10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry
Essential idea:
Organic chemistry focuses on the chemistry of compounds containing carbon.
Understandings:
- A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ from each other by a common structural unit.
- Structural formulas can be represented in full and condensed format.
- Structural isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms.
- Functional groups are the reactive parts of molecules.
- Saturated compounds contain single bonds only and unsaturated compounds contain double or triple bonds.
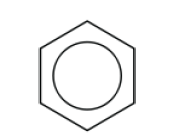
- Benzene is an aromatic, unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Applications and Skills:
- Explanation of the trends in boiling points of members of a homologous series.
- Distinction between empirical, molecular and structural formulas.
- Identification of different classes: alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, halogenoalkanes, alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, esters, carboxylic acids, amines, amides, nitriles and arenes.
- Identification of typical functional groups in molecules eg phenyl, hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, carboxamide, aldehyde, ester, ether, amine, nitrile, alkyl, alkenyl and alkynyl.
- Construction of 3-D models (real or virtual) of organic molecules.
- Application of IUPAC rules in the nomenclature of straight-chain and branched-chain isomers.
- Identification of primary, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms in halogenoalkanes and alcohols and primary, secondary and tertiary nitrogen atoms in amines.
- Discussion of the structure of benzene using physical and chemical evidence.