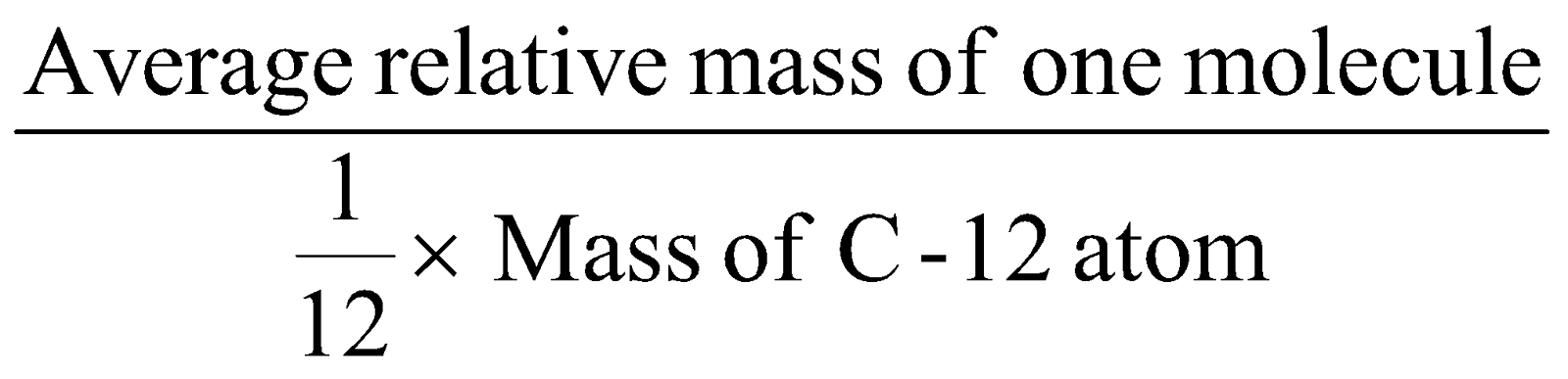
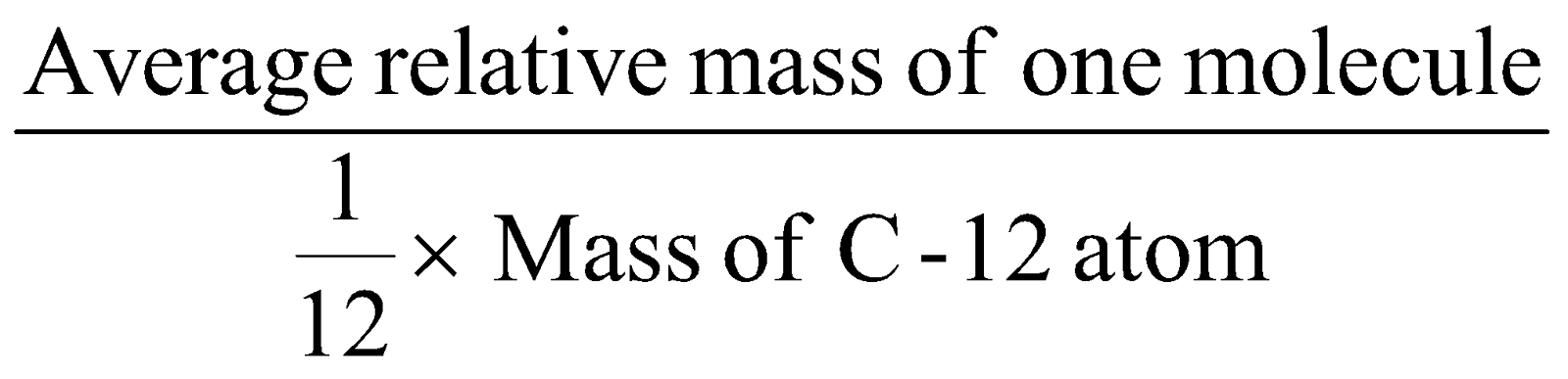
CALCULATION OF MOLECULAR MASS :
- Graham’s law of diffusion : It states that rate of diffusion of two gases is inversely proportional to the square root of ratio of their molecular weights.
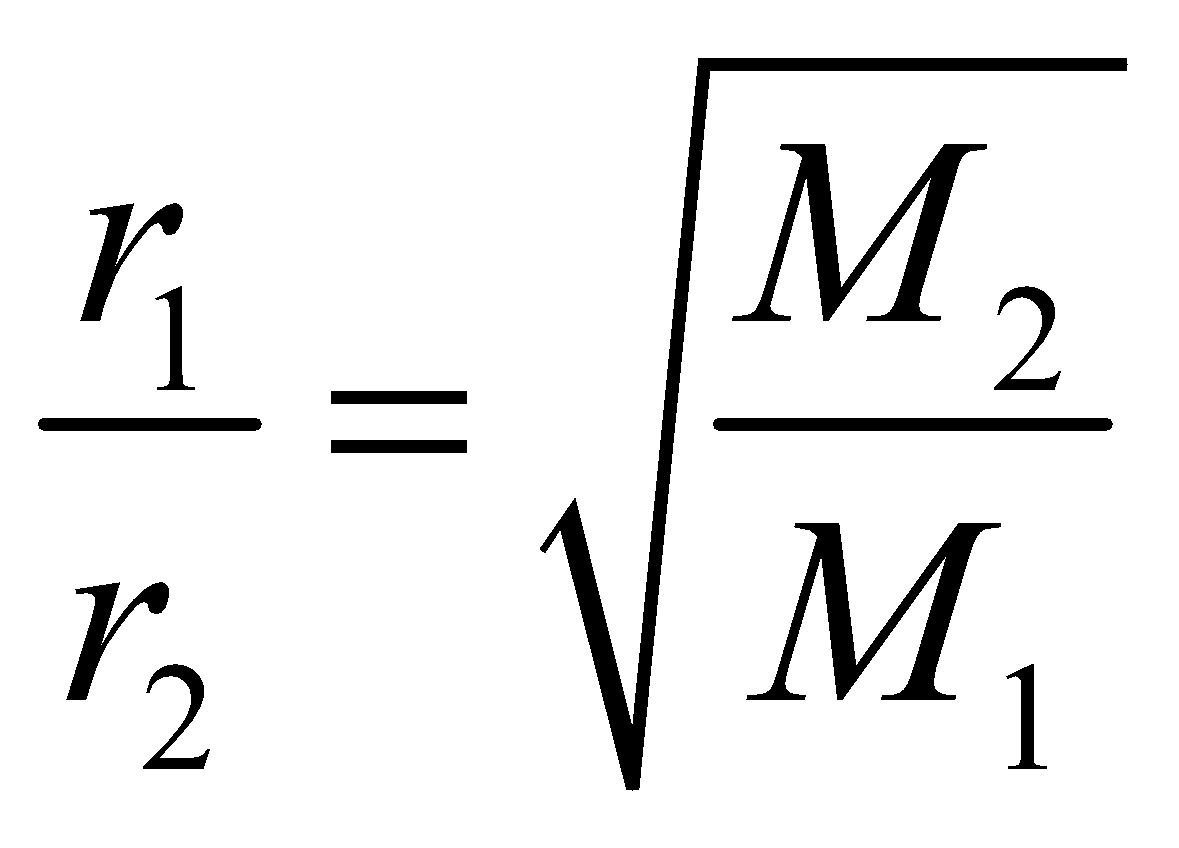
- Victor meyer method : This method can determine the molecular mass as
Molecular mass =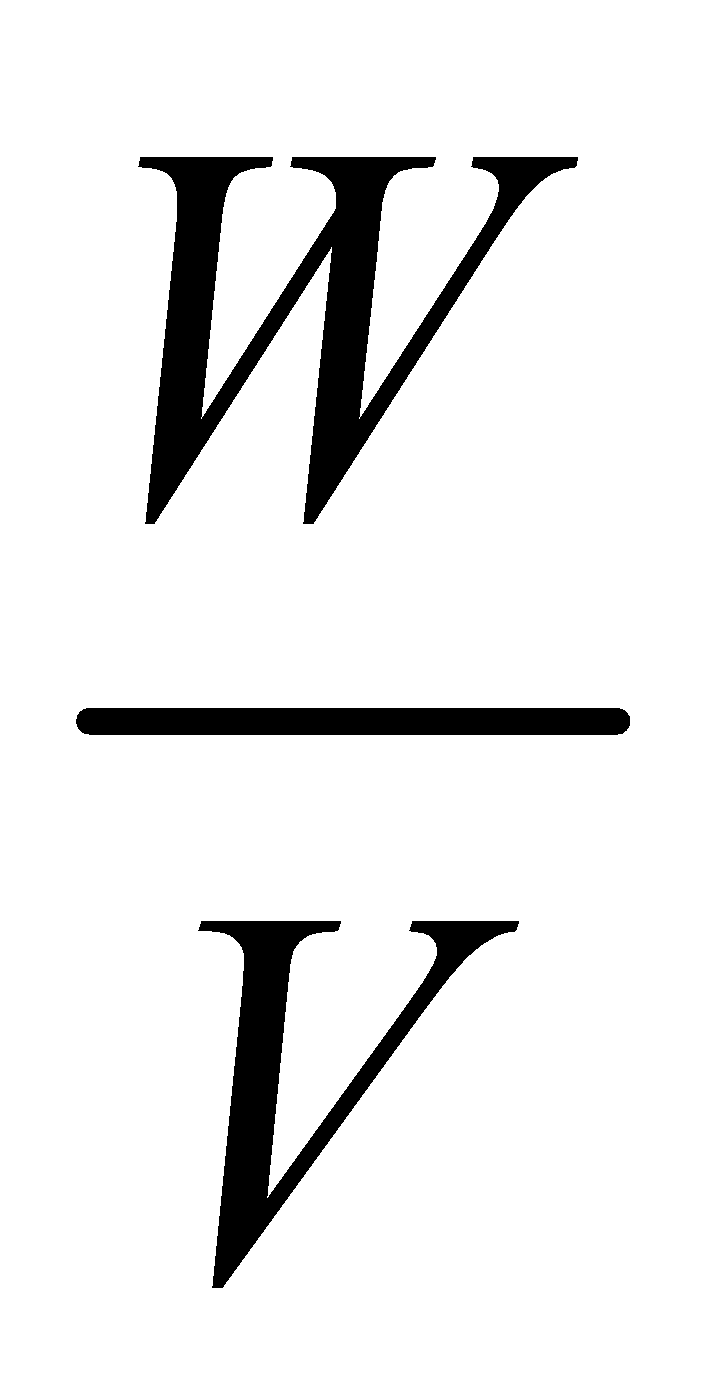 × 22400
× 22400
where W is the mass of liquid in gm. occupying a volume V ml at STP.
