Question
The following table shows values of ln x and ln y.
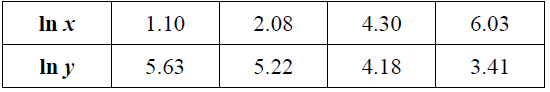
The relationship between ln x and ln y can be modelled by the regression equation ln y = a ln x + b.
Find the value of a and of b.[3]
Use the regression equation to estimate the value of y when x = 3.57.[3]
The relationship between x and y can be modelled using the formula y = kxn, where k ≠ 0 , n ≠ 0 , n ≠ 1.
By expressing ln y in terms of ln x, find the value of n and of k.[7]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
valid approach (M1)
eg one correct value
−0.453620, 6.14210
a = −0.454, b = 6.14 A1A1 N3
[3 marks]
correct substitution (A1)
eg −0.454 ln 3.57 + 6.14
correct working (A1)
eg ln y = 5.56484
261.083 (260.409 from 3 sf)
y = 261, (y = 260 from 3sf) A1 N3
Note: If no working shown, award N1 for 5.56484.
If no working shown, award N2 for ln y = 5.56484.
[3 marks]
METHOD 1
valid approach for expressing ln y in terms of ln x (M1)
eg \({\text{ln}}\,y = {\text{ln}}\,\left( {k{x^n}} \right),\,\,{\text{ln}}\,\left( {k{x^n}} \right) = a\,{\text{ln}}\,x + b\)
correct application of addition rule for logs (A1)
eg \({\text{ln}}\,k + {\text{ln}}\,\left( {{x^n}} \right)\)
correct application of exponent rule for logs A1
eg \({\text{ln}}\,k + n\,{\text{ln}}\,x\)
comparing one term with regression equation (check FT) (M1)
eg \(n = a,\,\,b = {\text{ln}}\,k\)
correct working for k (A1)
eg \({\text{ln}}\,k = 6.14210,\,\,\,k = {e^{6.14210}}\)
465.030
\(n = – 0.454,\,\,k = 465\) (464 from 3sf) A1A1 N2N2
METHOD 2
valid approach (M1)
eg \({e^{{\text{ln}}\,y}} = {e^{a\,{\text{ln}}\,x + b}}\)
correct use of exponent laws for \({e^{a\,{\text{ln}}\,x + b}}\) (A1)
eg \({e^{a\,{\text{ln}}\,x}} \times {e^b}\)
correct application of exponent rule for \(a\,{\text{ln}}\,x\) (A1)
eg \({\text{ln}}\,{x^a}\)
correct equation in y A1
eg \(y = {x^a} \times {e^b}\)
comparing one term with equation of model (check FT) (M1)
eg \(k = {e^b},\,\,n = a\)
465.030
\(n = – 0.454,\,\,k = 465\) (464 from 3sf) A1A1 N2N2
METHOD 3
valid approach for expressing ln y in terms of ln x (seen anywhere) (M1)
eg \({\text{ln}}\,y = {\text{ln}}\,\left( {k{x^n}} \right),\,\,{\text{ln}}\,\left( {k{x^n}} \right) = a\,{\text{ln}}\,x + b\)
correct application of exponent rule for logs (seen anywhere) (A1)
eg \({\text{ln}}\,\left( {{x^a}} \right) + b\)
correct working for b (seen anywhere) (A1)
eg \(b = {\text{ln}}\,\left( {{e^b}} \right)\)
correct application of addition rule for logs A1
eg \({\text{ln}}\,\left( {{e^b}{x^a}} \right)\)
comparing one term with equation of model (check FT) (M1)
eg \(k = {e^b},\,\,n = a\)
465.030
\(n = – 0.454,\,\,k = 465\) (464 from 3sf) A1A1 N2N2
[7 marks]
Question
Expand \({(x – 2)^4}\) and simplify your result.
Find the term in \({x^3}\) in \((3x + 4){(x – 2)^4}\) .
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
evidence of expanding M1
e.g. \({(x – 2)^4} = {x^4} + 4{x^3}( – 2) + 6{x^2}{( – 2)^2} + 4x{( – 2)^3} + {( – 2)^4}\) A2 N2
\({(x – 2)^4} = {x^4} – 8{x^3} + 24{x^2} – 32x + 16\)
[3 marks]
finding coefficients, \(3 \times 24( = 72)\) , \(4 \times( – 8)( = – 32)\) (A1)(A1)
term is \(40{x^3}\) A1 N3
[3 marks]
Question
Let \(f(x) = {\log _3}\frac{x}{2} + {\log _3}16 – {\log _3}4\) , for \(x > 0\) .
Show that \(f(x) = {\log _3}2x\) .
Find the value of \(f(0.5)\) and of \(f(4.5)\) .
The function f can also be written in the form \(f(x) = \frac{{\ln ax}}{{\ln b}}\) .
(i) Write down the value of a and of b .
(ii) Hence on graph paper, sketch the graph of f , for \( – 5 \le x \le 5\) , \( – 5 \le y \le 5\) , using a scale of 1 cm to 1 unit on each axis.
(iii) Write down the equation of the asymptote.
Write down the value of \({f^{ – 1}}(0)\) .
The point A lies on the graph of f . At A, \(x = 4.5\) .
On your diagram, sketch the graph of \({f^{ – 1}}\) , noting clearly the image of point A.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
combining 2 terms (A1)
e.g. \({\log _3}8x – {\log _3}4\) , \({\log _3}\frac{1}{2}x + {\log _3}4\)
expression which clearly leads to answer given A1
e.g. \({\log _3}\frac{{8x}}{4}\) , \({\log _3}\frac{{4x}}{2}\)
\(f(x) = {\log _3}2x\) AG N0
[2 marks]
attempt to substitute either value into f (M1)
e.g. \({\log _3}1\) , \({\log _3}9\)
\(f(0.5) = 0\) , \(f(4.5) = 2\) A1A1 N3
[3 marks]
(i) \(a = 2\) , \(b = 3\) A1A1 N1N1
(ii)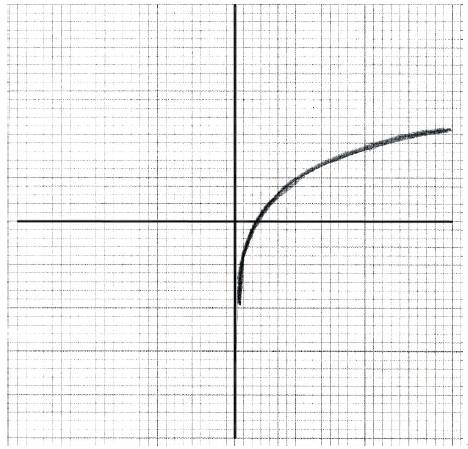 A1A1A1 N3
A1A1A1 N3
Note: Award A1 for sketch approximately through \((0.5 \pm 0.1{\text{, }}0 \pm 0.1)\) , A1 for approximately correct shape, A1 for sketch asymptotic to the y-axis.
(iii) \(x = 0\) (must be an equation) A1 N1
[6 marks]
\({f^{ – 1}}(0) = 0.5\) A1 N1
[1 mark]
 A1A1A1A1 N4
A1A1A1A1 N4
Note: Award A1 for sketch approximately through \((0 \pm 0.1{\text{, }}0.5 \pm 0.1)\) , A1 for approximately correct shape of the graph reflected over \(y = x\) , A1 for sketch asymptotic to x-axis, A1 for point \((2 \pm 0.1{\text{, }}4.5 \pm 0.1)\) clearly marked and on curve.
[4 marks]
