Question
[Maximum mark: 17] [without GDC]
Given that sin 20° = p , and cos 20° = q (so that \(\left.p^{2}+q^{2}=1\right)\) [5]
(a) 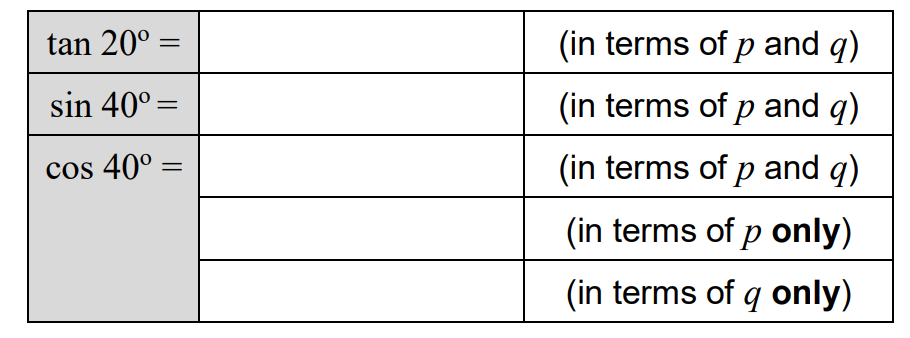
(b) By observing the unit circle [12]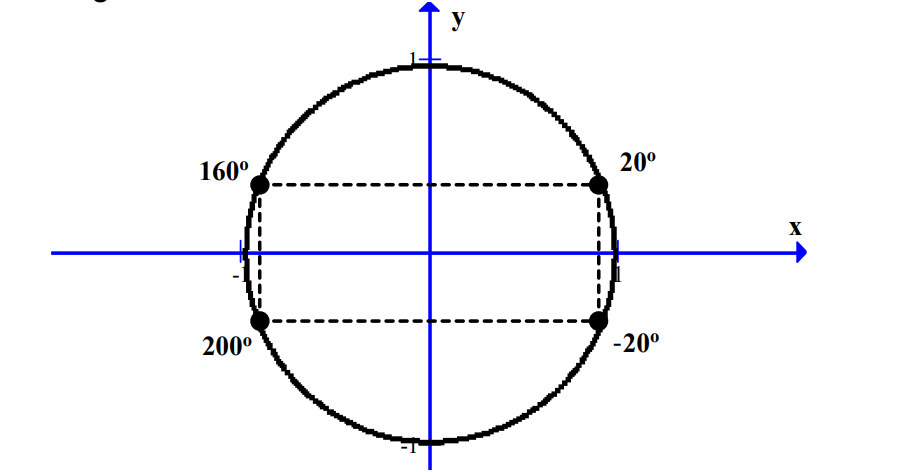
express the following in terms of p and/or q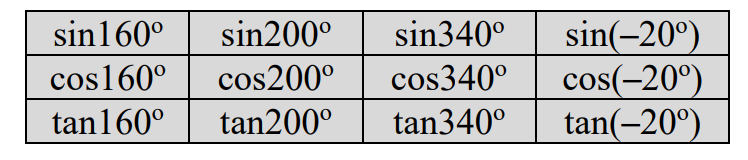
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) \(\tan 20^{\circ}=\frac{p}{q}, \quad \sin 40^{\circ}=2 p q, \quad \cos 40^{\circ}=q^{2}-p^{2}=1-2 p^{2}=2 q^{2}-1\)
(b) 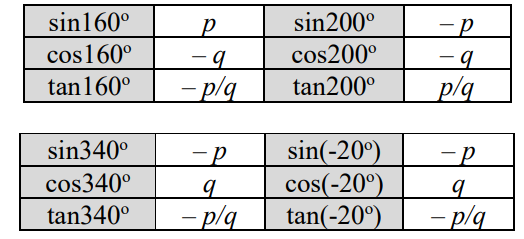
Question
[Maximum mark: 10] [without GDC]
Consider the equation 3cos 2x + sinx = 1.
(a) Write this equation in the form \(f(x)=0, \text { where } f(x)=p \sin ^{2} x+q \sin x+r\) and \(p, q, r \in \mathbb{Z}\). [2]
(b) Factorize f (x). [2]
(c) Write down the number of solutions of \(f(x)=0, \text { for } 0 \leq x \leq 2 \pi\). [2]
Extra Questions:
(d) Find the two solutions in the 3rd and fourth quadrant [4]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) \(3 \cos 2 x+\sin x=1 \Leftrightarrow 3\left(1-2 \sin ^{2} x\right)+\sin x=1\)
6 sinx2 – sinx – 2 = 0
(b) (3 sin x – 2)(2 sin x + 1)
(c) 4 solutions
Extra Question
(d) The last equation gives \(\sin x=\frac{2}{3} \text { or } \sin x=-\frac{1}{2}\)
In the 3rd and 4th quadrants sin x is negative. Hence \(\sin x=-\frac{1}{2}\)
\(x=\frac{\pi}{6}+\pi=\frac{7 \pi}{6} \quad \text { or } x=2 \pi-\frac{\pi}{6}=\frac{11 \pi}{6}\)