- Vapour density method : Vapour density is the ratio of volume of a gas to the mass of same volume of hydrogen under identical conditions.
or 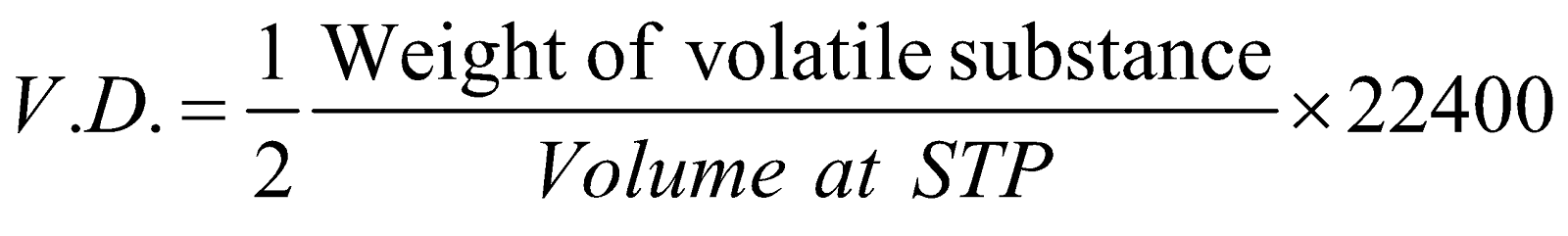
Thus molecular mass = 2 × V.D.
- Colligative properties method : This method can be helpful in determining molecular mass as
elevation in boiling point 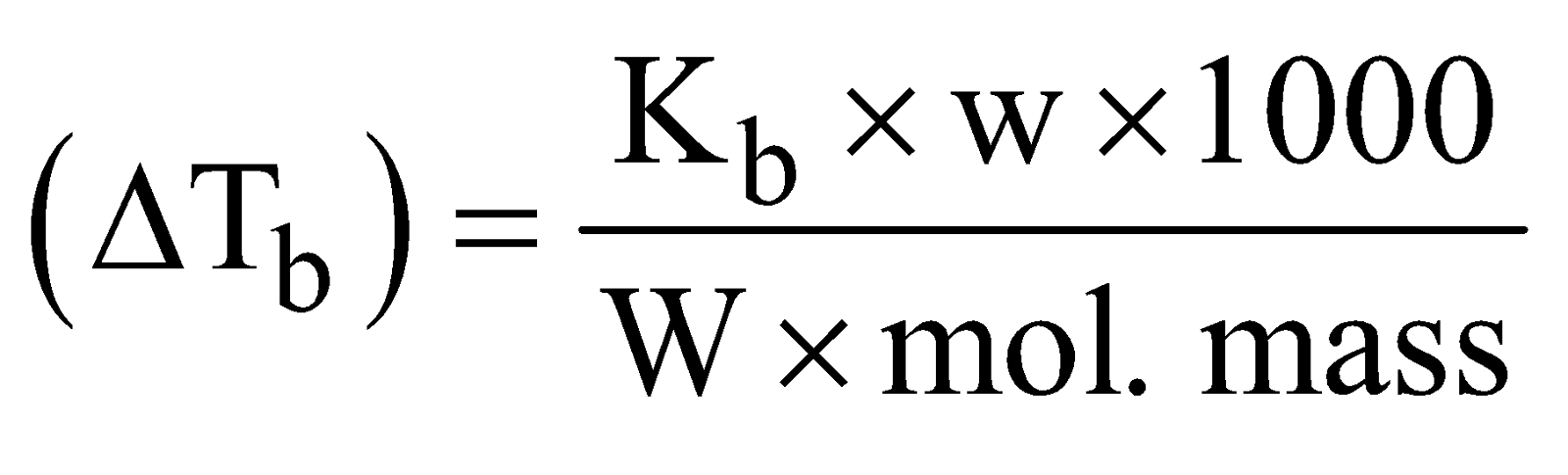
Where 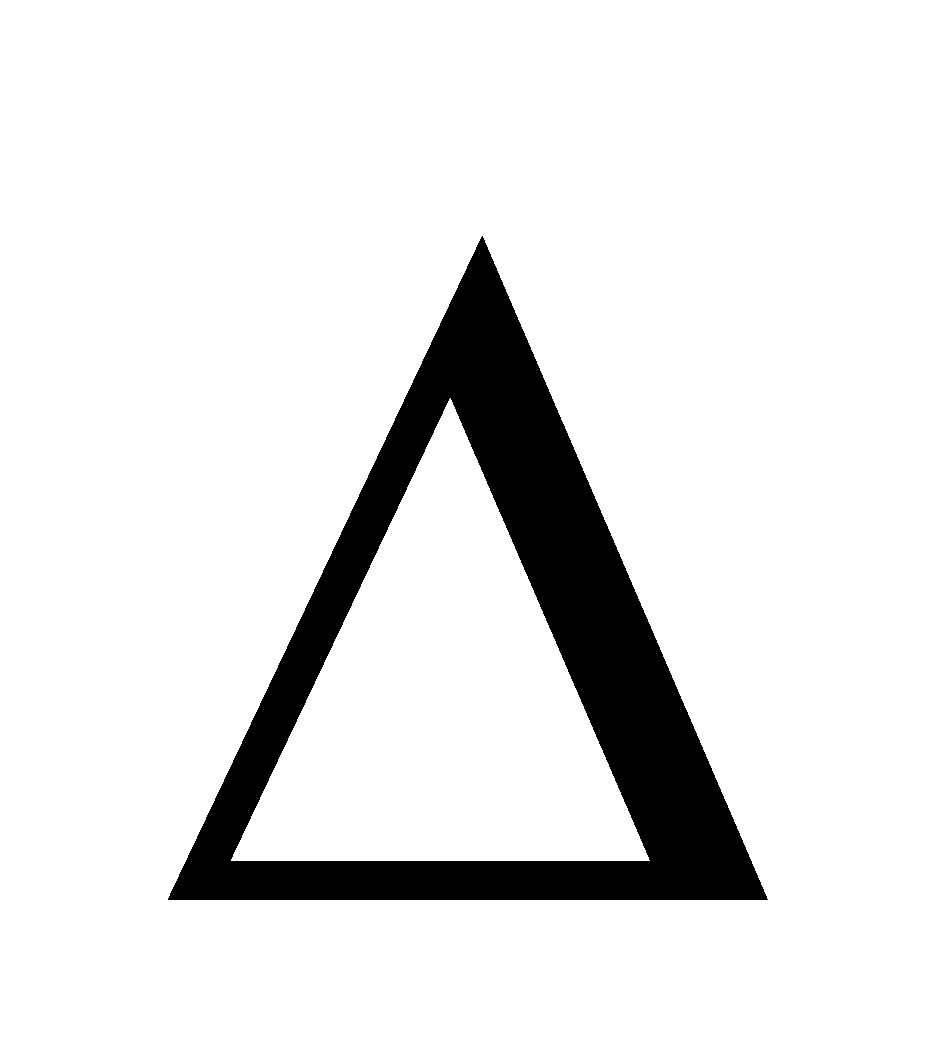 Tb is elevation in b.p., Kb is molal elevation constant w is wt. of solute W is wt. of solvent
Tb is elevation in b.p., Kb is molal elevation constant w is wt. of solute W is wt. of solvent
Depression in freezing point 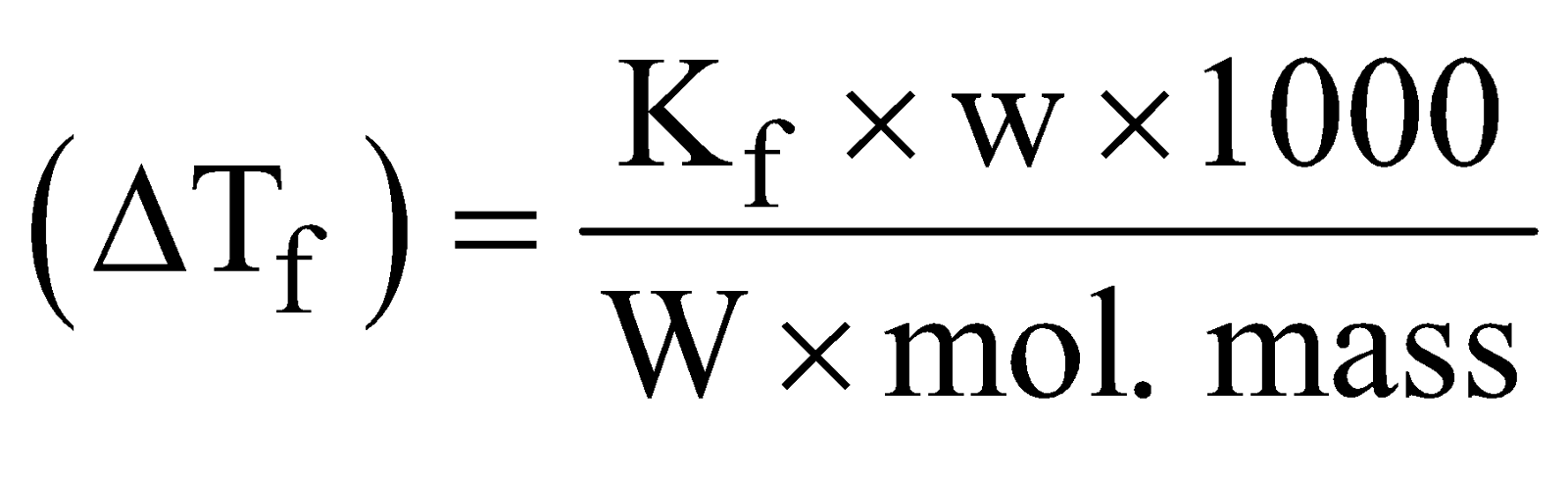
GRAM MOLECULAR MASS OR MOLAR MASS :
