Question
The Voronoi diagram below shows four supermarkets represented by points with coordinates
A(0, 0), B(6, 0), C(0, 6) and D(2 , 2). The vertices X, Y, Z are also shown. All distances
are measured in kilometres.
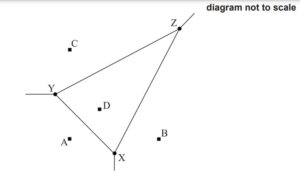
(a) Find the midpoint of [BD]. [2]
(b) Find the equation of (XZ). [4]
The equation of (XY) is y = 2 − x and the equation of (YZ) is y = 0.5x + 3.5.
(c) Find the coordinates of X. [3]
The coordinates of Y are (−1 , 3) and the coordinates of Z are (7 , 7).
(d) Determine the exact length of [YZ]. [2]
(e) Given that the exact length of [XY] is \(\sqrt{32}\) , find the size of XŶZ in degrees. [4]
(f) Hence find the area of triangle XYZ. [2]
A town planner believes that the larger the area of the Voronoi cell XYZ, the more people will
shop at supermarket D.
(g) State one criticism of this interpretation. [1]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
3. (a) \(\left ( \frac{2+6}{2},\frac{2+0}{2} \right )\) (M1)
(4, 1) A1
Note: Award A0 if parentheses are omitted in the final answer.
[2 marks]
(b) attempt to substitute values into gradient formula (M1)
\(\left ( \frac{0-2}{6-2} =\right )-\frac{1}{2}\) (A1)
therefore the gradient of perpendicular bisector is 2 (M1)
so y -1 = 2 (x − 4 ) (y = 2x − 7) A1
[4 marks]
(c) identifying the correct equations to use: (M1)
y = 2 − x and y = 2x − 7
evidence of solving their correct equations or finding points of intersection graphically
(M1)
(3, −1) A1
Note: Accept an answer expressed as “ x = 3, y = −1”.
[3 marks]
(d) attempt to use distance formula (M1)
\(YZ=\sqrt{(7-(-1))^{2}+(7-3)^{2}}\)
\(=\sqrt{80}(4\sqrt{5})\) A1
[2 marks]
(e) METHOD 1 (cosine rule)
length of XZ is \(=\sqrt{80}(4\sqrt{5},8.94427…)\) (A1)
Note: Accept 8.94 and 8.9.
attempt to substitute into cosine rule (M1)
\(\cos X\hat{Y}Z=\frac{80+32-80}{2x\sqrt{80}\sqrt{32}}(=0.316227)\) (A1)
Note: Award A1 for correct substitution of XZ, YZ, \(\sqrt{32}\) values in the cos rule. Exact
values do not need to be used in the substitution.
\((X\hat{Y}Z=)71.6^{o}(71.5650…^{o})\) A1
Note: Last A1 mark may be lost if prematurely rounded values of XZ,
YZ and/or XY are used.
METHOD 2 (splitting isosceles triangle in half)
length of XZ \(\sqrt{80}(4\sqrt{5},8.94427…)\) (A1)
Note: Accept 8.94 and 8.9.
required angle is \(\cos ^{-1}\left ( \frac{\sqrt{32}}{2\sqrt{80}} \right )\) (M1)(A1)
Note: Award A1 for correct substitution of XZ (or YZ), \(\frac{\sqrt{32}}{2}\) values in the cos rule. Exact
values do not need to be used in the substitution.
\((X\hat{Y}Z=)71.6^{o}(71.5650^{o})\) A1
Note: Last A1 mark may be lost if prematurely rounded values of XZ,
YZ and/or XY are used.
[4 marks]
(f) \((area=)\frac{1}{2}\sqrt{80}\sqrt{32}\sin 71.5650… \ OR \(area=)\frac{1}{2}\sqrt{32}\sqrt{72}\) (M1)
= 24 km2
A1
[2 marks]
(g) Any sensible answer such as:
There might be factors other than proximity which influence shopping choices.
A larger area does not necessarily result in an increase in population.
The supermarkets might be specialized / have a particular clientele who
visit even if other shops are closer.
Transport links might not be represented by Euclidean distances.
etc. R1
[1 mark]
Total [18 marks]
Question
The diagram shows a pyramid \({\text{VABCD}}\) which has a square base of length \(10{\text{ cm}}\) and edges of length \(13{\text{ cm}}\). \({\text{M}}\) is the midpoint of the side \({\text{BC}}\).
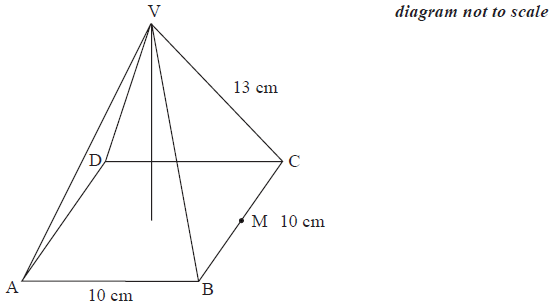
a.Calculate the length of \({\text{VM}}\).[2]
b.Calculate the vertical height of the pyramid.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Unit penalty (UP) applies in this question.
