Question
Consider the following example relation. It holds data about a number of teachers and students from different schools who volunteer to support the local community on particular days.
SCHOOL_VOLUNTEERS_TABLE (School_Name, Code, Address, Date, Num_Volunteers)
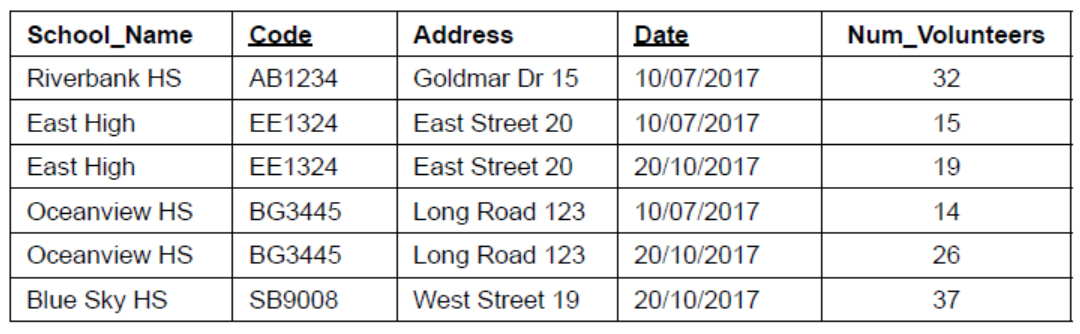
The key attributes are underlined.
a.i. State what is meant by redundant data in databases.[1]
a.ii.Explain one issue that can be caused by redundant data in a database.[2]
b. Identify three characteristics of the 1st Normal Form (1NF) which are evident in this relation.[3]
c. Explain why a compound key is used for the SCHOOL_VOLUNTEERS_TABLE relation.[2]
d. The following shows the normalized SCHOOL_VOLUNTEERS_TABLE relation:[5]
SCHOOLS_TABLE
Code, School_Name, Address
VOLUNTEERS_TABLE
Code, Date, Num_Volunteers
Discuss whether these relations are in third normal form (3NF).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a.i. )
Redundant data means data that is held in two different places within a database;
a.ii Award [1] for identifying an issue caused by data redundancy and [1] for a brief explanation up to [2 max].
It could give the system unwanted/unexpected results; due to the use of inaccurate data;
It may lead to additional storage requirements; As data is used more times than necessary;
b. )
Each attribute has a single value/is atomic;
All values for a given attribute are of the same data type;
Each attribute is unique;
This is a unique key;
There are no repeating fields;
There are no two identical tuples in this relation;
Order of attributes/tuples is not significant for the relation;
Key $($ Date + Code $)$ is unique for each tuple;
c. )
The alternative is to use an autonumber field; But this would use additional storage space;
Are used because it is not possible to designate a primary key from a single field;
Neither the code nor the date field on their own uniquely identify a record;
Is based on two primary keys in other tables;
d. )
Example answer 1
$2 \mathrm{NF}=3 \mathrm{NF}$ if there are no transitive relationships/if any non-key attributes are more dependent on another non-key attribute than the key field Schools_Table could be the above if a school had more than 1 address;
Then the Address would depend upon the school_Name;
And the schools_Table code would be split as follows:
(code, School_Name)
(School_Name, Address);
If the school had only 1 address then $2 \mathrm{NF}=3 \mathrm{NF}$;
The volunteers_Table has no transitive dependencies;
There is no redundant data;
Example answer 2
A relation is in $3 N F$ if it is in $2 N F$ and it contains no transitive dependencies;
Assuming that schools name is not unchangeable;
OR there are two schools with different names and same addresses;
OR two schools with same name and different addresses;
Then the school name cannot be treated as a key;
From the 2NF (two created relations above) the functional dependencies are not evident in the relation
School_Table (School_Name, Code, Address):
The relation given above (in $2 \mathrm{NF}$ ) is also in $3 \mathrm{NF}$;
School_Table (School_Name, Code, Address)
Volunteers_Table (Code, Date, Num_Volunteers)