That amount of substance whose mass in grams is equal to its molecular mass or the equivalently molecular mass of a substance expressed in grams is called gram molecular mass. Gram molecular mass is also called one gram molecule. thus
No. of gm molecules = 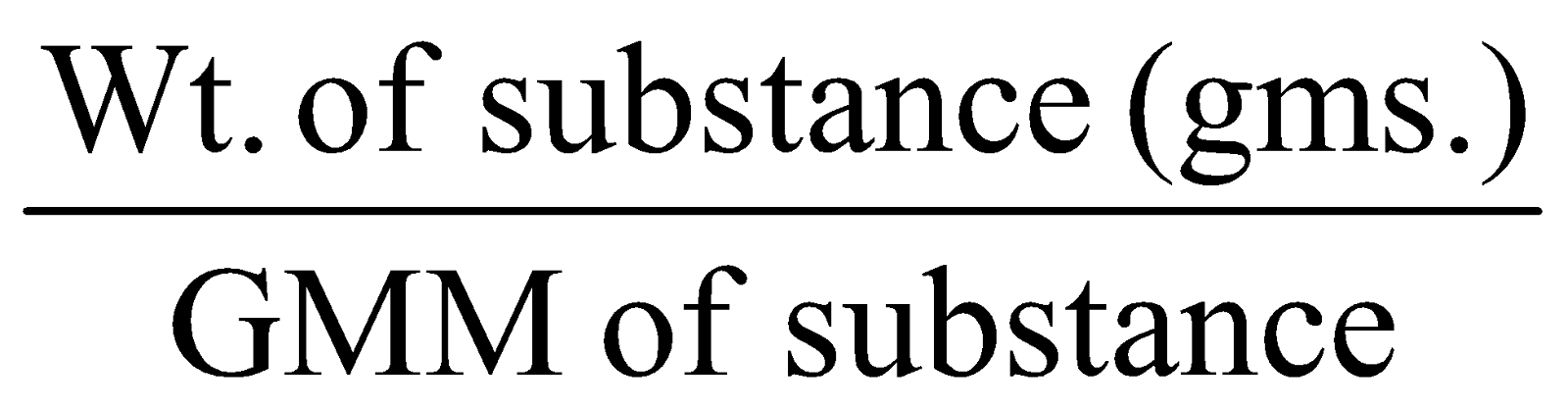
EQUIVALENT MASS :
It is the number of parts by weight of the substance that combines or displaces, directly or indirectly, 1.008 parts by mass of hydrogen or 8 parts by mass of oxygen or 35.5 parts by mass of chlorine. It can be calculated as-
- Equivalent mass for elements =
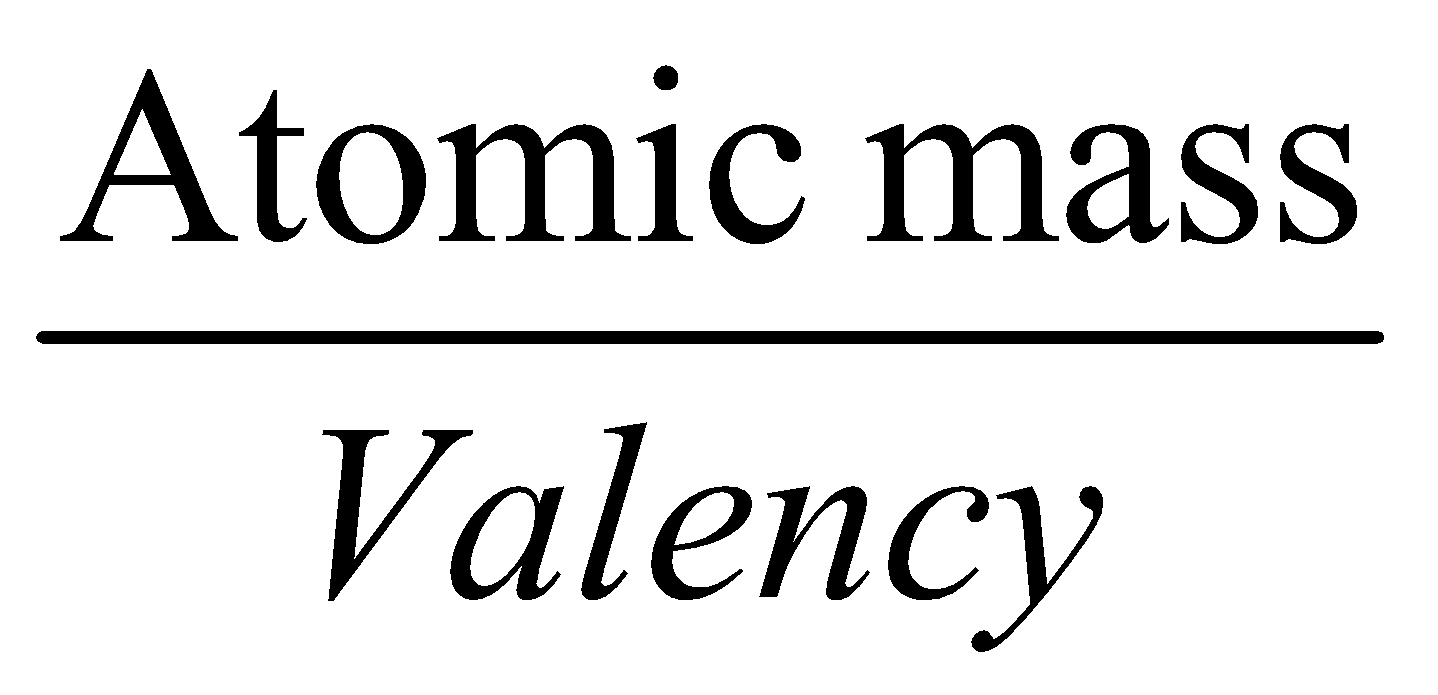
- Equivalent mass for acids =
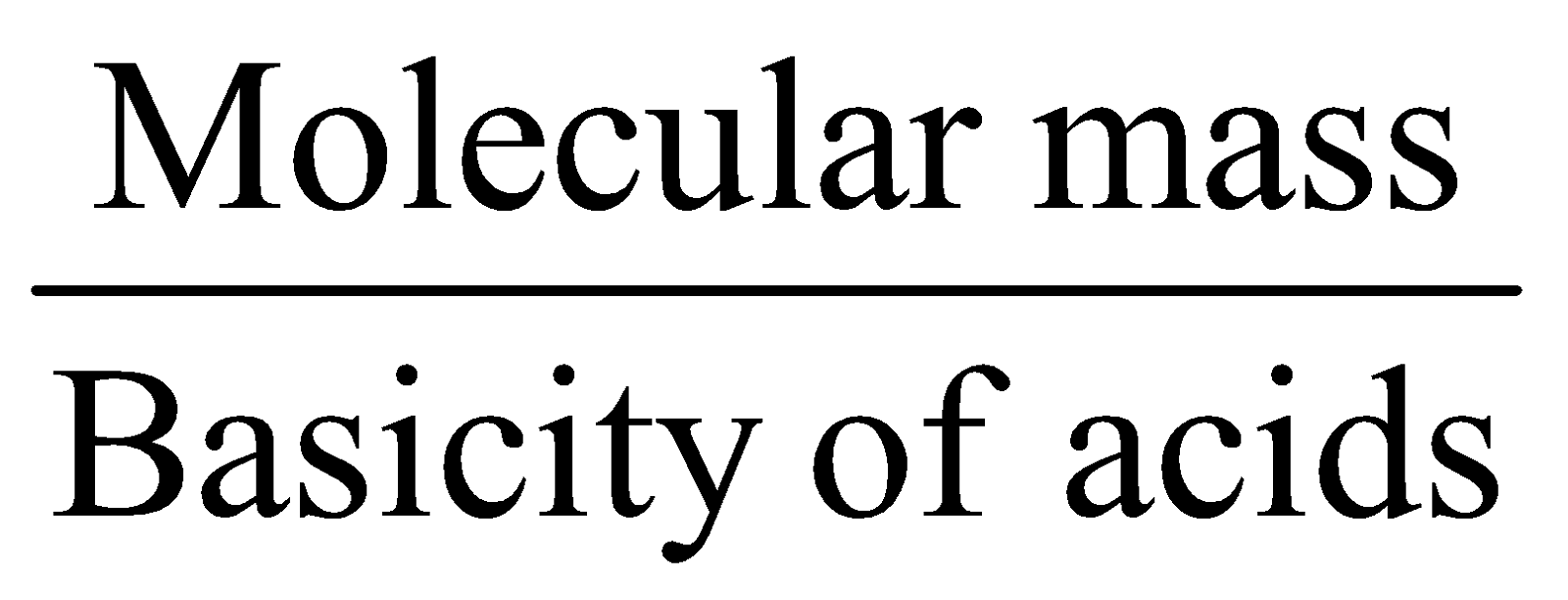
- Equivalent mass for bases =
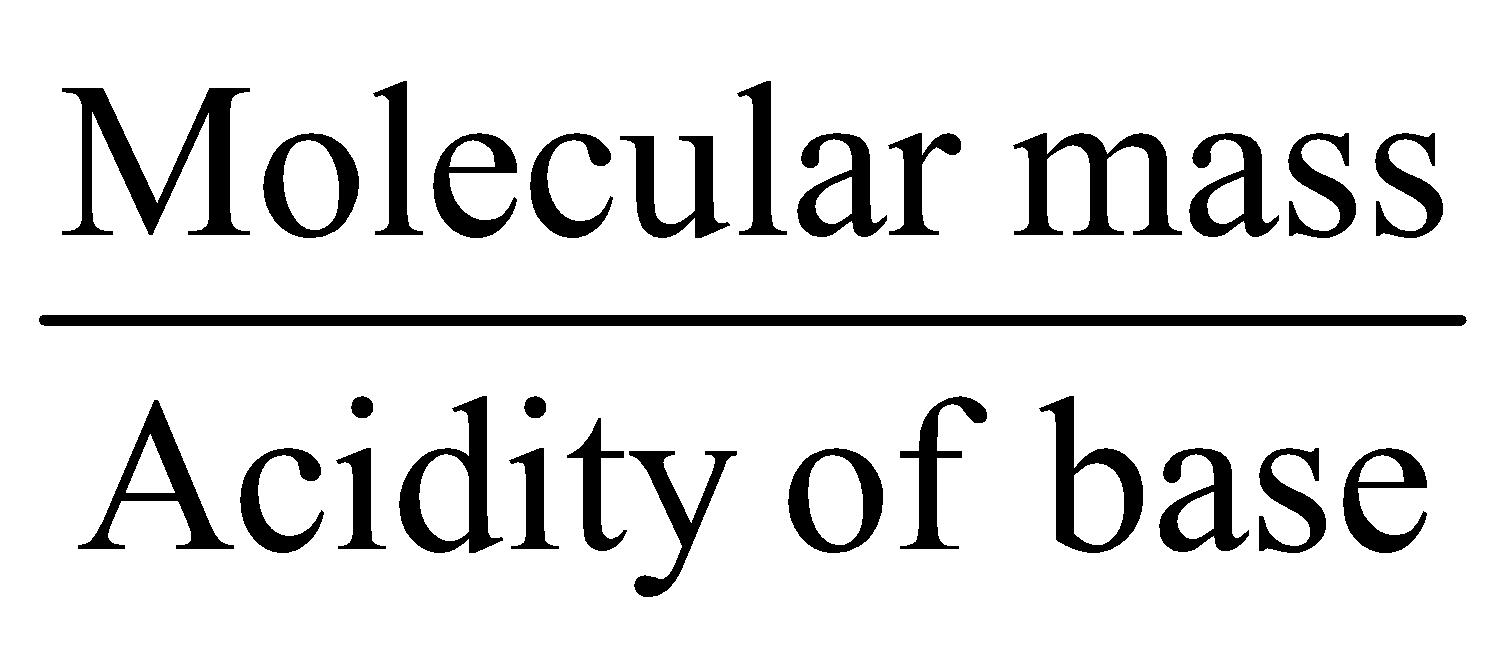
- Equivalent mass for salts =
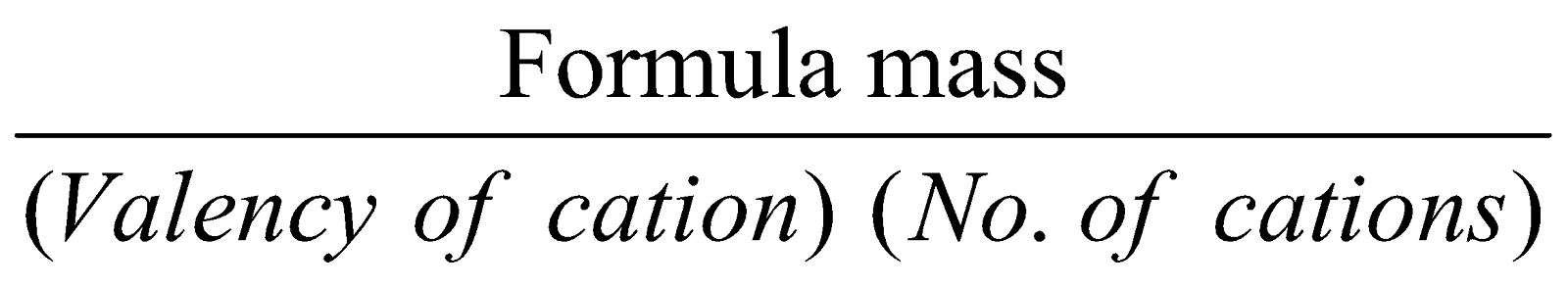
- Equivalent mass for oxidising agents =