\({\text{VM}}^{2} = {13^2} – {5^2}\) (M1)
UP \( = 12{\text{ cm}}\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
Unit penalty (UP) applies in this question.
\({h^2} = {12^2} – {5^2}\) (or equivalent) (M1)
UP \( = 10.9{\text{ cm}}\) (A1)(ft) (C2)[2 marks]
Question
The right pyramid shown in the diagram has a square base with sides of length 40 cm. The height of the pyramid is also 40 cm.
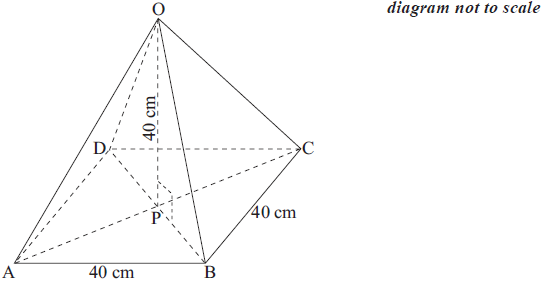
a.Find the length of OB.[4]
b.Find the size of angle OBP.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Note: Unit penalty (UP) applies in this part
\({\rm{PB}} = \frac{1}{2}\sqrt {{{40}^2} + {{40}^2}} = \sqrt {800} = 28.28(28.3)\) (M1)(A1)
Note: Award (M1) for correct substitutions, (A1) for correct answer.
(UP) \({\rm{OB}} = \sqrt {{{40}^2} + {{28.28}^2}} = 49.0{\text{ cm }}\left( {\sqrt {2400} {\text{ cm}}} \right)\) (M1)(A1)(ft) (C4)
Note: Award (M1) for correct substitution, can (ft) from any answer to PB.[4 marks]
\({\sin ^{ – 1}}\left( {\frac{{40}}{{49}}} \right)\)
OR
\({\cos ^{ – 1}}\left( {\frac{{28.28}}{{49}}} \right)\)
OR
\({\tan ^{ – 1}}\left( {\frac{{40}}{{28.28}}} \right)\) (M1)
= 54.7 (54.8) (A1)(ft) (C2)
Note: Award (M1) for any correct trig. ratio.
In radians = 0.616, award (M1)(A0).
Note: Common error: (a) \(OB = \sqrt {40^2 + 20^2} = 44.7 {\text{ cm}}\). Award (M0)(A0)(M1), (A1)(ft), and (b) angle OBP = 63.4° (63.5°) (M1)(A1)(ft).[2 marks]
Question
A shipping container is a cuboid with dimensions \({\text{16 m}}\), \({\text{1}}\frac{{\text{3}}}{{\text{4}}}{\text{ m}}\) and \({\text{2}}\frac{{\text{2}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{ m}}\).
a.Calculate the exact volume of the container. Give your answer as a fraction.[3]
b.Jim estimates the dimensions of the container as 15 m, 2 m and 3 m and uses these to estimate the volume of the container.
Calculate the percentage error in Jim’s estimated volume of the container.[3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(V = 16 \times 1\frac{3}{4} \times 2\frac{2}{3}\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for correct substitution in volume formula. Accept decimal substitution of \(2.66\) or better.
\( = 74.6666{\text{ }} \ldots \) (A1)
\( = {\text{74}}\frac{{\text{2}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ }}\left( {\frac{{{\text{224}}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}} \right)\) (A1) (C3)
Note: Correct answer only.[3 marks]
\({\text{% error}} = \frac{{\left( {90 – 74\frac{2}{3}} \right) \times 100}}{{74\frac{2}{3}}}\) (A1)(M1)
Note: Award (A1) for \(90\) seen, or inferred in numerator, (M1) for correct substitution into percentage error formula.
\( = 20.5\) (A1)(ft) (C3)
Note: Accept \( – 20.5\).[3 marks]
Question
A rectangular cuboid has the following dimensions.
Length 0.80 metres (AD)
Width 0.50 metres (DG)
Height 1.80 metres (DC)
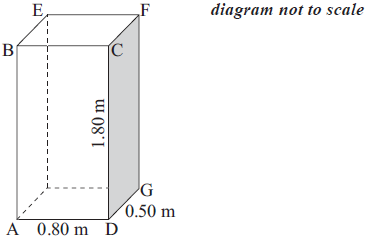
a.Calculate the length of AG.[2]
b.Calculate the length of AF.[2]
c.Find the size of the angle between AF and AG.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\({\text{AG}} = \sqrt {{{0.8}^2} + {{0.5}^2}} \) (M1)
AG = 0.943 m (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
\({\text{AF}} = \sqrt {{\text{A}}{{\text{G}}^2} + {{1.80}^2}} \) (M1)
= 2.03 m (A1)(ft) (C2)
Note: Follow through from their answer to part (a).[2 marks]
\(\cos {\rm{G\hat AF}} = \frac{{0.943(39 \ldots )}}{{2.03(22 \ldots )}}\) (M1)
\(\operatorname{G\hat AF} = 62.3^\circ \) (A1)(ft) (C2)
Notes: Award (M1) for substitution into correct trig ratio.
Accept alternative ratios which give 62.4° or 62.5°.
Follow through from their answers to parts (a) and (b).[2 marks]