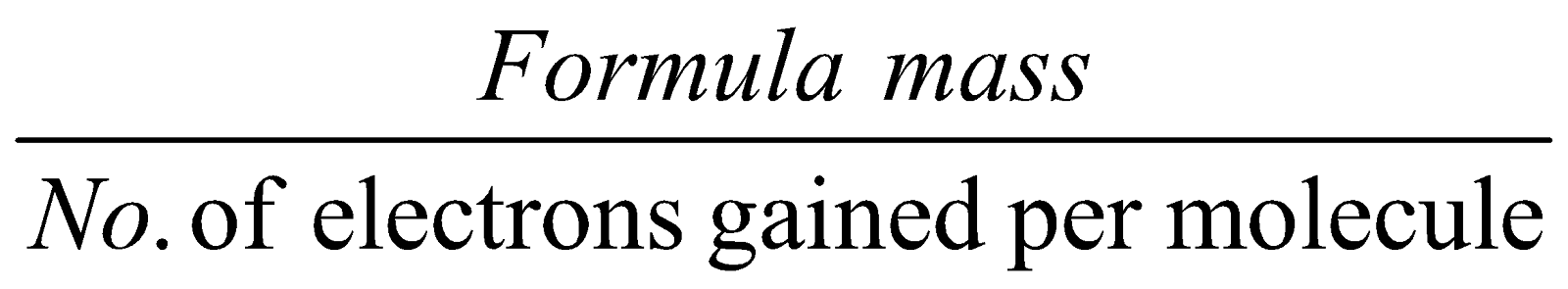
- Equivalent mass for reducing agents =
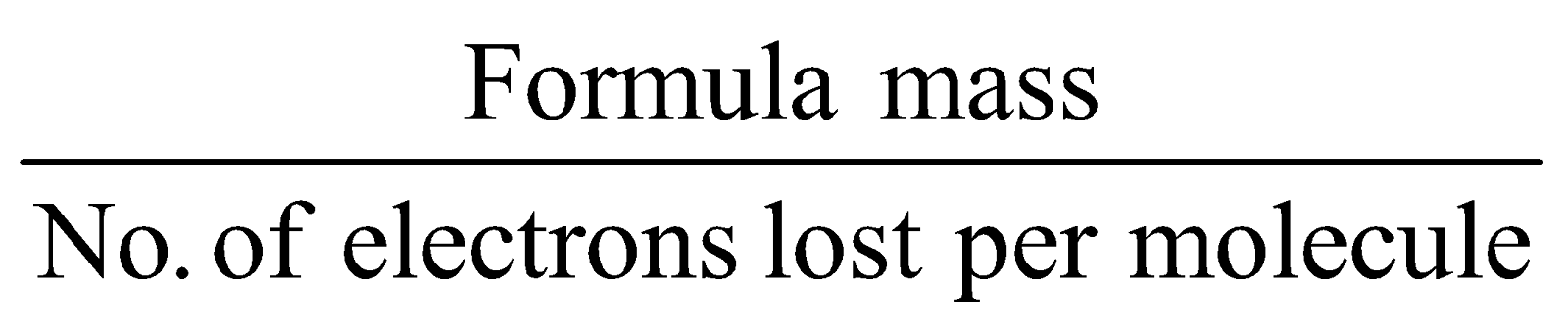
- Equivalent weight of radicals =
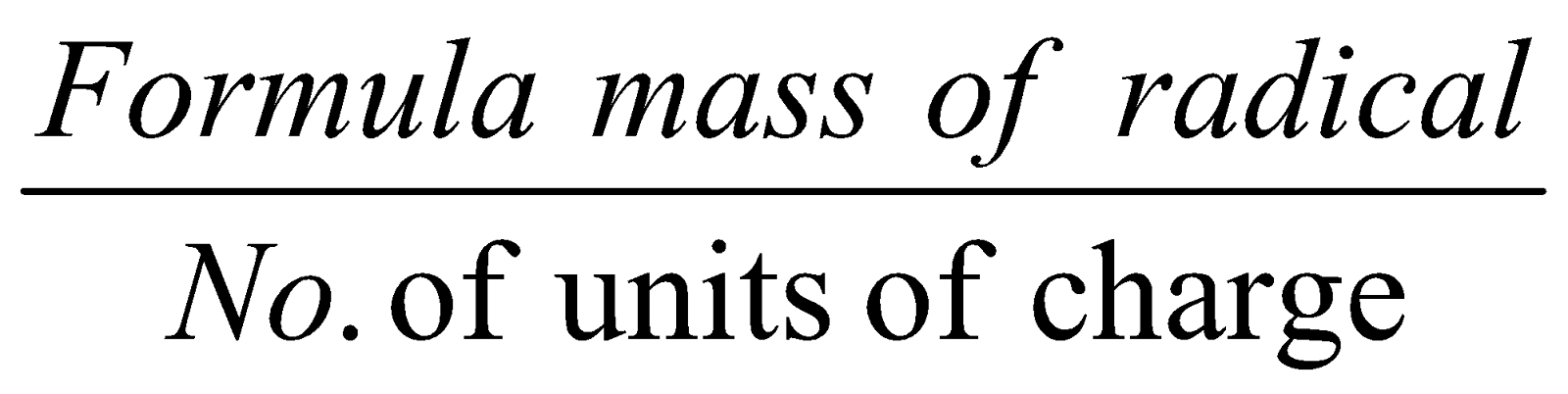
FORMULA MASS :
It is obtained by adding atomic masses of various atoms present in the formula and this term replaces molecular mass in ionic compounds.
ACIDITY :
It is the number of OH– ions that can be displaced from one molecule of a substance.
BASICITY :
It is the number of H+ ions that can be displaced from one molecule of a substance.
GRAM EQUIVALENT MASS (GEM) :
It is the mass of a substance expressed in grams or equivalently the quantity of substance whose mass in grams is equal to its equivalent mass is called one gram equivalent or gram equivalent mass.
No. of gm equivalents = 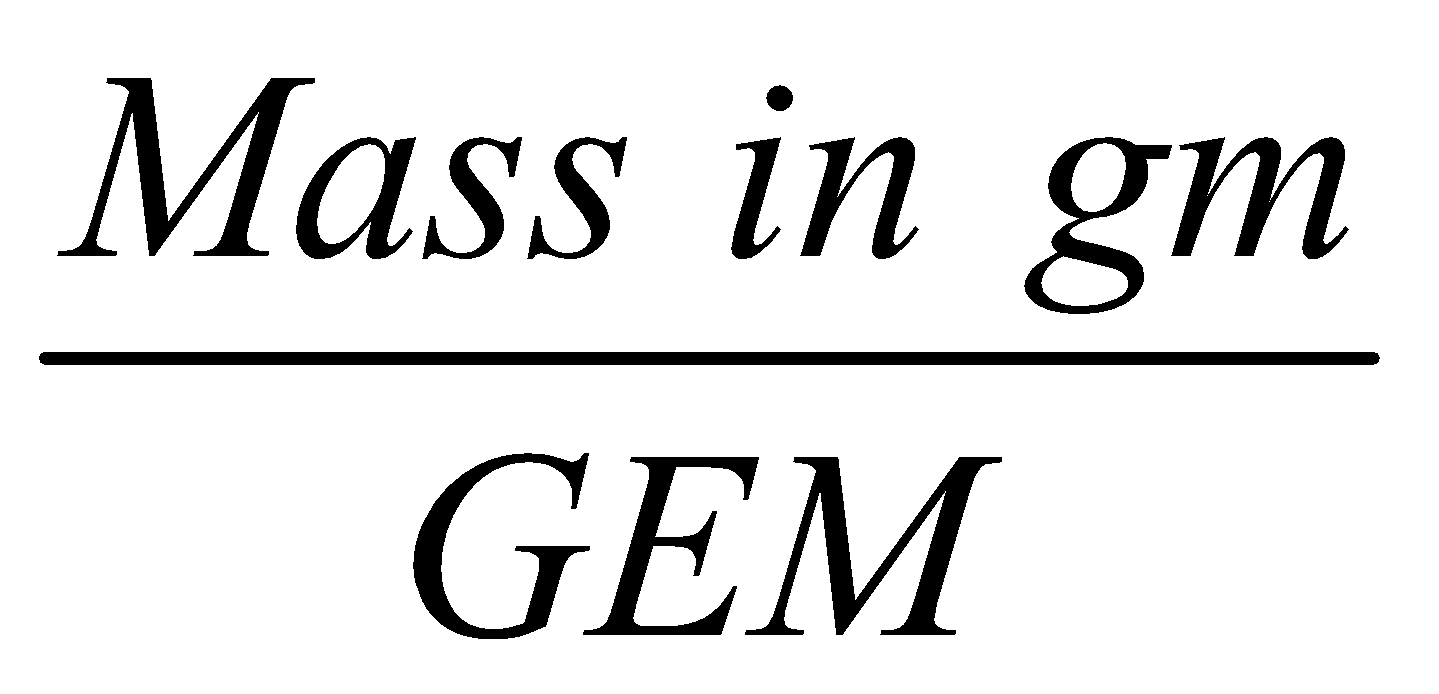 .
.
METHODS OF DETERMINING EQUIVALENT MASSES :
- Hydrogen displacement method : It is for metals which can displace H2 from acids.
Equivalent mass of metal
= 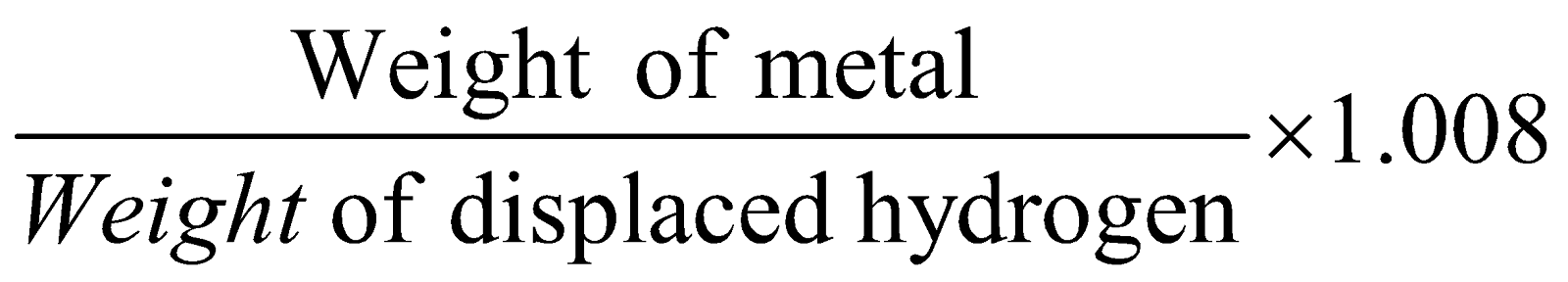
- Metal displacement method : It utilises the fact that one GEM of a more electropositive metal displaces one GEM of a less electropositive metal from its salt
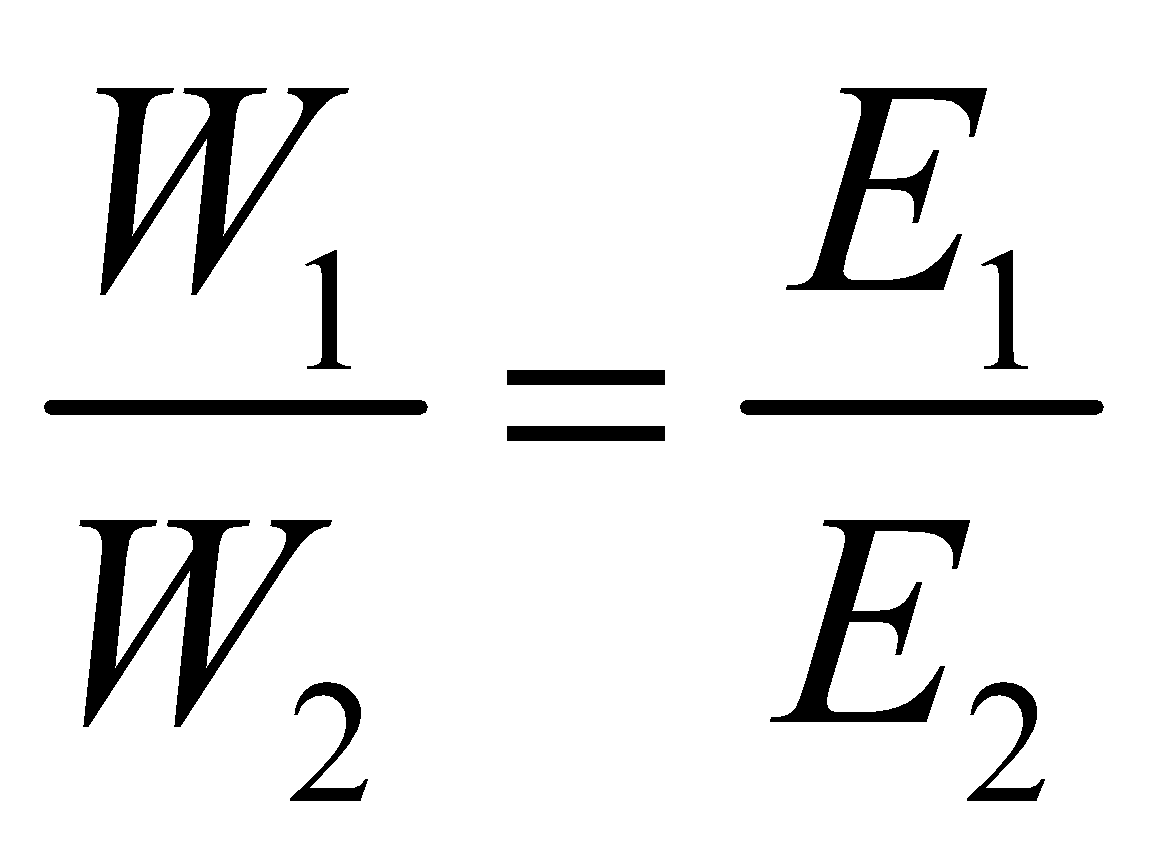 .
. - Conversion method : When one compound of a metal is converted to another compound of similar metal then
where E is the eqv. mass of the metal.
- Electrolytic method :
It states that the quantity of substance that reacts at electrode when Faraday of electricity is passed is equal to its GEM.
GEM = Electrochemical equivalent × 96500
and ratio of weights deposited by equal amount of electricity is in ratio of their equivalent masses.
- Oxide method :
Equivalent mass of metal = 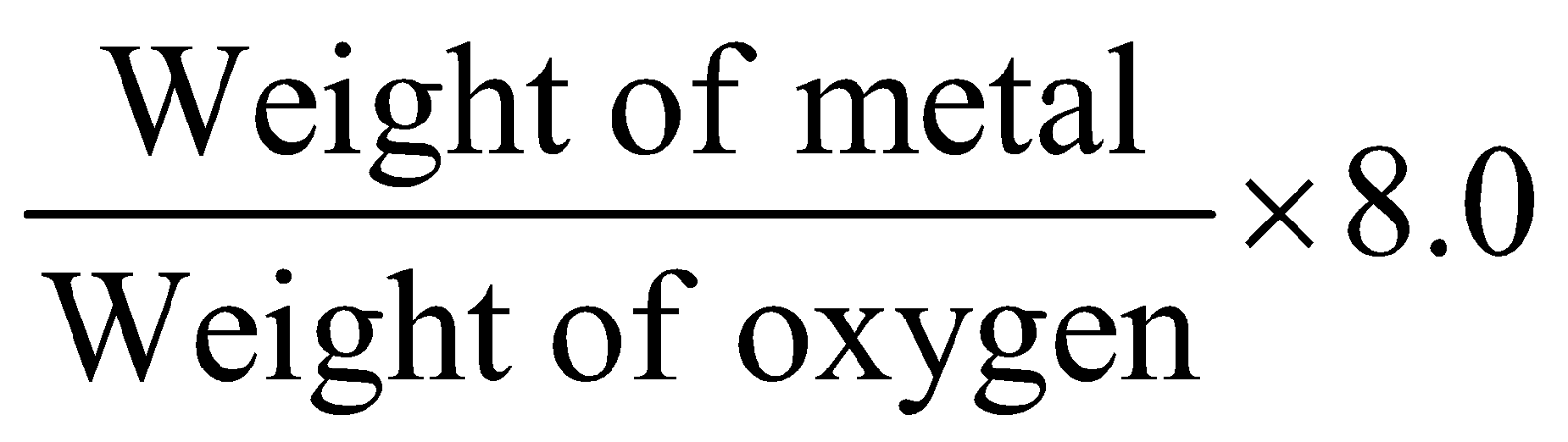
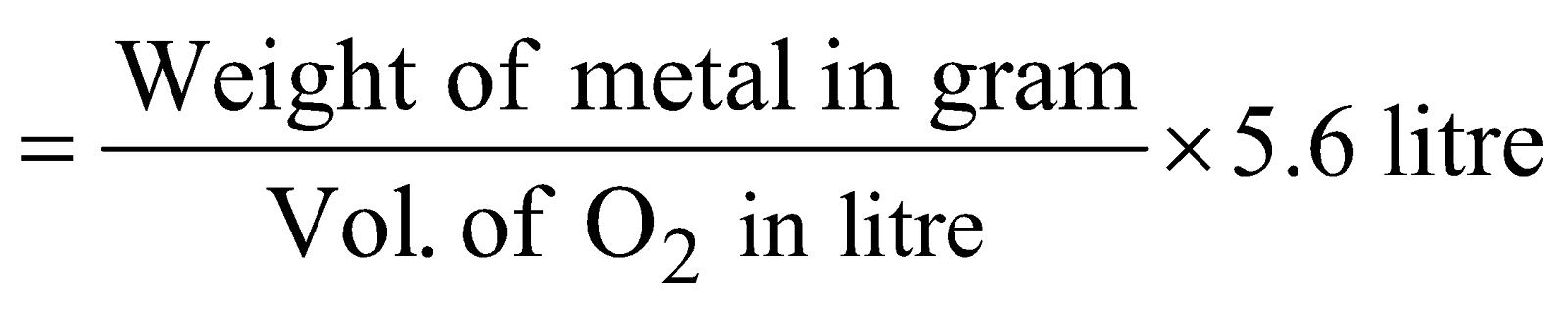
- Double decomposition :
- Neutralisation method for acids and bases :
Equivalent mass of acid (base)
= 

- Silver salt is method commonly used for organic acids.
Eqv. mass of acid = 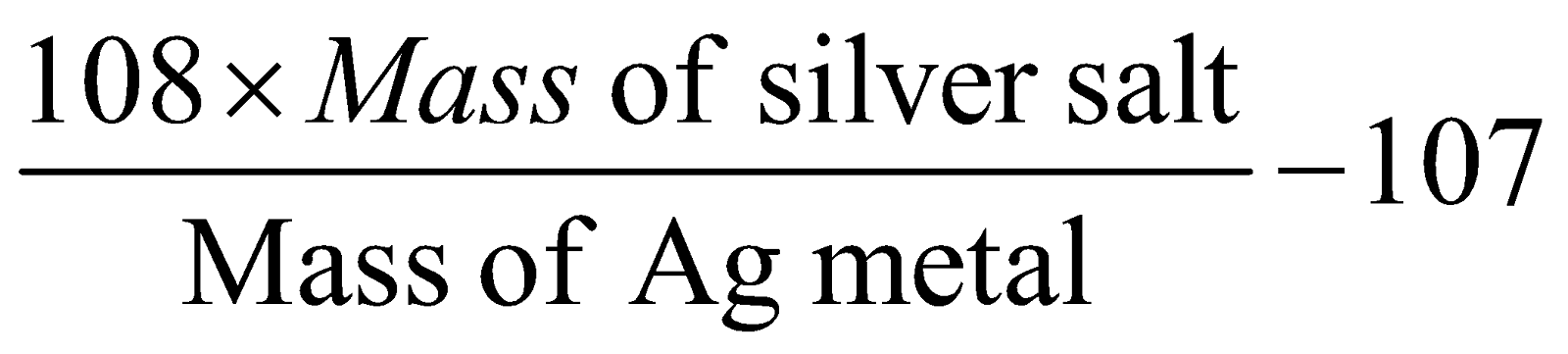
Mol. mass of acid = Eqv. mass of acid × Basicity
- Platinichloride method for bases :
Eqv. mass of base
=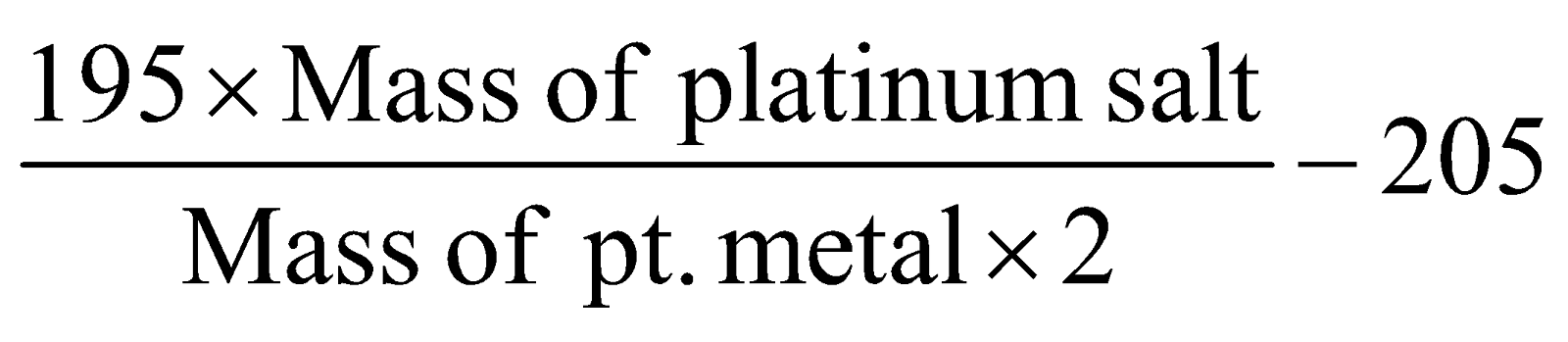
Mol. mass of base = Eqv. mass of base × Acidity
- Chloride method :
Eqv. mass of metal = 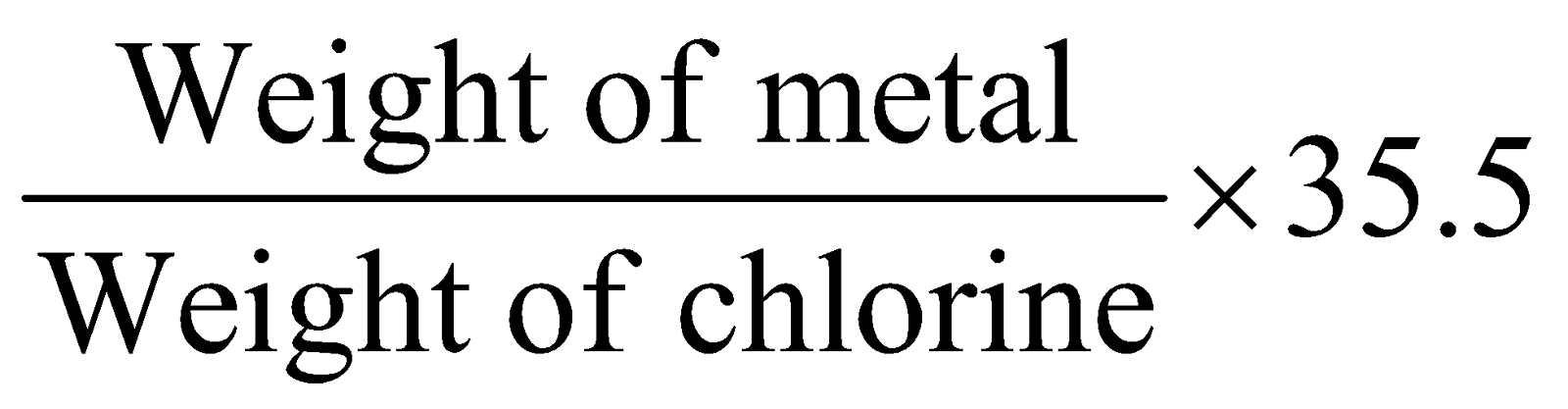
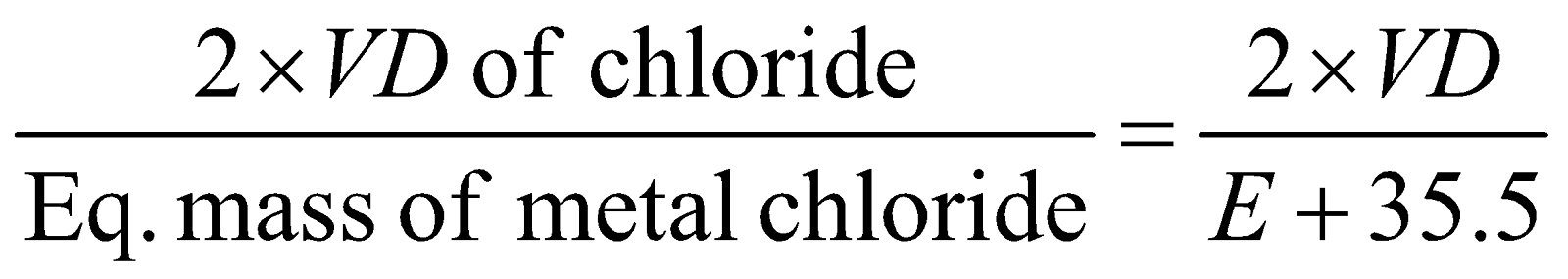
- Volatile chloride method :
Valency of metal
= 
CHEMICAL EQUATION :
It is the equation representing chemical change in terms of formula of reactants and products.
- An equation which has not been equalised in terms of number of atoms of reactants and products is called a skeleton equation.
- An equation having equal number of atoms of various kinds on both sides is a balanced equation.
EMPIRICAL FORMULA :
It is the simplest formula of a compound giving simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in one molecule. e.g. CH is empirical formula of benzene.
MOLECULAR FORMULA :
It is the actual formula of a compound showing the total number of atoms of constituent elements e.g. C6H6 is molecular formula of benzene.
Molecular formula = n × empirical formula, where n is simple whole number.
SOLUTION :
It is a homogenous mixture of two or more substances. The component of solution having larger proportion is solvent and others are solute.
MOLE FRACTION :
It is the ratio of moles of a constituent to the total number of moles in a solution.
Let A be solute & B is solvent then mole fraction of solute (xA)
=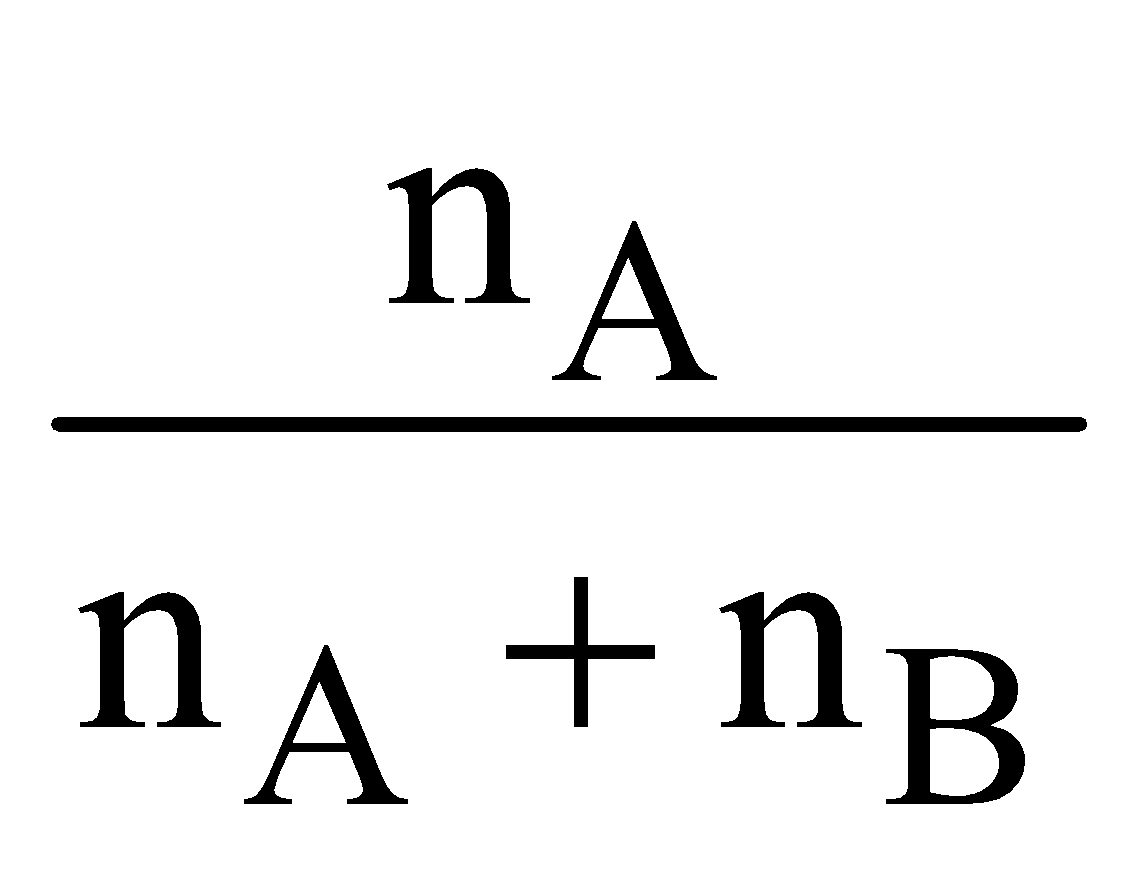 , where n is the number of moles.
, where n is the number of moles.
Mole fraction of solution 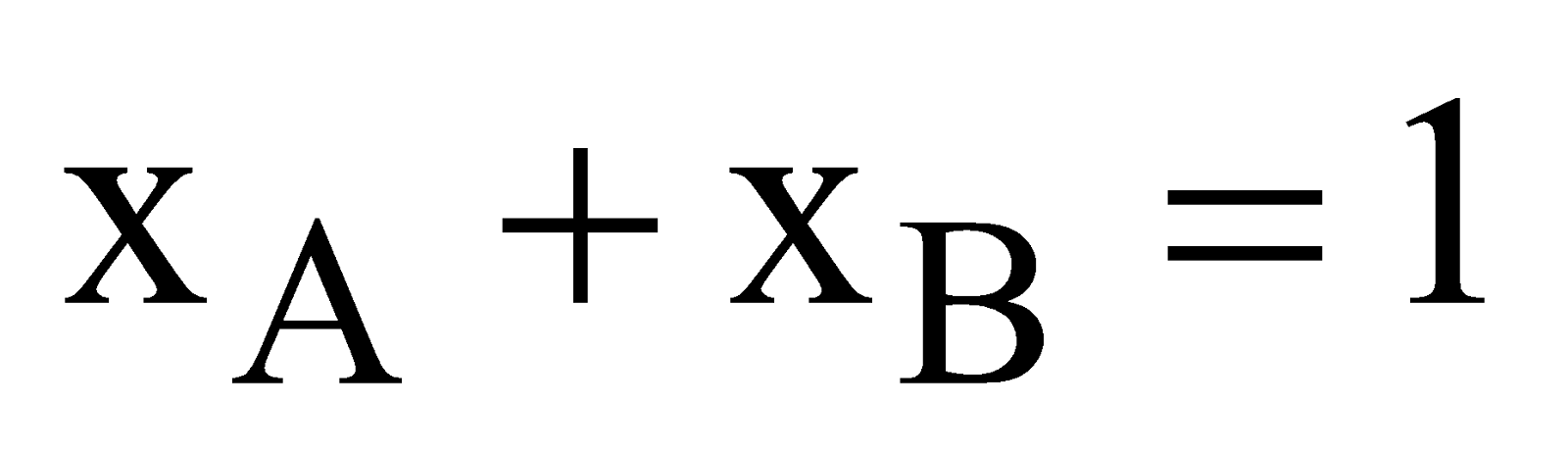
MASS PERCENTAGE :
It is the number of parts by mass of solute per hundred parts by mass of solution. If WA is mass of solute and WB the mass of solvent, then
Mass percentage of A = . 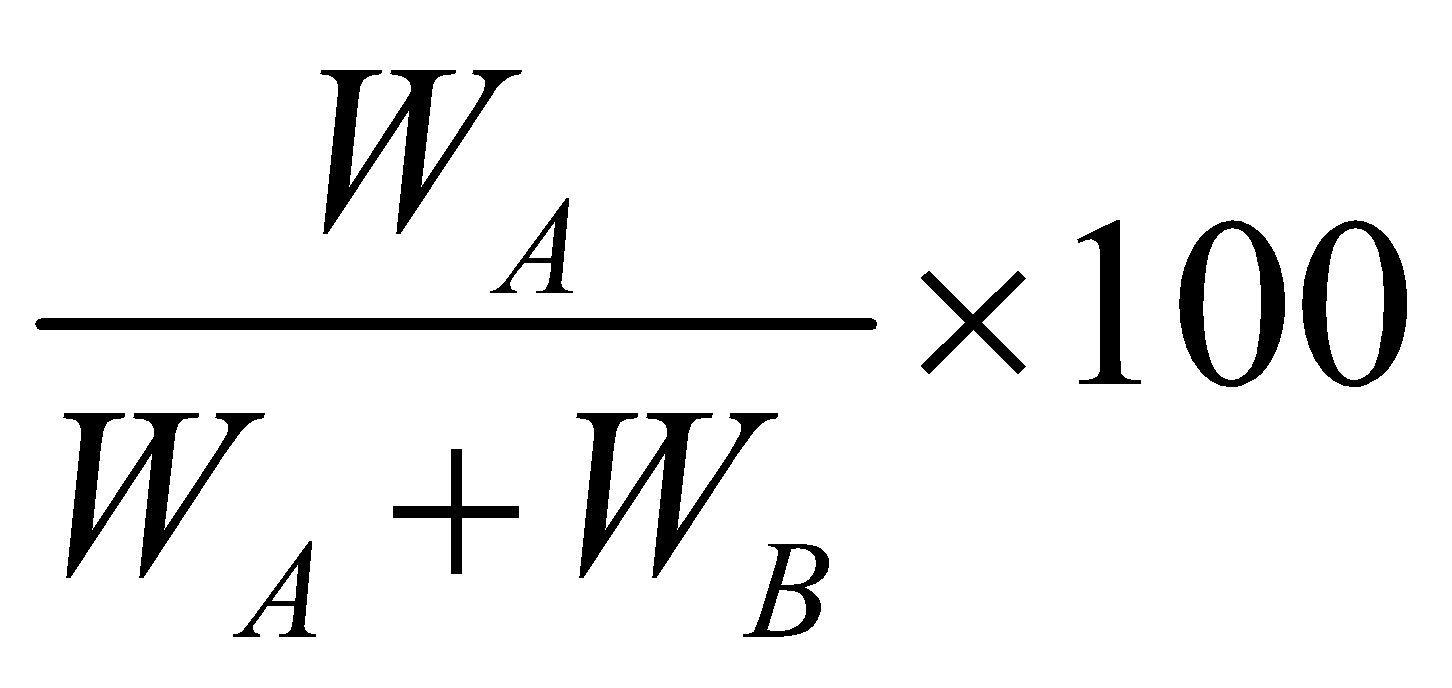
VOLUME PERCENTAGE :
It is the number of parts by volume of solute per hundred parts by volume of solution. If VA is volume of solute and VB is the volume of solvent then
Volume percentage of A = 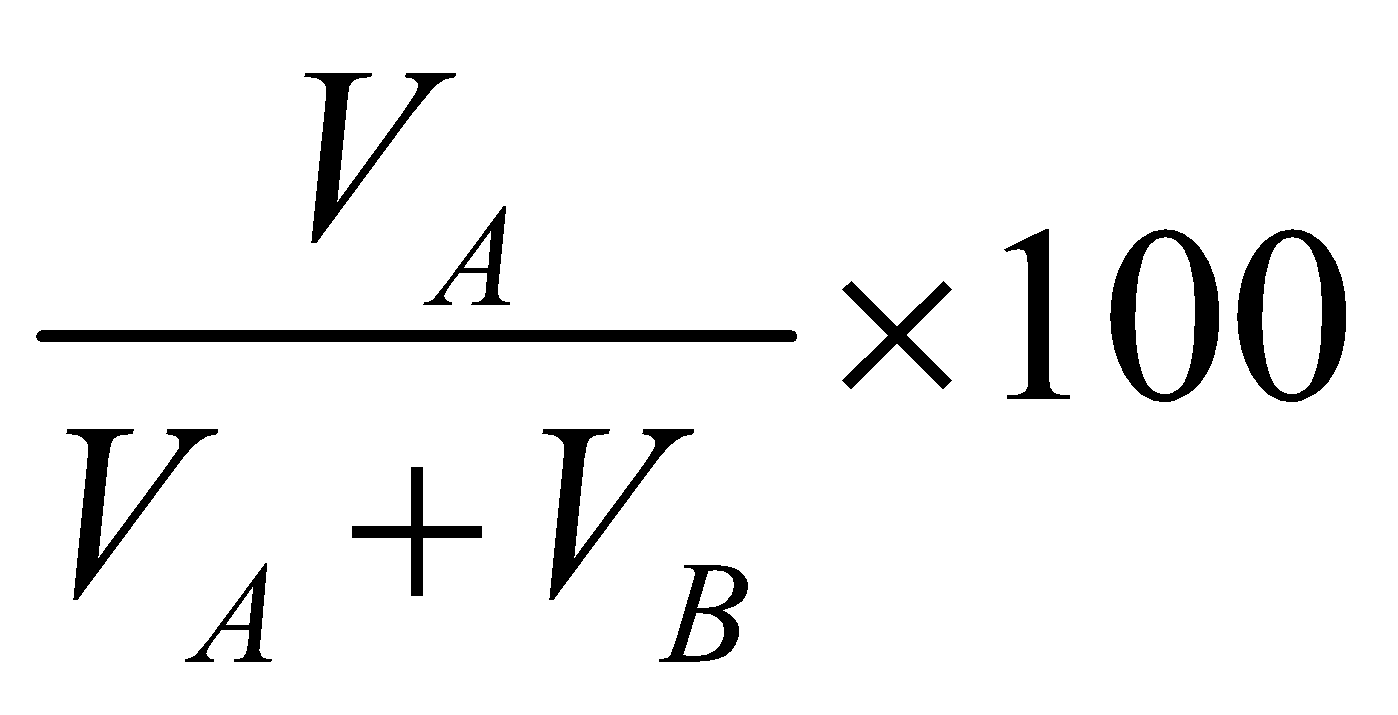
PARTS PER MILLION (PPM) :
It is the mass of solute present in one million parts by mass of solution.
NORMALITY :
It is the number of gram equivalents of a solute present in one litre of solution.
Normality depends on temperature. Also if strength is given in normalities, N1 of A & N2 of B
Then N1V1 = N2V2.
MOLARITY :
It is the number of moles of solute present in one litre of solution.
and millimoles = M × V(in ml).
Molarity and mass percentage have the relation M
If a solution of molarity M1 and volume V1 adds up with a solvent to a final volume V2, then molarity M2 is given by
If two different solutions (M1, V1) and (M2, V2) are mixed then molarity of resulting solution is
M = 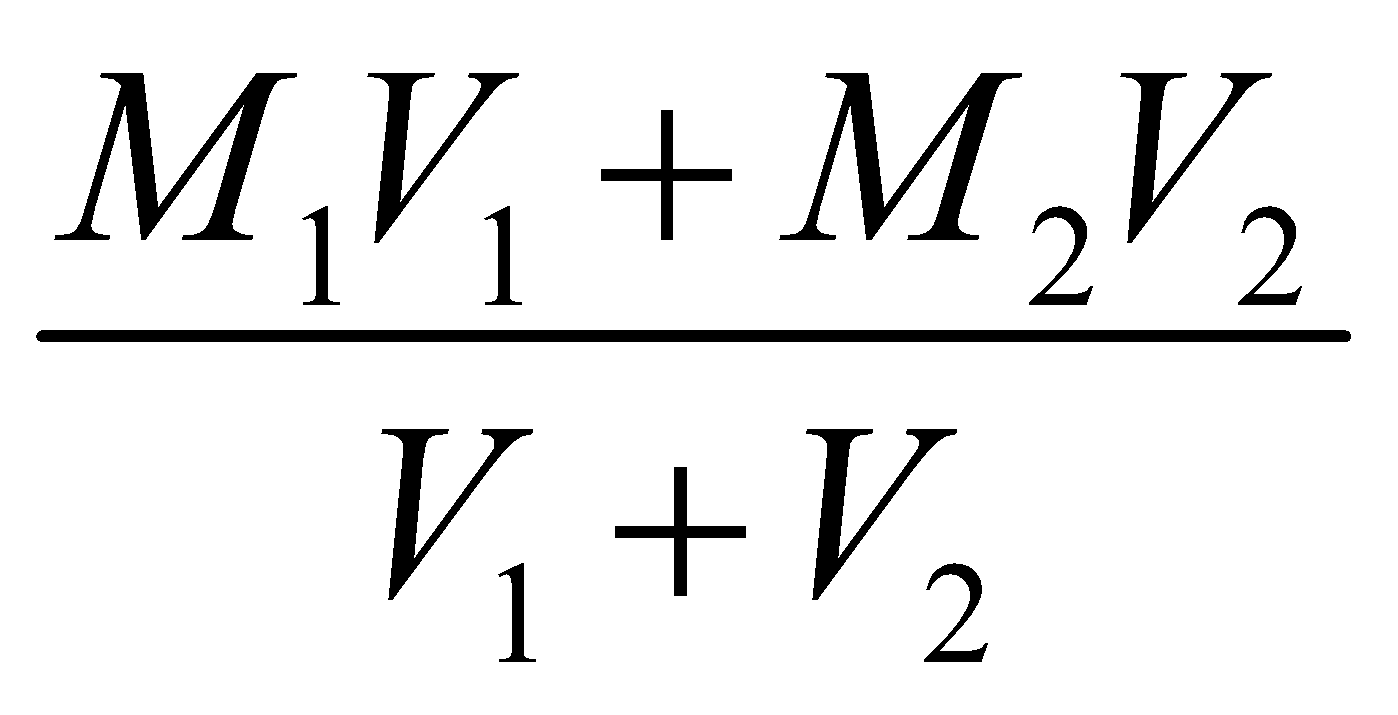
Also, Molarity × GMM of solute = Normality × GEM of solute
MOLALITY :
It is the number of moles of solute in 1 kg of solvent.
Molality (m) = 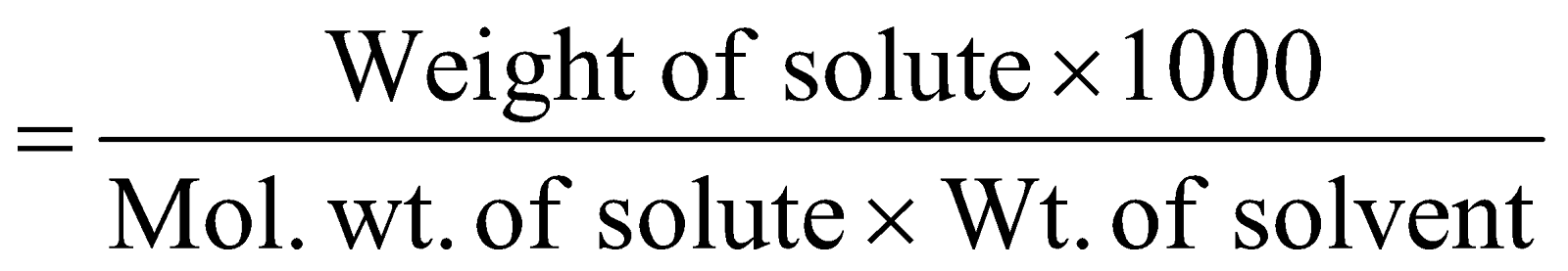
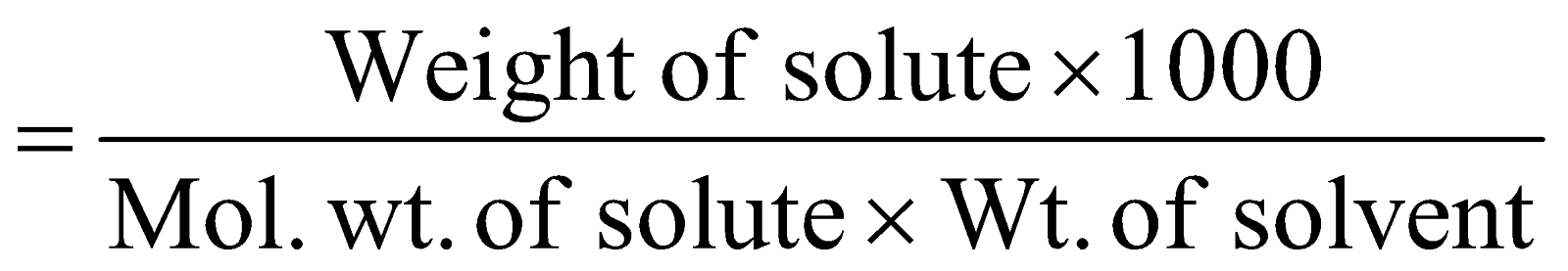
Molality is independent of temperature.
FORMALITY (F) :
It is the number of gram formula mass of ionic solute dissolved in 1 litre of solution.
Formality = 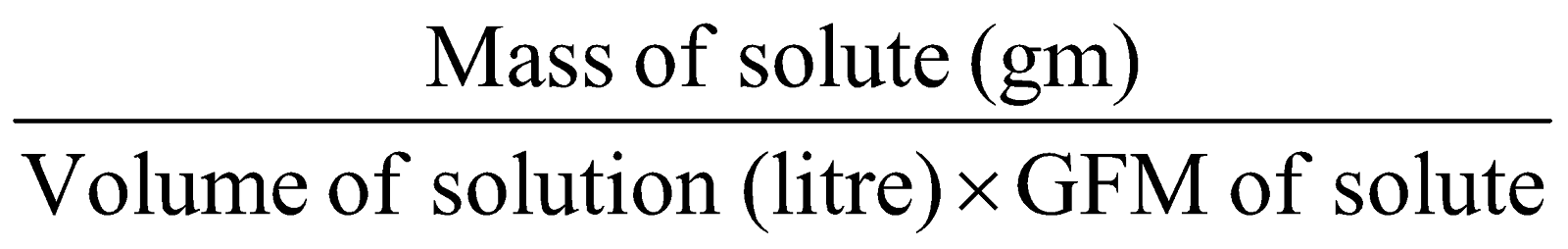
LIMITING REAGENT :
It is the reactant which is completely consumed during the reaction.

